Intest Res.
2017 Jul;15(3):358-367. 10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.358.
Comparison of efficacies of once-daily dose multimatrix mesalazine and multiple-dose mesalazine for the maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis: a randomized, double-blind study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Center for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Keio University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan. hogata@z8.keio.jp
- 2Inogashiradori Proctology and Gastroenterology Clinic, Tokyo, Japan.
- 3Matsushima Clinic, Kanagawa, Japan.
- 4Clinical Development Department, Mochida Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan.
- 5Center for Advanced IBD Research and Treatment, Kitasato Institute Hospital, Kitasato University, Tokyo, Japan.
- KMID: 2382380
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.358
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
This study compared the efficacy of once-daily administration of multimatrix mesalazine 2.4 g/day with multiple-dose mesalazine for the maintenance of remission.
METHODS
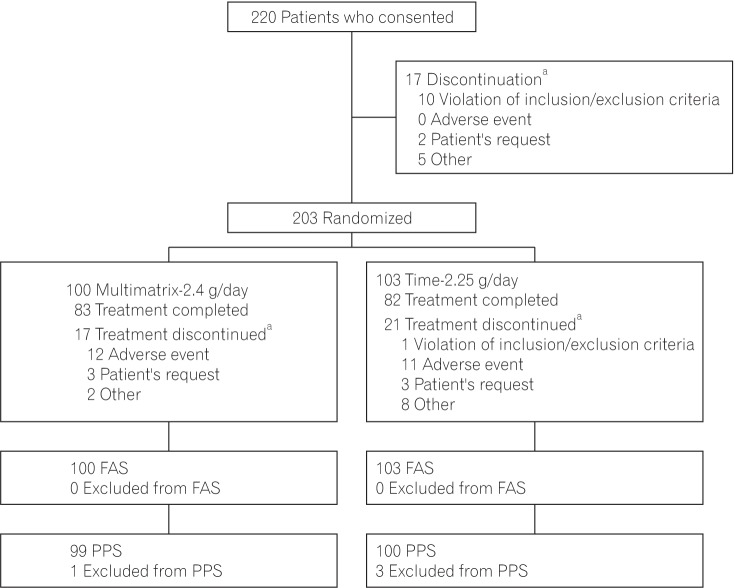
In this multicenter, randomized, double-blind study, 203 patients with ulcerative colitis in remission received multimatrix mesalazine 2.4 g/day once-daily or time-dependent (controlled-release) mesalazine 2.25 g/day 3 times-daily for 48 weeks. The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients without rectal bleeding.
RESULTS
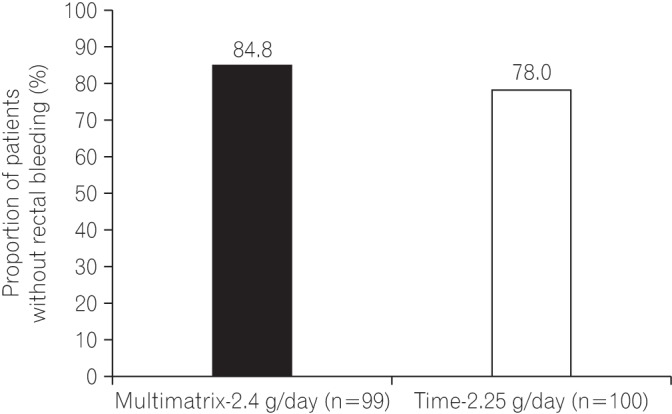
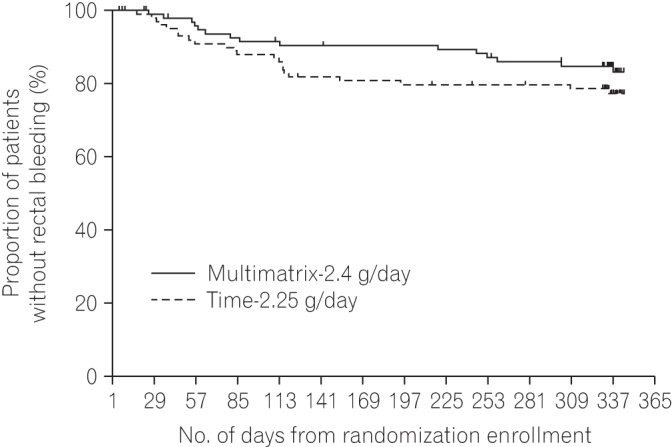
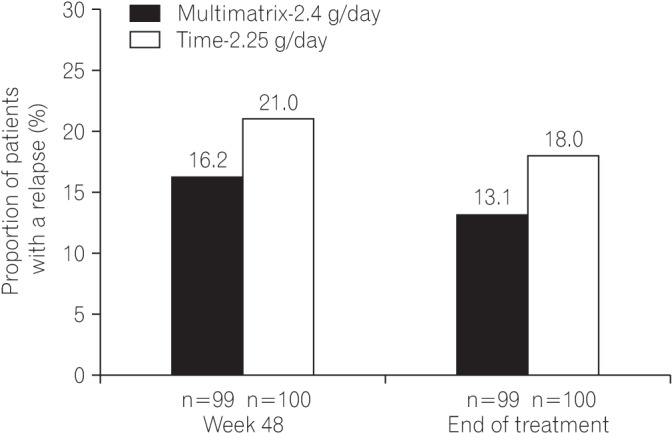
The proportion of patients without rectal bleeding during the 48-week treatment period in the per protocol set was 84.8% (84/99) in the multimatrix mesalazine 2.4 g/day group and 78.0% (78/100) in the controlled-release mesalazine 2.25 g/day group. The difference between the 2 treatment groups was 6.8% (two-sided 95% confidence interval, −3.9% to 17.6%). The noninferiority margin of −10% was met in the comparison of multimatrix mesalazine 2.4 g/day once-daily with controlled-release mesalazine 2.25 g/day. Multimatrix mesalazine 2.4 g/day once-daily demonstrated consistent efficacy in all subgroups. There was no difference between the 2 treatment groups with regard to safety.
CONCLUSIONS
A once-daily dose of 2 multimatrix mesalazine tablets (2.4 g) was not inferior to controlled-release mesalazine 2.25 g/day 3 times-daily in maintaining absence of rectal bleeding in ulcerative colitis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
How to Optimally Use Currently Available Drugs in a Therapeutic Algorithm?
You Sun Kim
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2018;71(2):74-80. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2018.71.2.74.
Reference
-
1. Miner P, Hanauer S, Robinson M, Schwartz J, Arora S. Safety and efficacy of controlled-release mesalamine for maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis: Pentasa UC Maintenance Study Group. Dig Dis Sci. 1995; 40:296–304. PMID: 7851193.
Article2. Ardizzone S, Petrillo M, Imbesi V, Cerutti R, Bollani S, Bianchi Porro G. Is maintenance therapy always necessary for patients with ulcerative colitis in remission? Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999; 13:373–379. PMID: 10102971.
Article3. Hanauer SB, Sninsky CA, Robinson M, et al. An oral preparation of mesalamine as long-term maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1996; 124:204–211. PMID: 8533995.
Article4. Hawkey CJ, Dube LM, Rountree LV, Linnen PJ, Lancaster JF. A trial of zileuton versus mesalazine or placebo in the maintenance of remission of ulcerative colitis: the European Zileuton Study Group for Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology. 1997; 112:718–724. PMID: 9041232.
Article5. Feagan BG, Macdonald JK. Oral 5-aminosalicylic acid for maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; 10:CD000544. PMID: 23076890.
Article6. D'Haens G, Sandborn WJ, Barrett K, Hodgson I, Streck P. Oncedaily MMX(®) mesalamine for endoscopic maintenance of remission of ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:1064–1077. PMID: 22565161.7. Prantera C, Kohn A, Campieri M, et al. Clinical trial: ulcerative colitis maintenance treatment with 5-ASA: a 1-year, randomized multicentre study comparing MMX with Asacol. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009; 30:908–918. PMID: 19678813.
Article8. Sutherland LR, Martin F, Greer S, et al. 5-Aminosalicylic acid enema in the treatment of distal ulcerative colitis, proctosigmoiditis, and proctitis. Gastroenterology. 1987; 92:1894–1898. PMID: 3569765.
Article9. Watanabe M, Hanai H, Nishino H, Yokoyama T, Terada T, Suzuki Y. Comparison of QD and TID oral mesalazine for maintenance of remission in quiescent ulcerative colitis: a double-blind, double-dummy, randomized multicenter study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013; 19:1681–1690. PMID: 23624890.
Article10. Sandborn WJ, Korzenik J, Lashner B, et al. Once-daily dosing of delayed-release oral mesalamine (400-mg tablet) is as effective as twice-daily dosing for maintenance of remission of ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2010; 138:1286–1296.e3. PMID: 20064514.
Article11. Dignass AU, Bokemeyer B, Adamek H, et al. Mesalamine once daily is more effective than twice daily in patients with quiescent ulcerative colitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 7:762–769. PMID: 19375519.
Article12. Dignass A, Lindsay JO, Sturm A, et al. Second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis part 2: current management. J Crohns Colitis. 2012; 6:991–1030. PMID: 23040451.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of efficacy of multimatrix mesalazine 4.8 g/day once-daily with other high-dose mesalazine in active ulcerative colitis: a randomized, double-blind study
- Comparison of efficacy of once daily multimatrix mesalazine 2.4 g/day and 4.8 g/day with other 5-aminosalicylic acid preparation in active ulcerative colitis: a randomized, double-blind study
- Is once daily multimatrix mesalazine therapy effective regardless of the dose in patients with mild to moderate ulcerative colitis?
- Recurrent Eosinophilic Pneumonia Associated with Mesalazine Suppository in a Patient with Ulcerative Colitis
- A Case of Pyoderma Gangrenosum with Ulcerative Colitis Treated with Mesalazine