J Educ Eval Health Prof.
2014;11:22. 10.3352/jeehp.2014.11.22.
Learning Style Scales: a valid and reliable questionnaire
- Affiliations
-
- 1Faculty of Nursing & Midwifery, Zabol Medical Sciences University, Zabol, Iran. abdalqani@gmail.com
- 2Department of Medical Education, School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Kubang Kerian, Malaysia.
- KMID: 2380941
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3352/jeehp.2014.11.22
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Learning-style instruments assist students in developing their own learning strategies and outcomes, in eliminating learning barriers, and in acknowledging peer diversity. Only a few psychometrically validated learning-style instruments are available. This study aimed to develop a valid and reliable learning-style instrument for nursing students.
METHODS
A cross-sectional survey study was conducted in two nursing schools in two countries. A purposive sample of 156 undergraduate nursing students participated in the study. Face and content validity was obtained from an expert panel. The LSS construct was established using principal axis factoring (PAF) with oblimin rotation, a scree plot test, and parallel analysis (PA). The reliability of LSS was tested using Cronbach's alpha, corrected item-total correlation, and test-retest.
RESULTS
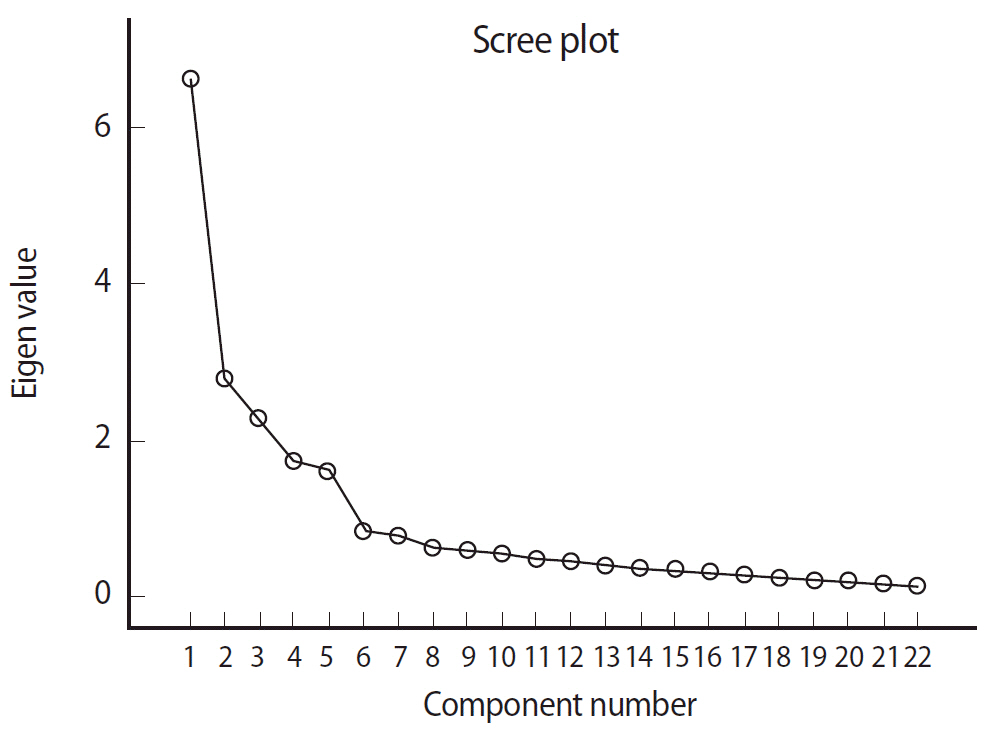
Factor analysis revealed five components, confirmed by PA and a relatively clear curve on the scree plot. Component strength and interpretability were also confirmed. The factors were labeled as perceptive, solitary, analytic, competitive, and imaginative learning styles. Cronbach's alpha was >0.70 for all subscales in both study populations. The corrected item-total correlations were >0.30 for the items in each component.
CONCLUSION
The LSS is a valid and reliable inventory for evaluating learning style preferences in nursing students in various multicultural environments.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Learning style preferences of nursing students at two universities in Iran and Malaysia
Abdolghani Abdollahimohammad, Rogayah Ja’afar
J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2014;11:30. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2014.11.30.Associations of learning style with cultural values and demographics in nursing students in Iran and Malaysia
Abdolghani Abdollahimohammad, Rogayah Ja’afar
J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2015;12:42. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2015.12.42.
Reference
-
1. Williams B, Brown T, Onsman A. Exploratory factor analysis: a five-step guide for novices. Australas J Paramed. 2012; 8(3):http://ro.ecu.edu.au/jephc/vol8/iss3/1.
Article2. Curry L. An organization of learning styles theory and constructs. Paper presented at: The Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. 1983 Apr; Montreal, Canada.3. Berings MG, Poell RF, Simons PR. Conceptualizing on-the-job learning styles. Hum Resour Dev Rev. 2005; 4:373–400. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1534484305281769.
Article4. Burns N, Grove SK. Understanding nursing research: building an evidence-based practice. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier;2007.5. Kappe FR, Boekholt L, den Rooyen C, Van der Flier H. A predictive validity study of the Learning Style Questionnaire (LSQ) using multiple, specific learning criteria. Learn Individ Differ. 2009; 19:464–467. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2009.04.001.
Article6. Hair JF, Black WC, Babin BJ, Anderson RE. Multivariate data analysis. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall;2010.7. Schweizer K, Rauch W, Gold A. Bipolar items for the measurement of personal optimism instead of unipolar items. Psychol Test Assess Model. 2011; 53:399–413.8. Field A. Discovering statistics using SPSS. Upper Saddle River, NJ: London: SAGE Publications Ltd;2009.9. Manolis C, Burns DJ, Assudani R, Chinta R. Assessing experiential learning styles: a methodological reconstruction and validation of the Kolb Learning Style Inventory. Learn Individ Differ. 2013; 23:44–52. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2012.10.009.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Participation and Academic Achievement by Learning Styles in Problem Based Learning
- Learning style preferences of nursing students at two universities in Iran and Malaysia
- Effects of Problem-Based Learning by Learning Style in Medical Education
- Associations of learning style with cultural values and demographics in nursing students in Iran and Malaysia
- The validity and reliability of a problem-based learning implementation questionnaire