Intest Res.
2017 Jul;15(3):395-401. 10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.395.
Long-term safety and efficacy of adalimumab for intestinal Behçet's disease in the open label study following a phase 3 clinical trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Center for Preventive Medicine, Keio University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan. nagamu@z6.keio.jp
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, Kitasato University Hospital, Kanagawa, Japan.
- 3Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keio University School of Medicine, Fukuoka, Japan.
- 4IBD Center, Fukuoka University Chikushi Hospital, Fukuoka, Japan.
- 5AbbVie GK, Tokyo, Japan.
- 6AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL, USA.
- 7Center for Advanced IBD Research and Treatment, Kitasato Institute Hospital, Kitasato University, Tokyo, Japan.
- KMID: 2382384
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.395
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
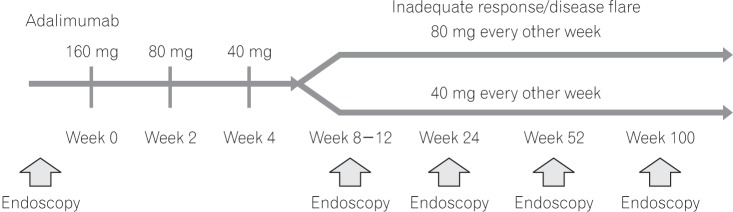
Intestinal Behçet's disease (BD) is an immune-mediated inflammatory disorder. We followed up the patients and evaluated safety profile and effectiveness of adalimumab for the treatment of intestinal BD through 100 weeks rolled over from the 52 week clinical trial (NCT01243671).
METHODS
Patients initiated adalimumab therapy at 160 mg at week 0, followed by 80 mg at week 2, followed by 40 mg every other week until the end of the study. Long-term safety and all adverse events (AEs) were examined. The efficacy was assessed on the basis of marked improvement (MI) and complete remission (CR) using a composite efficacy index, which combined global gastrointestinal symptoms and endoscopic assessments.
RESULTS
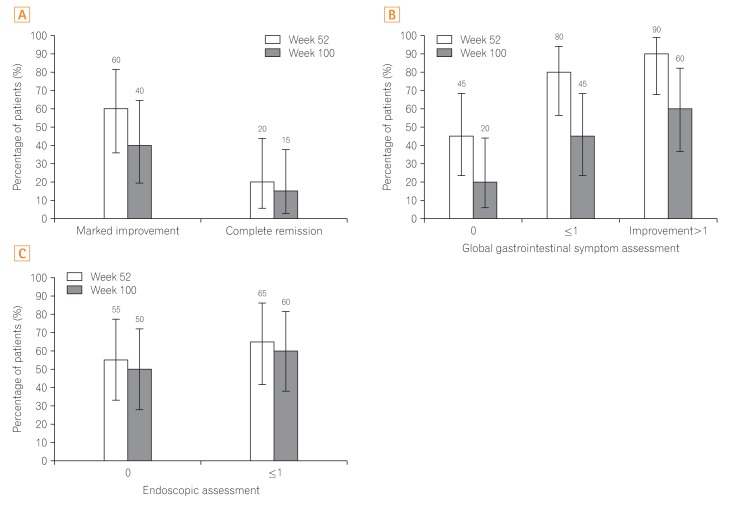
Twenty patients were enrolled in this study; 15 patients received adalimumab treatment until study completion. The incidence of AEs through week 100 was 544.4 events/100 person-years, which was comparable to the incidence through week 52 (560.4 events/100 person-years). No unexpected trend was observed and adalimumab was well tolerated. At weeks 52 and 100, 60.0% and 40.0% of patients showed MI, respectively, and 20.0% and 15.0% of patients showed CR, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
This report demonstrates 2 years safety and effectiveness of adalimumab in intestinal BD patients. Patients with intestinal BD refractory to conventional treatment receiving up to 2 years of adalimumab treatment demonstrated safety outcomes consistent with the known profile of adalimumab, and the treatment led to sustained reduction of clinical and endoscopic disease activity.
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Advances in Management of Intestinal Behçet’s Disease: A Perspective From Gastroenterologists
Jae Hee Cheon
J Rheum Dis. 2021;28(1):4-16. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.1.4.Long-term safety and effectiveness of adalimumab in 462 patients with intestinal Behçet’s disease: results from a large real-world observational study
Yasuo Suzuki, Takashi Hagiwara, Mariko Kobayashi, Kazuo Morita, Tomoyo Shimamoto, Toshifumi Hibi
Intest Res. 2021;19(3):301-312. doi: 10.5217/ir.2020.00013.Could adalimumab be used safely and effectively in intestinal Behçet's disease refractory to conventional therapy?
Jihye Park, Jae Hee Cheon
Intest Res. 2017;15(3):263-265. doi: 10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.263.
Reference
-
1. Sakane T, Takeno M, Suzuki N, Inaba G. Behçet's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:1284–1291. PMID: 10528040.
Article2. Tanida S, Inoue N, Kobayashi K, et al. Adalimumab for the treatment of Japanese patients with intestinal Behçet's disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 13:940–948.e3. PMID: 25245624.
Article3. The diagnostic criteria for Behçet's disease (2003). Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Web site. Accessed April 4, 2017. http://www.mhlw.go.jp/file/06-Seisakujouhou-10900000-Kenkoukyoku/0000089968.pdf.4. Hibi T, Hirohata S, Kikuchi H, et al. Infliximab therapy for intestinal, neurological, and vascular involvement in Behcet disease: efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics in a multicenter, prospective, open-label, single-arm phase 3 study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e3863. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003863. PMID: 27310969.5. Burmester GR, Panaccione R, Gordon KB, McIlraith MJ, Lacerda AP. Adalimumab: long-term safety in 23 458 patients from global clinical trials in rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis and Crohn's disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013; 72:517–524. PMID: 22562972.
Article6. Watanabe M, Hibi T, Mostafa NM, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of adalimumab in Japanese patients with moderate to severe Crohn's disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2014; 8:1407–1416. PMID: 24874893.
Article7. Panaccione R, Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, et al. Adalimumab maintains remission of Crohn's disease after up to 4 years of treatment: data from CHARM and ADHERE. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013; 38:1236–1247. PMID: 24134498.
Article8. Hatemi G, Silman A, Bang D, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of Behçet disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008; 67:1656–1662. PMID: 18245110.9. Hisamatsu T, Ueno F, Matsumoto T, et al. The 2nd edition of consensus statements for the diagnosis and management of intestinal Behçet’s disease: indication of anti-TNFalpha monoclonal antibodies. J Gastroenterol. 2014; 49:156–162. PMID: 23955155.
Article10. Chung MJ, Cheon JH, Kim SU, et al. Response rates to medical treatments and long-term clinical outcomes of nonsurgical patients with intestinal Behçet disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010; 44:e116–e122. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181c8a50f. PMID: 20054283.
Article11. Naganuma M, Iwao Y, Inoue N, et al. Analysis of clinical course and long-term prognosis of surgical and nonsurgical patients with intestinal Behçet's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000; 95:2848–2851. PMID: 11051358.
Article12. REMICADE: package insert. Osaka: Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation;2017.13. Lee JH, Cheon JH, Jeon SW, et al. Efficacy of infliximab in intestinal Behçet's disease: a Korean multicenter retrospective study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013; 19:1833–1838. PMID: 23702810.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Therapy in Intestinal Behçet's Disease
- Could adalimumab be used safely and effectively in intestinal Behçet's disease refractory to conventional therapy?
- Is adalimumab safe and effective in patients with intestinal Behcet’s disease in real-world practice?
- Succinate-treated macrophages attenuate dextran sodium sulfate colitis in mice
- Long-term Safety and Efficacy of Abatacept in Koreans with Rheumatoid Arthritis