Korean J Gastroenterol.
2016 Nov;68(5):265-269. 10.4166/kjg.2016.68.5.265.
A Case of Endoscopically Complete Remission of Esophageal Neuroendocrine Tumors by Concurrent Chemoradiation Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. mhs1357@cnuh.co.kr
- KMID: 2383504
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2016.68.5.265
Abstract
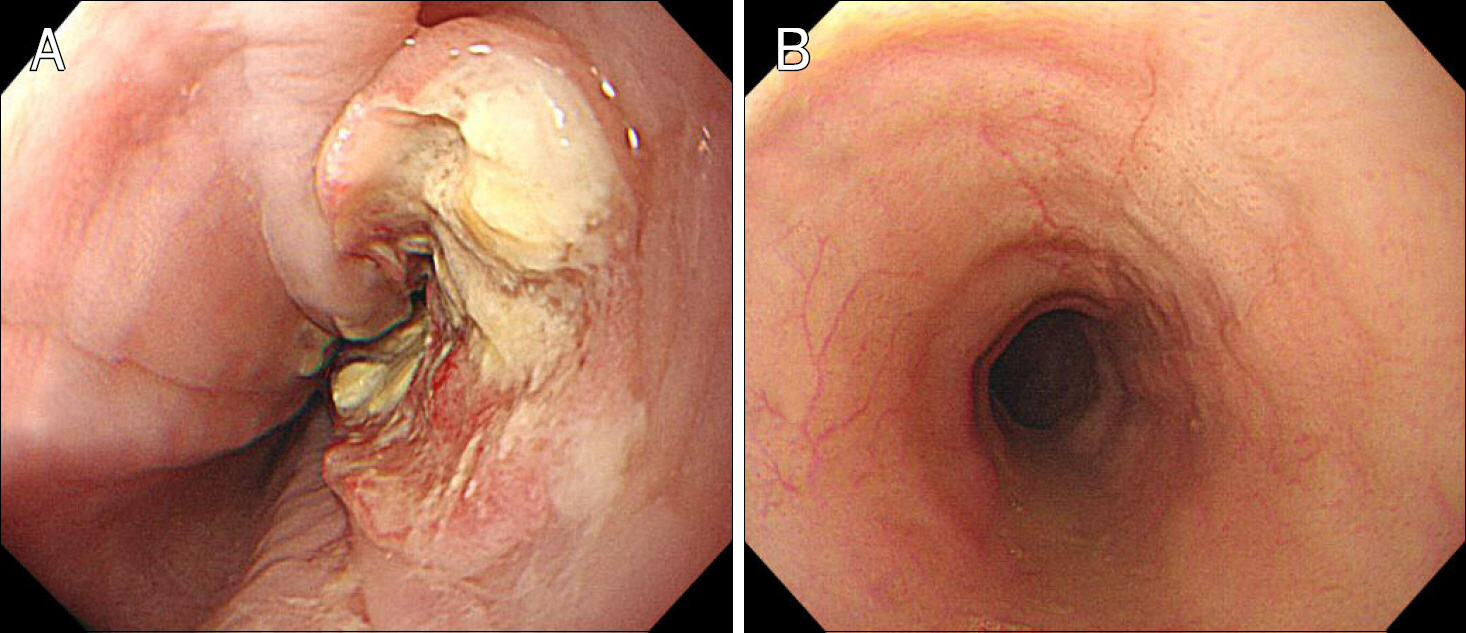
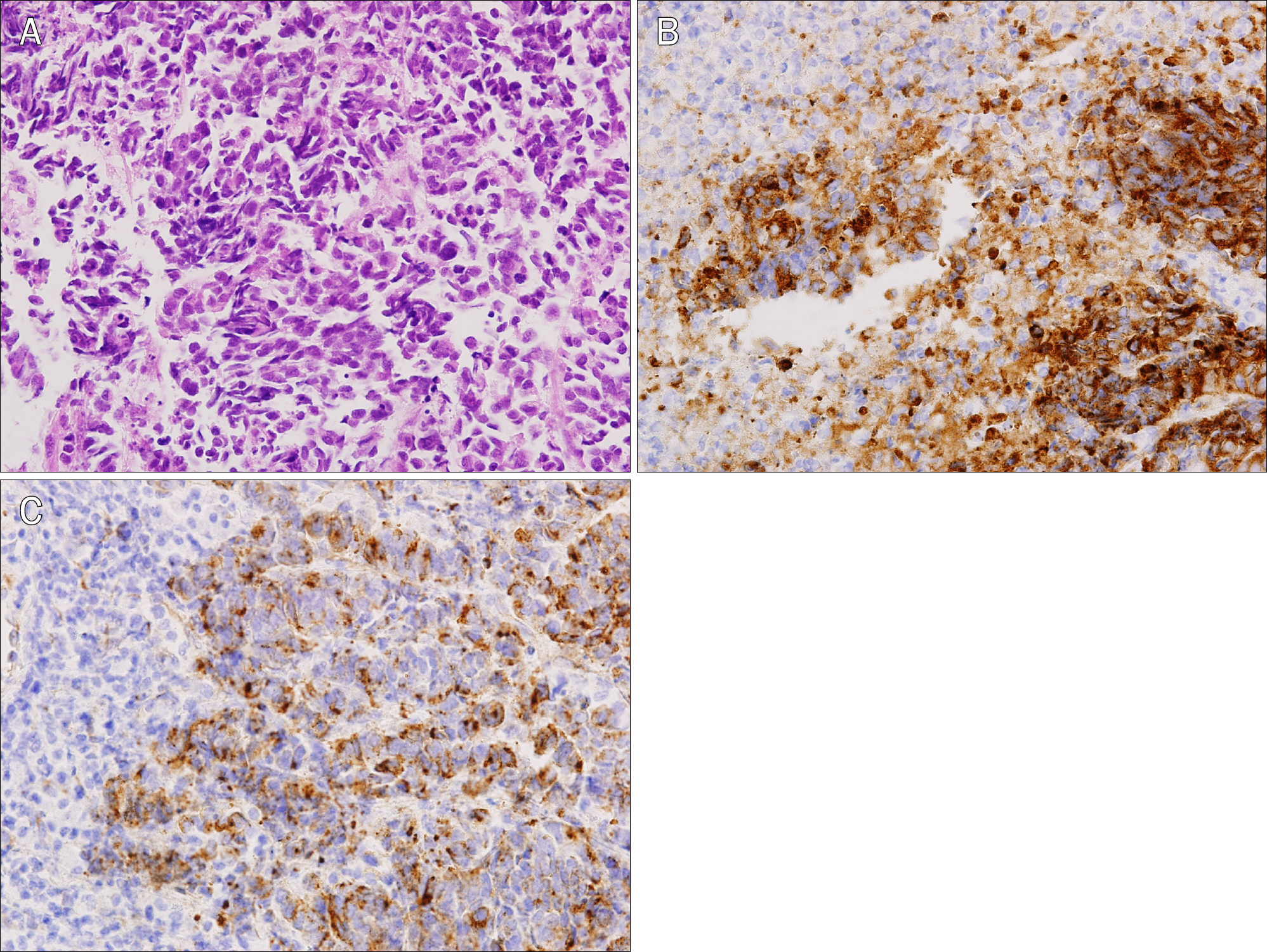
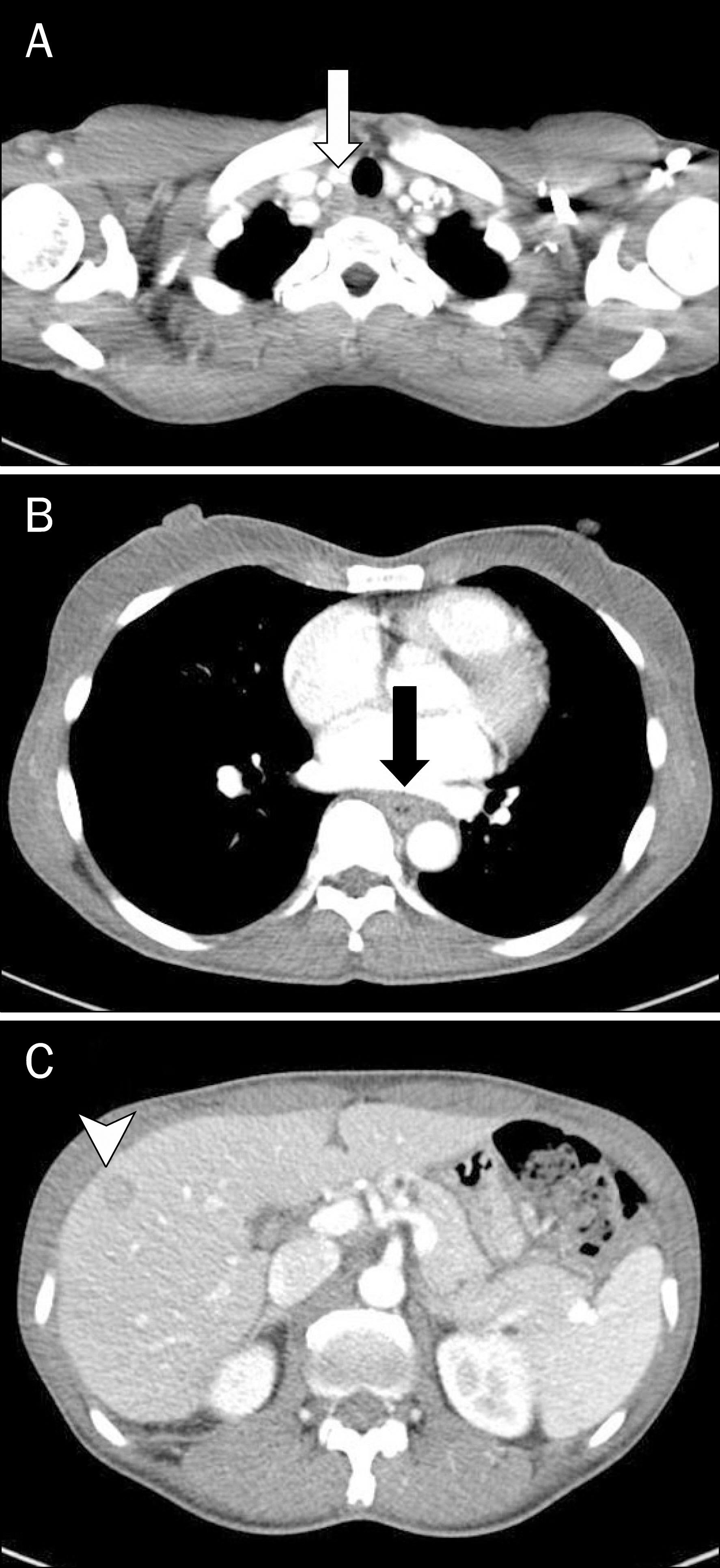
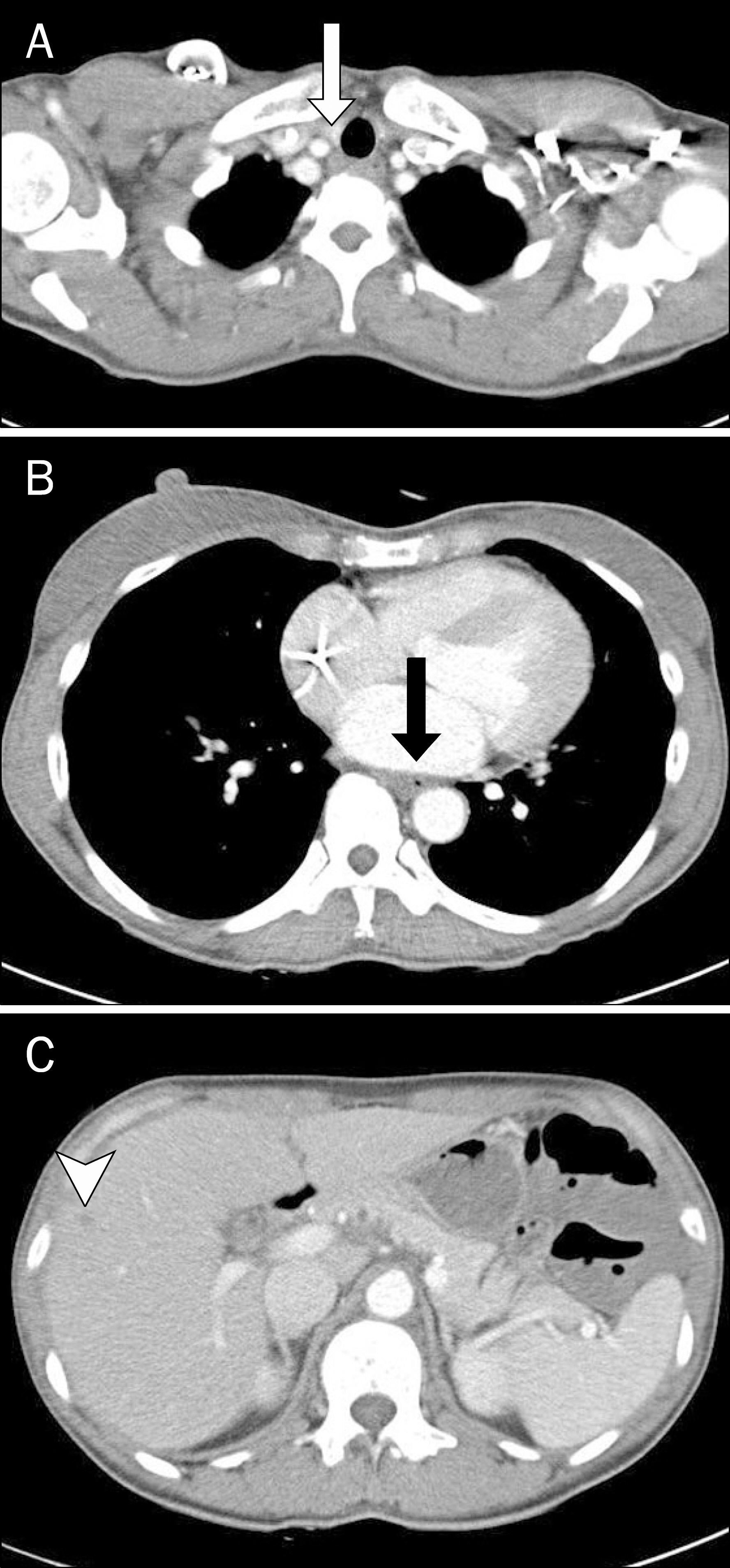
- Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) of the esophagus are extremely rare, aggressive and have a poor prognosis. Combined therapy using chemotherapy, radiotherapy and/or surgery appear effective. Here, we present a patient with a complaint of dysphagia who was diagnosed with this rare tumor. Upper gastrointestinal endoscope of a 46-year-old female revealed a localized ulcerative lesion in the middle esophagus. Histologic exam of biopsy specimens indicated a neuroendocrine carcinoma. The tumor cells were arranged in microtubular structures, with small and round cells containing scanty cytoplasm. They were positive for synaptophysin and chromogranin A on immunohistochemical staining. A computed tomography scan showed an esophageal tumor with enlarged superior mediastinal lymph nodes and about 1.2 cm sized liver metastasis, similar to findings in PET-CT scanning. The patient was prescribed chemotherapy consisting of etoposide and cisplatin, which led to regression of disease on follow-up imaging study. She continues under clinical observation. We seek to increase awareness of this exceedingly rare but hazardous disease by sharing our unexpected finding.
MeSH Terms
-
Biopsy
Carcinoma, Neuroendocrine
Chromogranin A
Cisplatin
Cytoplasm
Deglutition Disorders
Drug Therapy
Endoscopes, Gastrointestinal
Endoscopy
Esophageal Neoplasms
Esophagus
Etoposide
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Humans
Liver
Lymph Nodes
Middle Aged
Neoplasm Metastasis
Neuroendocrine Tumors*
Prognosis
Radiotherapy
Synaptophysin
Ulcer
Chromogranin A
Cisplatin
Etoposide
Synaptophysin
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Lee CG, Lim YJ, Park SJ, et al. The clinical features and treatment modality of esophageal neuroendocrine tumors: a multicenter study in Korea. BMC Cancer. 2014; 14:569.
Article2. Cho MY, Kim JM, Sohn JH, et al. Gastrointestinal Pathology Study Group of Korean Society of Pathologists. Current trends of the incidence and pathological diagnosis of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs) in Korea 2000–2009: multicenter study. Cancer Res Treat. 2012; 44:157–165.
Article3. Hoang MP, Hobbs CM, Sobin LH, Albores-Saavedra J. Carcinoid tumor of the esophagus: a clinicopathologic study of four cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002; 26:517–522.4. Huang Q, Wu H, Nie L, et al. Primary high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma of the esophagus: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 42 resection cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013; 37:467–483.5. Casas F, Ferrer F, Farrús B, Casals J, Biete A. Primary small cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a review of the literature with emphasis on therapy and prognosis. Cancer. 1997; 80:1366–1372.6. Maru DM, Khurana H, Rashid A, et al. Retrospective study of clinicopathologic features and prognosis of high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma of the esophagus. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008; 32:1404–1411.
Article7. Watson KJ, Shulkes A, Smallwood RA, et al. Watery diarrhea-hy-pokalemia-achlorhydria syndrome and carcinoma of the esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1985; 88:798–803.
Article8. Hudson E, Powell J, Mukherjee S, et al. Small cell oesophageal carcinoma: an institutional experience and review of the literature. Br J Cancer. 2007; 96:708–711.
Article9. Yun JP, Zhang MF, Hou JH, et al. Primary small cell carcinoma of the esophagus: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical features of 21 cases. BMC Cancer. 2007; 7:38.
Article10. Noda K, Nishiwaki Y, Kawahara M, et al. Irinotecan plus cisplatin compared with etoposide plus cisplatin for extensive small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:85–91.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Complete Remission to Advanced Esophageal Cancer by a Concurrent Chemoradiation Therapy
- Treatment of Primary Esophageal Malignant Lymphoma in Complete Remission and Associated with Stricture
- Long-term survival after concurrent chemoradiation therapy for esophageal cancer with tracheal invasion
- A case of pathologic complete remission of advanced gastric cancer induced by concurrent chemoradiation with S1 and cisplatin
- Chemoradiotherapy for Esophageal Cancer