J Pathol Transl Med.
2015 Mar;49(2):129-135. 10.4132/jptm.2015.01.28.
Image-Guided Fine Needle Cytology with Aspiration Versus Non-Aspiration in Retroperitoneal Masses: Is Aspiration Necessary?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, B.R.D. Medical College, Gorakhpur, India. shaila.prasad14@yahoo.co.in
- 2Department of Radiology, B.R.D. Medical College, Gorakhpur, India.
- 3Apollo Hospital, New Delhi, India.
- KMID: 2381367
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.01.28
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Although using fine needle cytology with aspiration (FNC-A) for establishing diagnoses in the retroperitoneal region has shown promise, there is scant literature supporting a role of non-aspiration cytology (FNC-NA) for this region. We assessed the accuracy and reliability of FNC-A and FNC-NA as tools for preoperative diagnosis of retroperitoneal masses and compared the results of both techniques with each other and with histopathology.
METHODS
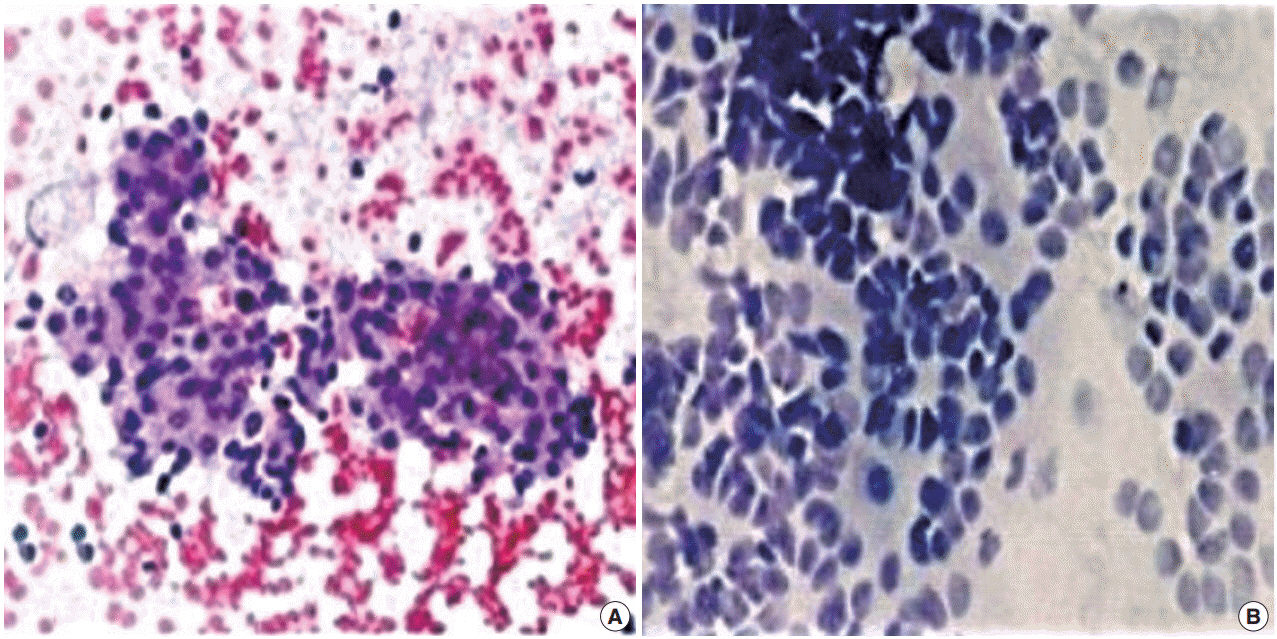
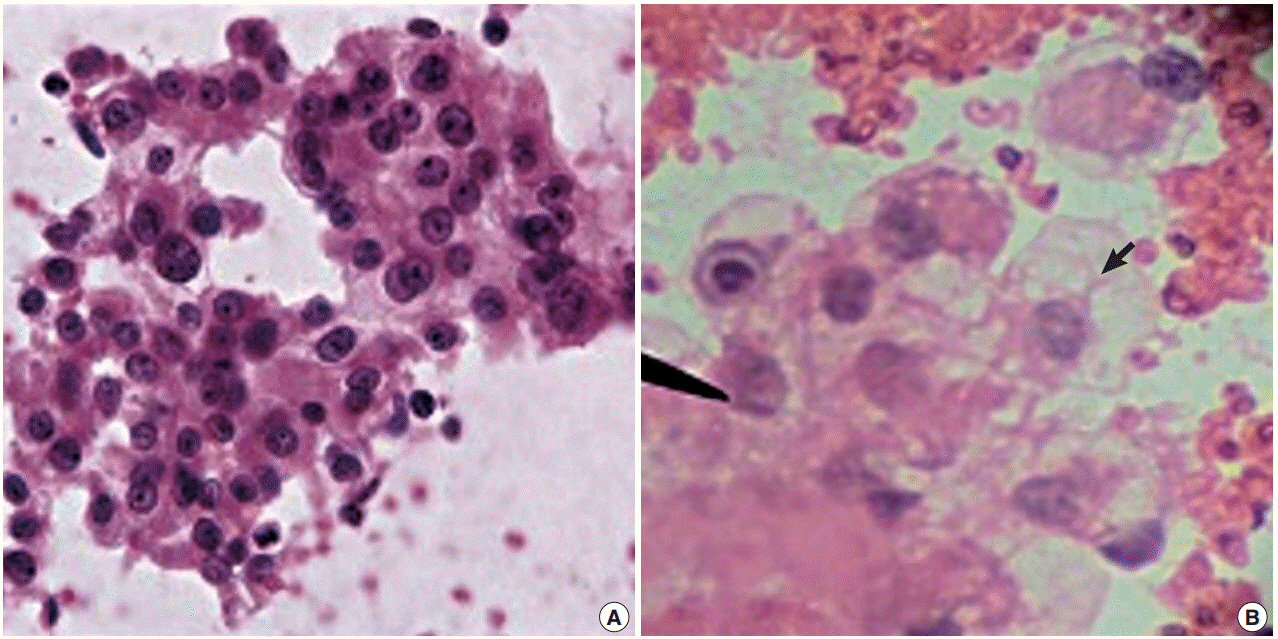
Fifty-seven patients with retroperitoneal masses were subjected to FNC-A and FNC-NA. Smears were stained with May-Grunwald Giemsa and hematoxylin and eosin stain. An individual slide was objectively analysed using a point scoring system to enable comparison between FNC-A and FNC-NA.
RESULTS
By FNC-A, 91.7% accuracy was obtained in cases of retroperitoneal lymph node lesions followed by renal masses (83.3%). The diagnostic accuracy of other sites by FNC-A varied from 75.0%-81.9%. By FNC-NA, 93.4% diagnostically accurate results were obtained in the kidney, followed by 75.0% in adrenal masses. The diagnostic accuracy of other sites by FNC-NA varied from 66.7%-72.8%.
CONCLUSIONS
Although both techniques have their own advantages and disadvantages, FNC-NA may be a more efficient adjuvant method of sampling in retroperitoneal lesions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Briffod M, Gentile A, Hebert H. Cytopuncture in the follow-up of breast carcinoma. Acta Cytol. 1982; 26:195–200.2. Zajdela A, de Maublanc MA, Schlienger P, Haye C. Cytologic diagnosis of orbital and periorbital palpable tumors using fine-needle sampling without aspiration. Diagn Cytopathol. 1986; 2:17–20.
Article3. Martin HE, Ellis EB. Biopsy by needle puncture and aspiration. Ann Surg. 1930; 92:169–81.
Article4. Mair S, Dunbar F, Becker PJ, Du Plessis W. Fine needle cytology: is aspiration suction necessary? A study of 100 masses in various sites. Acta Cytol. 1989; 33:809–13.5. Orell SR, Sterrett GF, Whitaker D. Fine needle aspiration cytology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone;2005. p. 125–64.6. Franzen S, Giertz G, Zajicek J. Cytological diagnosis of prostatic tumours by transrectal aspiration biopsy: a preliminary report. Br J Urol. 1960; 32:193–6.7. Zajicek J, Franzén S, Jakobsson P, Rubio C, Unsgaard B. Aspiration biopsy of mammary tumors in diagnosis and research: a critical review of 2,200 cases. Acta Cytol. 1967; 11:169–75.8. Kate MS, Kamal MM, Bobhate SK, Kher AV. Evaluation of fine needle capillary sampling in superficial and deep-seated lesions. An analysis of 670 cases. Acta Cytol. 1998; 42:679–84.9. Kamal MM, Arjune DG, Kulkarni HR. Comparative study of fine needle aspiration and fine needle capillary sampling of thyroid lesions. Acta Cytol. 2002; 46:30–4.
Article10. Gadkari RU, Pangarkar M, Dandige S, Munshi M, Kher A. Efficacy of fine needle capillary sampling in the diagnosis of stage III and IV cervical carcinoma. Acta Cytol. 1999; 43:114–6.
Article11. Pothier DD, Narula AA. Should we apply suction during fine needle cytology of thyroid lesions? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2006; 88:643–5.
Article12. Suen KC, Quenville NF. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid gland: a study of 304 cases. J Clin Pathol. 1983; 36:1036–45.
Article13. Jayaram N, Chetan M, Prasad SR, Ramaprasad AV. Thyroiditis: thyroid function and cytologic correlation: a study of 66 cases. J Cytol. 1996; 13:21–4.14. Raghuveer CV, Leekha I, Pai MR, Adhikari P. Fine needle aspiration cytology versus fine needle sampling without aspiration: a prospective study of 200 cases. Indian J Med Sci. 2002; 56:431–9.15. Pinki P, Alok D, Ranjan A, Chand MN. Fine needle aspiration cytology versus fine needle capillary sampling in cytological diagnosis of thyroid lesion. Iran J Pathol. 2015; 10:47–53.16. Santos JE, Leiman G. Nonaspiration fine needle cytology: application of a new technique to nodular thyroid disease. Acta Cytol. 1988; 32:353–6.17. Zajdela A, Zillhardt P, Voillemot N. Cytological diagnosis by fine needle sampling without aspiration. Cancer. 1987; 59:1201–5.
Article18. Rajasekhar A, Sundaram C, Chowdhary T, Charanpal M, Ratnakar KS. Diagnostic utility of fine-needle sampling without aspiration: a prospective study. Diagn Cytopathol. 1991; 7:473–6.
Article19. Rizvi SA, Husain M, Khan S, Mohsin M. A comparative study of fine needle aspiration cytology versus non-aspiration technique in thyroid lesions. Surgeon. 2005; 3:273–6.
Article20. Haddadi-Nezhad S, Larijani B, Tavangar SM, Nouraei SM. Comparison of fine-needle-nonaspiration with fine-needle-aspiration technique in the cytologic studies of thyroid nodules. Endocr Pathol. 2003; 14:369–73.
Article21. Kristensen JK, Bartels E, Jorgensen HE. Percutaneous renal biopsy under the guidance of ultrasound. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1974; 8:223–6.
Article22. Renshaw AA, Granter SR, Cibas ES. Fine-needle aspiration of the adult kidney. Cancer. 1997; 81:71–88.
Article23. Jayaram G, Gupta B. Nonaspiration fine needle cytology in diffuse and nodular thyroid lesions: a study of 220 cases. Acta Cytol. 1991; 35:789–90.24. Zhou JQ, Zhang JW, Zhan WW, et al. Comparison of fine-needle aspiration and fine-needle capillary sampling of thyroid nodules: a prospective study with emphasis on the influence of nodule size. Cancer Cytopathol. 2014; 122:266–73.
Article25. Stewart CJ, Coldewey J, Stewart IS. Comparison of fine needle aspiration cytology and needle core biopsy in the diagnosis of radiologically detected abdominal lesions. J Clin Pathol. 2002; 55:93–7.
Article26. Hamburger JI, Hamburger SW. Fine needle biopsy of thyroid nodules: avoiding the pitfalls. N Y State J Med. 1986; 86:241–9.27. Lowhagen T, Sprenger E. Cytologic presentation of thyroid tumors in aspiration biopsy smear. A review of 60 cases. Acta Cytol. 1974; 18:192–7.28. Ghosh A, Misra RK, Sharma SP, Singh HN, Chaturvedi AK. Aspiration vs nonaspiration technique of cytodiagnosis: a critical evaluation in 160 cases. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2000; 43:107–12.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Usefulness of Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration in Breast Lesions
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Fine Needle Aspiration versus Core Biopsy for the Diagnosis of Subepithelial Tumors
- Percutaneous Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Lung Masses
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Retroperitoneal Paraganglioma with an Unusual Pattern: A Case Report
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Thyroid Follicular Proliferative Lesions