Clin Nutr Res.
2017 Apr;6(2):122-129. 10.7762/cnr.2017.6.2.122.
Carbohydrate Composition Associated with the 2-Year Incidence of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon 16499, Korea. chnaha@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Division of Epidemiology and Health Index, Center for Genome Science, Korea National Institute of Health, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Cheongwon 28159, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam 13620, Korea.
- 4Department of Foods and Nutrition, Kookmin University College of Science and Technology, Seoul 02707, Korea. ibaik@kookmin.ac.kr
- KMID: 2383700
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7762/cnr.2017.6.2.122
Abstract
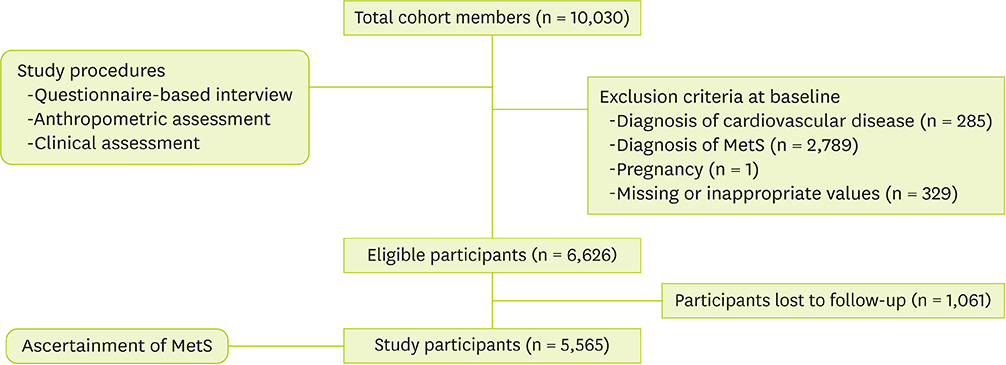
- The aim of this study was to investigate the association between macronutrient composition and metabolic syndrome (MetS) incidence in Korean adults. Data were obtained from a cohort of 10,030 members aged 40 to 69 years who were enrolled from the 2 cities (Ansung and Ansan) between 2001 and 2002 to participate in the Korean Genome Epidemiology Study. Of these members, 5,565 participants, who were free of MetS and reported no diagnosis of cardiovascular disease at baseline, were included in this study. MetS was defined using the criteria of the National Cholesterol Education Program-Adult Treatment Panel III and Asia-Pacific criteria for waist circumference. MetS incidence rate were identified during a 2-year follow-up period. Baseline dietary information was obtained using a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate the association between the quartiles of percentages of total calorie from macronutrients consumed and MetS incidence. In analyses, baseline information, including age, sex, body mass index, income status, educational status, smoking status, alcohol drinking status, and physical activity level was considered as confounding variables. Participants with the second quartile of the percentages of carbohydrate calorie (67%-70%) had a 23% reduced odds ratio (95% confidence interval, 0.61-0.97) for MetS incidence compared with those with the fourth quartile after adjusting for confounding variables. The findings suggest that middle aged or elderly Korean adults who consume approximately 67%-70% of calorie from carbohydrate have a reduced risk of MetS.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult*
Aged
Alcohol Drinking
Body Mass Index
Cardiovascular Diseases
Cholesterol
Cohort Studies
Confounding Factors (Epidemiology)
Diagnosis
Education
Educational Status
Epidemiology
Follow-Up Studies
Genome
Humans
Incidence*
Logistic Models
Middle Aged
Motor Activity
Odds Ratio
Smoke
Smoking
Waist Circumference
Cholesterol
Smoke
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
High-Carbohydrate Diets and Food Patterns and Their Associations with Metabolic Disease in the Korean Population
Yun Jung Lee, SuJin Song, YoonJu Song
Yonsei Med J. 2018;59(7):834-842. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.7.834.
Reference
-
1. Reaven GM. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988; 37:1595–1607.
Article2. National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation. 2002; 106:3143–3421.3. Lim S, Shin H, Song JH, Kwak SH, Kang SM, Won Yoon J, Choi SH, Cho SI, Park KS, Lee HK, Jang HC, Koh KK. Increasing prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Korea: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for 1998–2007. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:1323–1328.4. Dallongeville J, Cottel D, Ferrières J, Arveiler D, Bingham A, Ruidavets JB, Haas B, Ducimetière P, Amouyel P. Household income is associated with the risk of metabolic syndrome in a sex-specific manner. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:409–415.
Article5. Wamala SP, Lynch J, Horsten M, Mittleman MA, Schenck-Gustafsson K, Orth-Gomér K. Education and the metabolic syndrome in women. Diabetes Care. 1999; 22:1999–2003.
Article6. Lee KS, Park CY, Meng KH, Bush A, Lee SH, Lee WC, Koo JW, Chung CK. The association of cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption with other cardiovascular risk factors in men from Seoul, Korea. Ann Epidemiol. 1998; 8:31–38.
Article7. Cefalu WT, Wang ZQ, Werbel S, Bell-Farrow A, Crouse JR 3rd, Hinson WH, Terry JG, Anderson R. Contribution of visceral fat mass to the insulin resistance of aging. Metabolism. 1995; 44:954–959.
Article8. Lutsey PL, Steffen LM, Stevens J. Dietary intake and the development of the metabolic syndrome: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. Circulation. 2008; 117:754–761.
Article9. Oh HY, Kim MK, Lee M, Kim YO. Macronutrient composition and sodium intake of diet are associated with risk of metabolic syndrome and hypertension in Korean women. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e78088.
Article10. Park S, Ahn J, Kim NS, Lee BK. High carbohydrate diets are positively associated with the risk of metabolic syndrome irrespective to fatty acid composition in women: the KNHANES 2007–2014. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2017; 68:479–487.
Article11. Brunner EJ, Wunsch H, Marmot MG. What is an optimal diet? Relationship of macronutrient intake to obesity, glucose tolerance, lipoprotein cholesterol levels and the metabolic syndrome in the Whitehall II study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2001; 25:45–53.
Article12. McKeown NM, Meigs JB, Liu S, Saltzman E, Wilson PW, Jacques PF. Carbohydrate nutrition, insulin resistance, and the prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in the Framingham Offspring Cohort. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:538–546.
Article13. Skilton MR, Laville M, Cust AE, Moulin P, Bonnet F. The association between dietary macronutrient intake and the prevalence of the metabolic syndrome. Br J Nutr. 2008; 100:400–407.
Article14. Ministry of Health and Welfare (KR). The Korean Nutrition Society. Dietary reference intakes for Koreans 2015. Sejong: Ministry of Health and Welfare of Korea;2016.15. Trumbo P, Schlicker S, Yates AA, Poos M; Food and Nutrition Board of the Institute of Medicine, The National Academies. Dietary reference intakes for energy, carbohydrate, fiber, fat, fatty acids, cholesterol, protein and amino acids. J Am Diet Assoc. 2002; 102:1621–1630.
Article16. Ahn Y, Lee JE, Paik HY, Lee HK, Jo I, Kimm K. Development of a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire based on dietary data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Nutr Sci. 2003; 6:173–184.17. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2011: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-2). Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2012.18. Hong AR, Lim S. Clinical characteristics of metabolic syndrome in Korea, and its comparison with other Asian countries. Diabetes Investig. 2015; 6:508–515.
Article19. Park S, Park MS, Ko JA. The association between carbohydrate intake and waist circumference. Korean J Obes. 2008; 17:175–181.20. Kannel WB, Cupples LA, Ramaswami R, Stokes J 3rd, Kreger BE, Higgins M. Regional obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease; the Framingham Study. J Clin Epidemiol. 1991; 44:183–190.
Article21. Choi H, Song S, Kim J, Chung J, Yoon J, Paik HY, Song Y. High carbohydrate intake was inversely associated with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol among Korean adults. Nutr Res. 2012; 32:100–106.
Article22. Zulkifli SN, Yu SM. The food frequency method for dietary assessment. J Am Diet Assoc. 1992; 92:681–685.
Article23. Willett WC. Nutritional Epidemiology. 2nd ed. New York (NY): Oxford University Press;1998.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- High fiber and high carbohydrate intake and its association with the metabolic disease using the data of KNHANES 2013 ~ 2017
- Association of Family Composition and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults Aged over 45 Years Old
- Therapeutic approaches to obesity and metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents
- The Cut-off Values of the Visceral Fat Area to Identify Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adults: Using Visceral Fat Area Presented by Body Composition Analyzer, InBody 4.0.
- Association between Daily Protein to Carbohydrate Intake Ratio and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Elderly: The 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey