Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2017 May;5(3):169-174. 10.4168/aard.2017.5.3.169.
Two patients with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia progressing to acute respiratory distress syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kyungbook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. bschoi@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2379946
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2017.5.3.169
Abstract
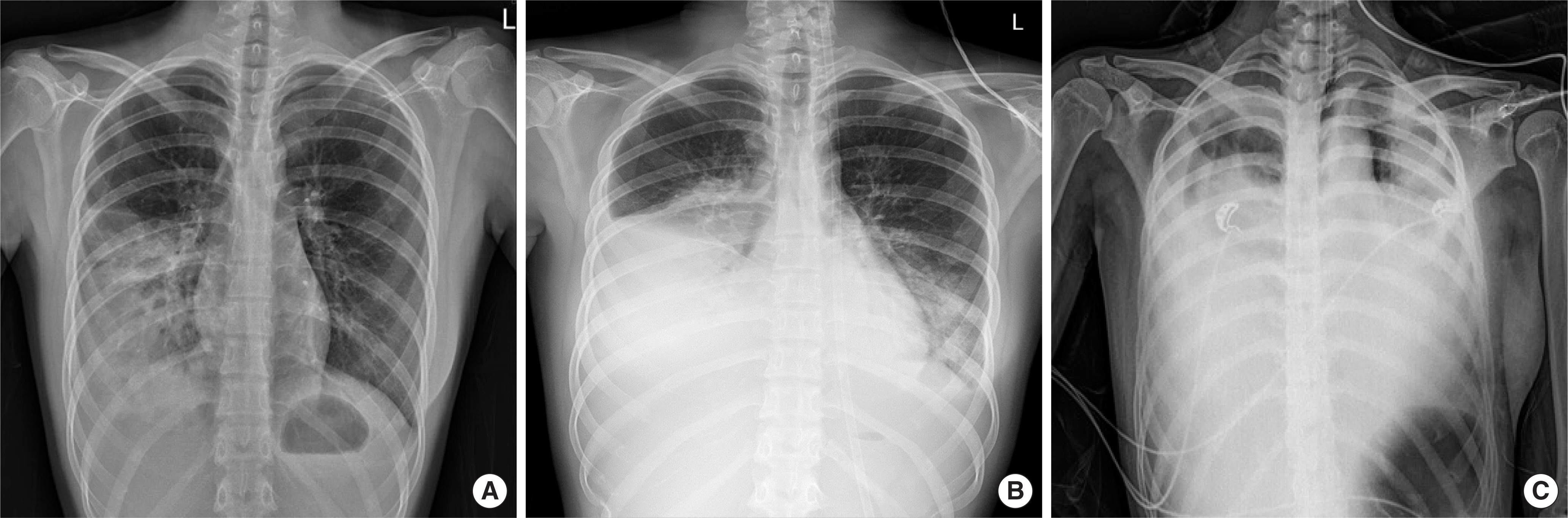
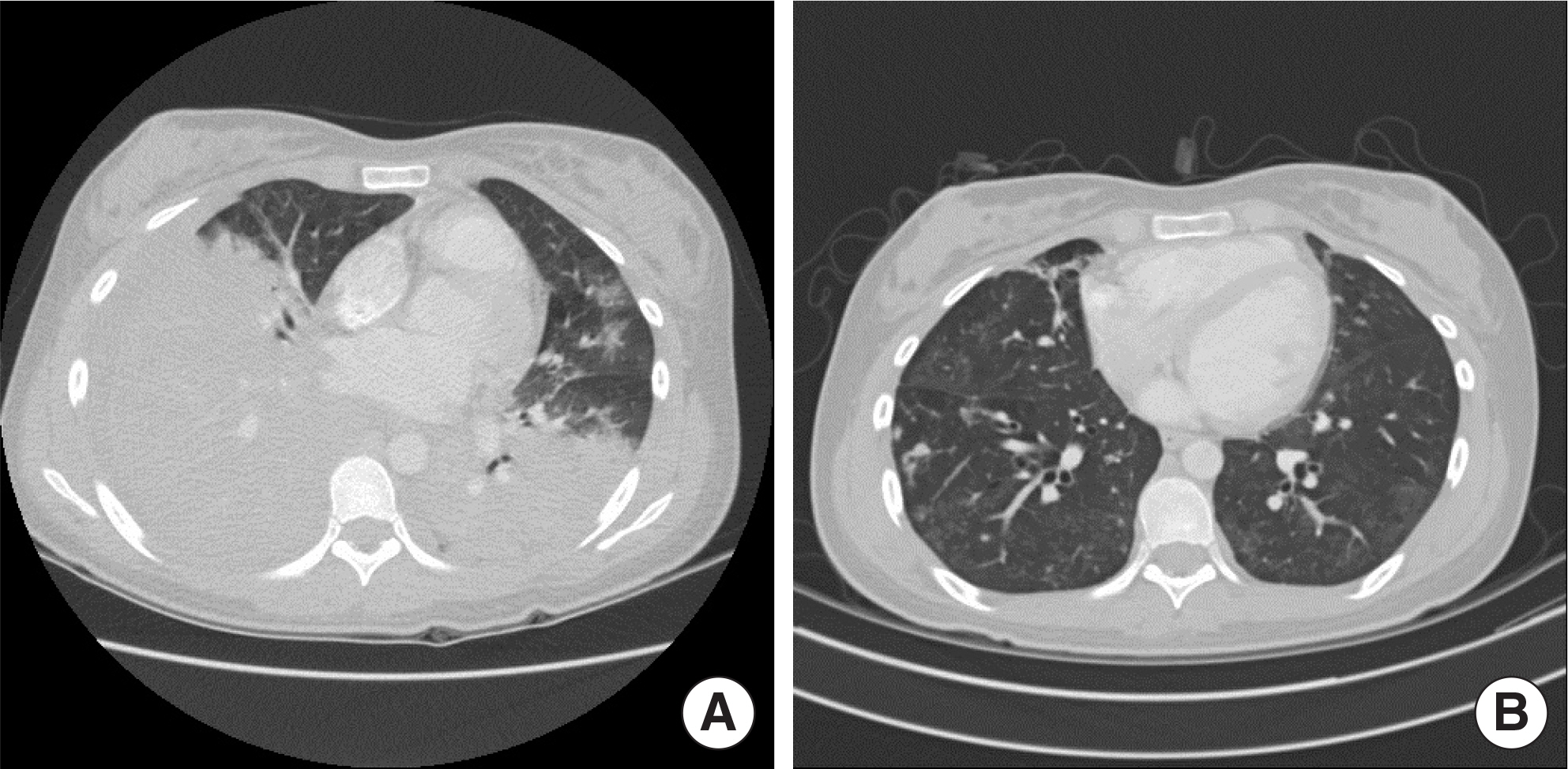
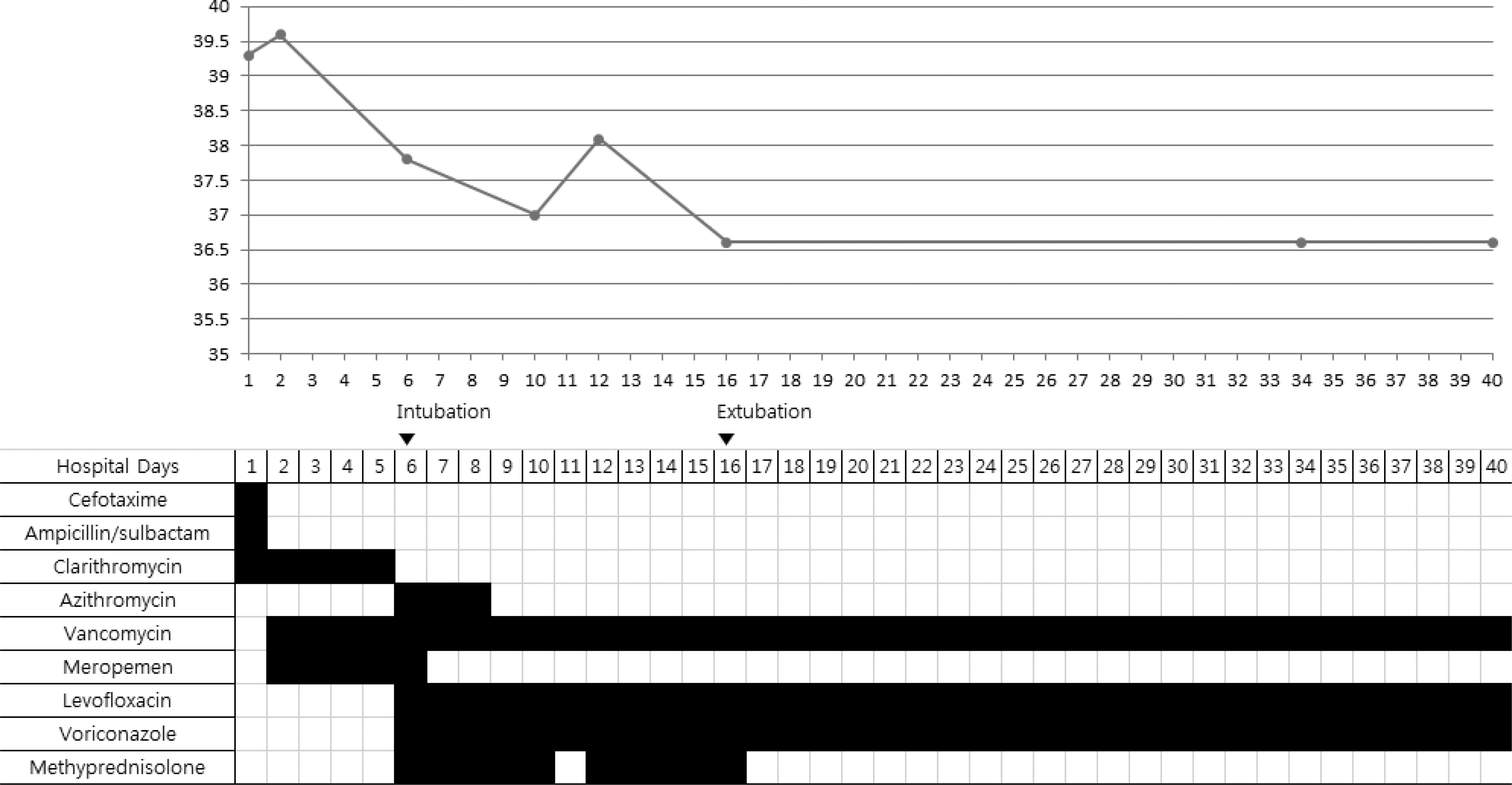
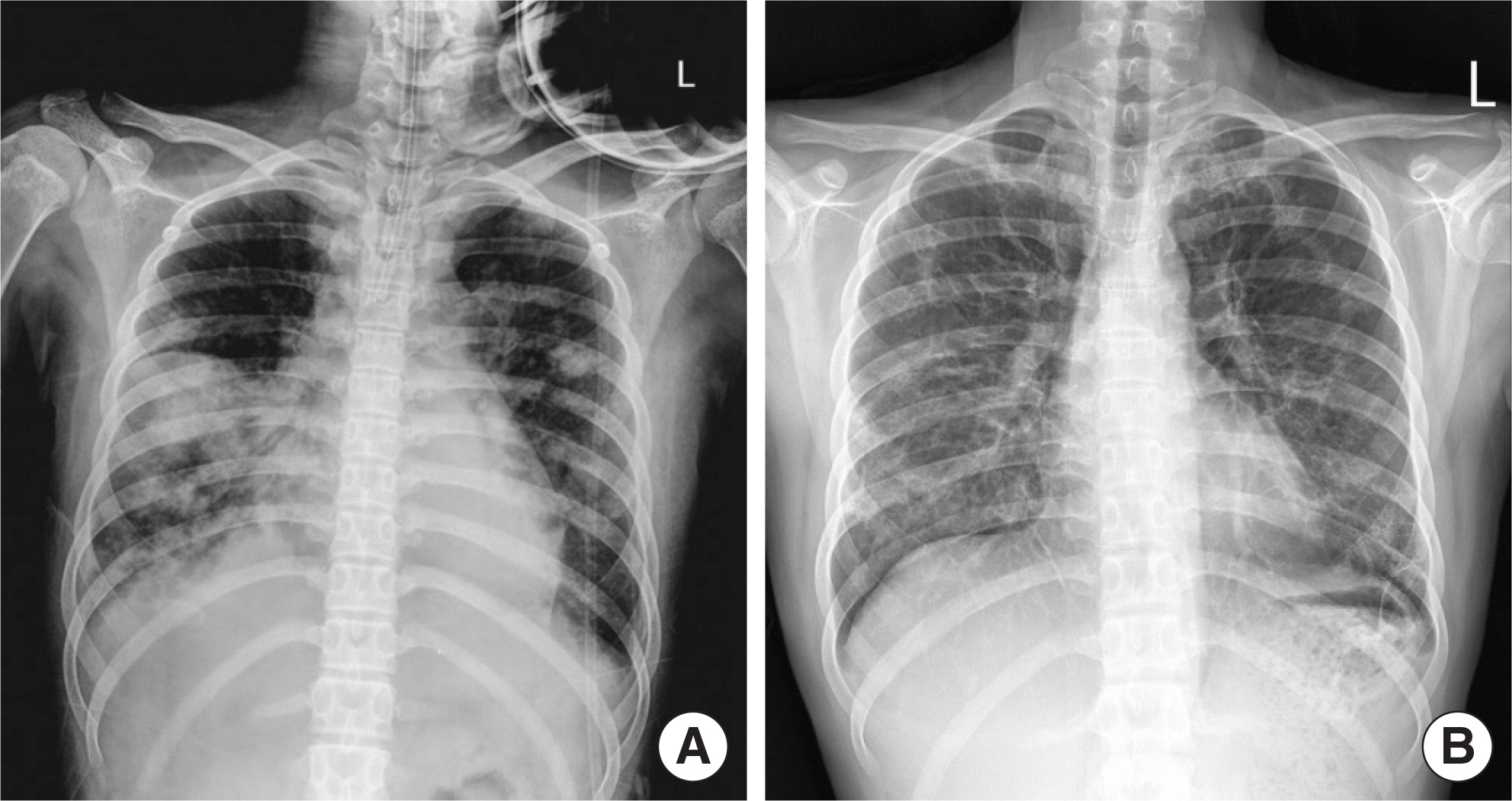
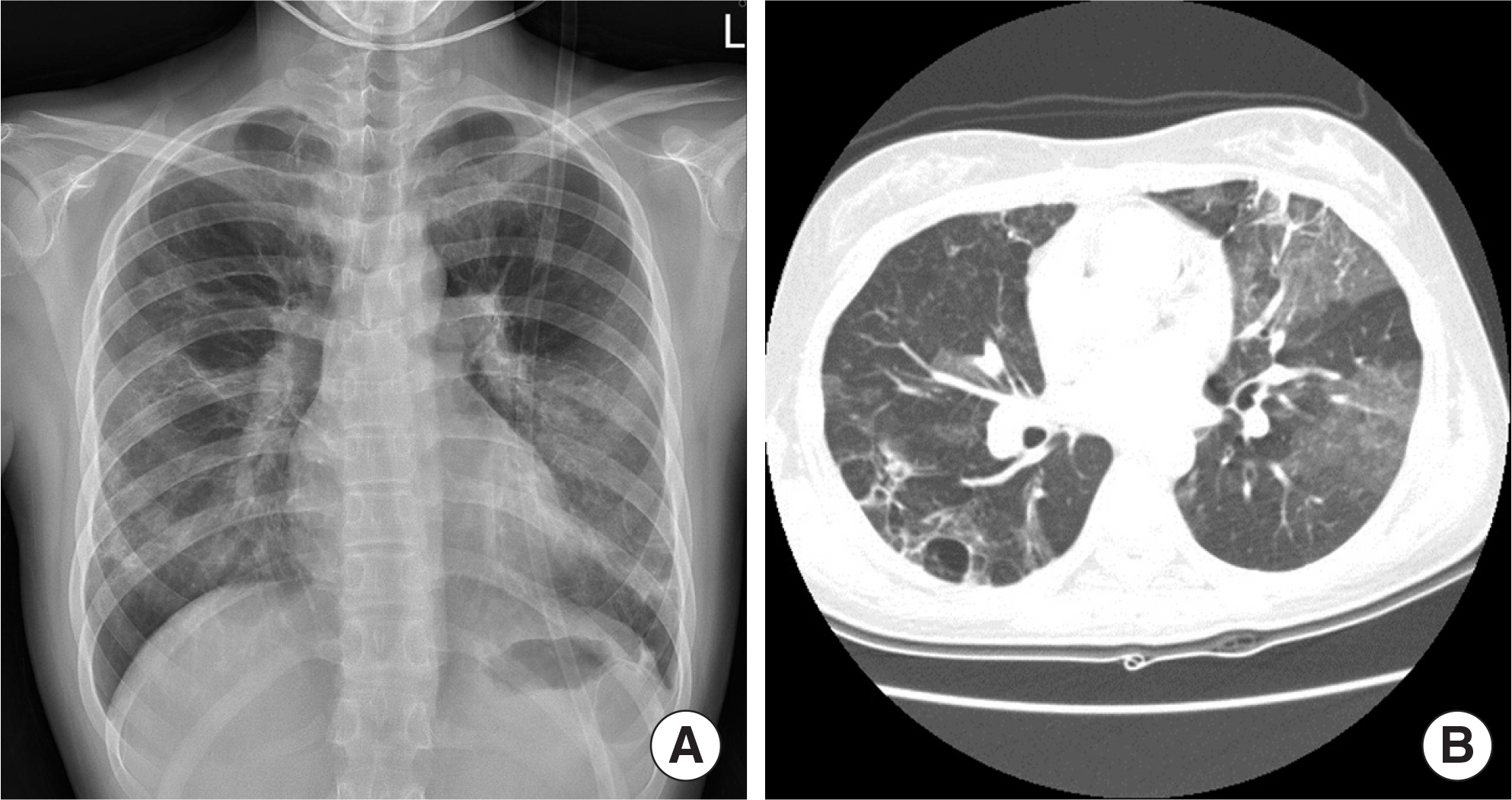
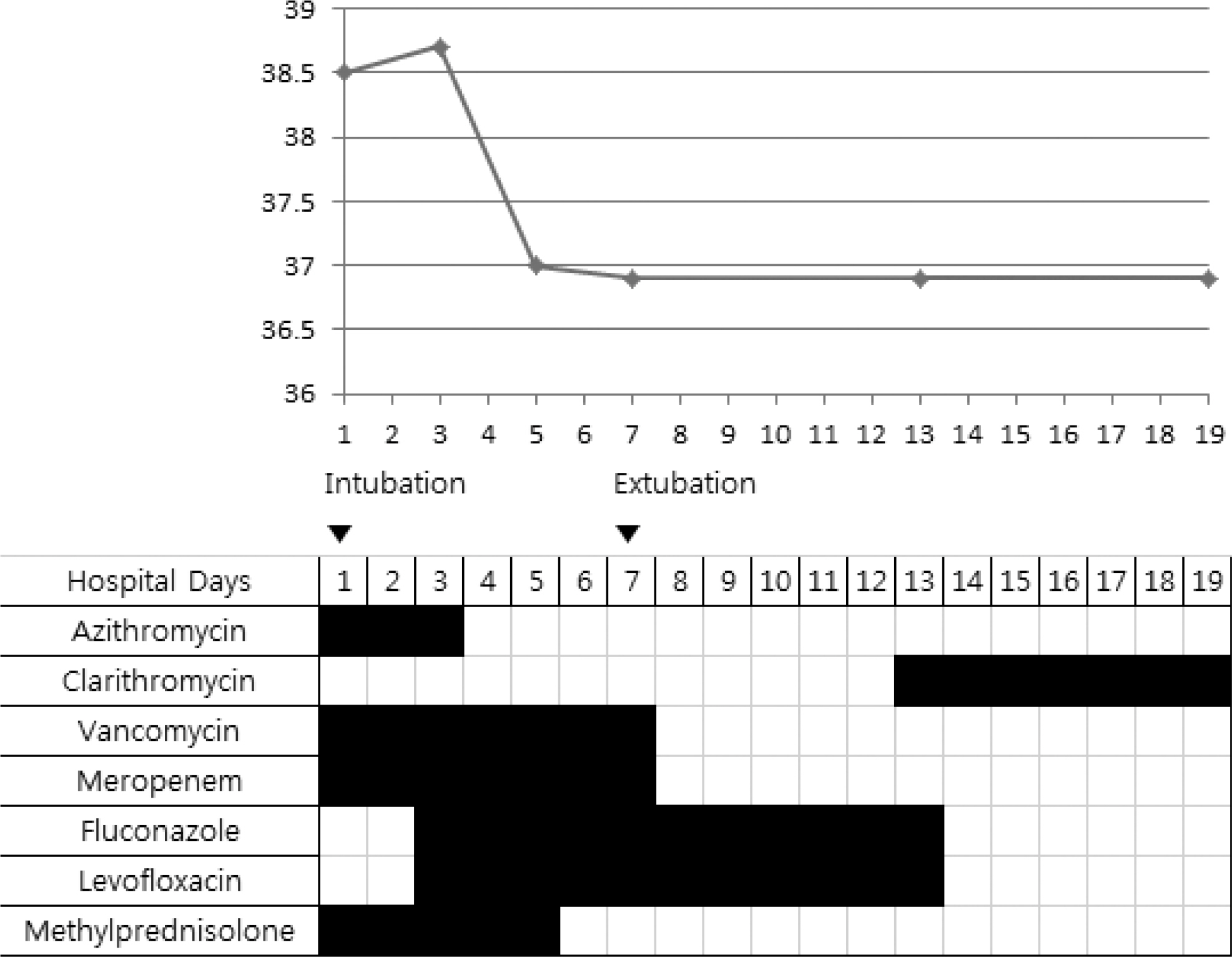
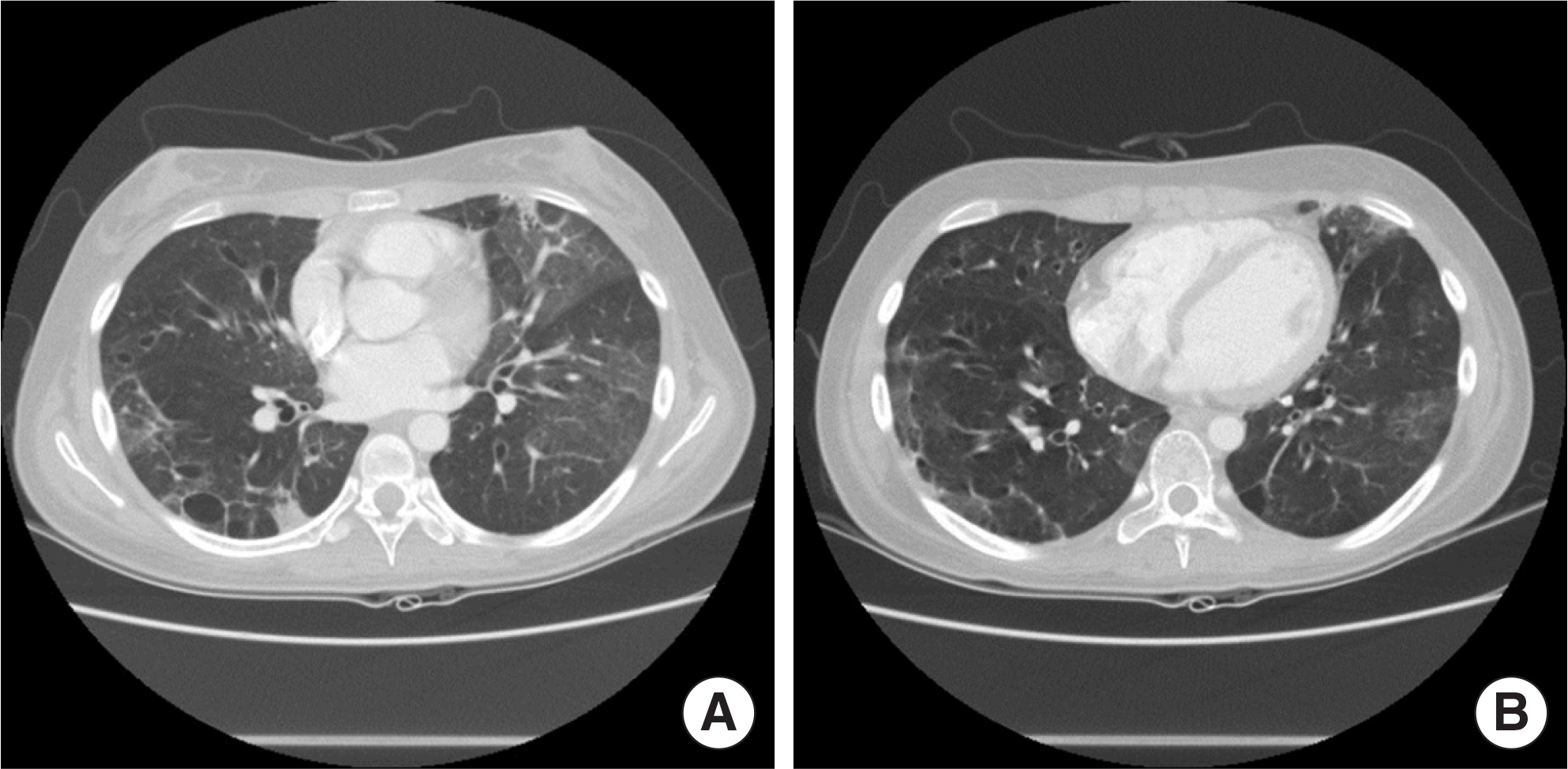
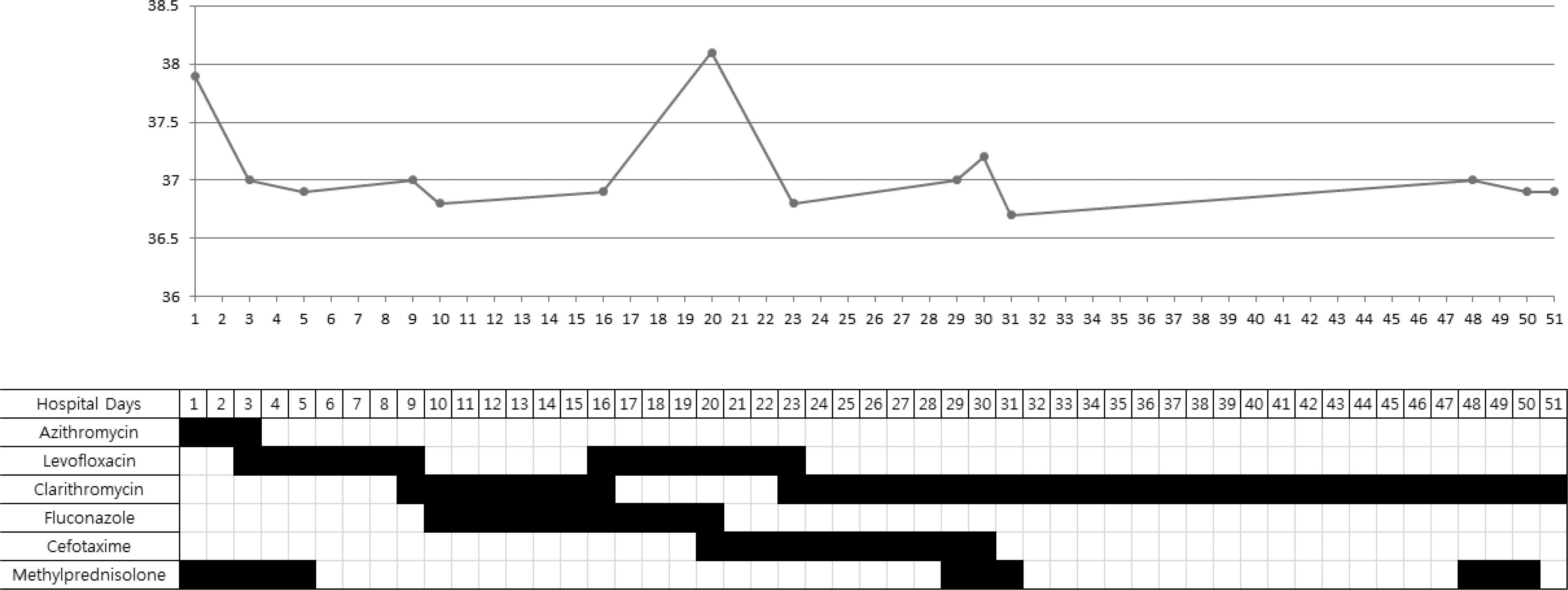
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia is one of the most prevalent community-acquired pneumonias in pediatric patients. It commonly presents with mild respiratory symptoms and is well controlled by macrolide antibiotics. Rarely, it can progress to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) despite appropriate antibiotic therapy, and systemic corticosteroids and quinolone antibiotics are required. We recently treated 2 patients who presented with M. pneumoniae pneumonia with ARDS. Case 1: A 17-year-old girl was admitted with pneumonia that showed no response to antibiotics and progressed to ARDS, which required initiation of mechanical ventilation therapy. The patient was negative for M. pneumoniae IgM; but positive for, M. pneumoniae. After treatment with methylprednisolone and levofloxacin, rapid improvement was observed in both clinical manifestations and chest radiographic findings. Two days after discontinuing a 5-day methylprednisolone treatment regimen, she developed fever, and investigations revealed an elevated C-reactive protein level; this necessitated additional methylprednisolone treatment. Subsequently, she showed complete recovery with no sequelae. Case 2: A 14-year-old girl was admitted with M. pneumoniae pneumonia with ARDS that required mechanical ventilation therapy. She showed a IgM titers against M. pneumoniae of 1:320. After treatment with antibiotics and methylprednisolone, she recovered and was discharged at 48 admission days; however, mild dyspnea persisted. The chest computed tomography showed multiple bronchiectasis areas. After 15 days, because of aggravated dyspnea, she was readmitted and adminis-tered methylprednisolone pulse therapy. Despite 3 courses of methylprednisolone pulse therapy, she still showed mild dyspnea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adrenal Cortex Hormones
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Bronchiectasis
C-Reactive Protein
Child
Dyspnea
Female
Fever
Humans
Immunoglobulin M
Levofloxacin
Methylprednisolone
Mycoplasma pneumoniae*
Mycoplasma*
Pneumonia*
Pneumonia, Mycoplasma*
Radiography, Thoracic
Respiration, Artificial
Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Adult*
Thorax
Adrenal Cortex Hormones
Anti-Bacterial Agents
C-Reactive Protein
Immunoglobulin M
Methylprednisolone
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Child of Severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia with Multiple Organ Failure Treated with ECMO and CRRT
Woojin Hwang, Yoonjin Lee, Eunjee Lee, Jiwon M. Lee, Hong Ryang Kil, Jae Hyeon Yu, Eun Hee Chung
Pediatr Infect Vaccine. 2019;26(1):71-79. doi: 10.14776/piv.2019.26.e9.
Reference
-
1. Ferwerda A, Moll HA, de Groot R. Respiratory tract infections by Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children: a review of diagnostic and therapeutic measures. Eur J Pediatr. 2001; 160:483–91.
Article2. Michelow IC, Olsen K, Lozano J, Rollins NK, Duffy LB, Ziegler T, et al. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children. Pediatrics. 2004; 113:701–7.
Article3. Korppi M, Heiskanen-Kosma T, Kleemola M. Incidence of community-acquired pneumonia in children caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae: serological results of a prospective, population-based study in primary health care. Respirology. 2004; 9:109–14.
Article4. Waites KB. New concepts of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2003; 36:267–78.5. Lee KY. Pediatric respiratory infections by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008; 6:509–21.6. Lee KY, Lee HS, Hong JH, Lee MH, Lee JS, Burgner D, et al. Role of prednisolone treatment in severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2006; 41:263–8.7. Radisic M, Torn A, Gutierrez P, Defranchi HA, Pardo P. Severe acute lung injury caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae: potential role for steroid pulses in treatment. Clin Infect Dis. 2000; 31:1507–11.8. Tamura A, Matsubara K, Tanaka T, Nigami H, Yura K, Fukaya T. Methylprednisolone pulse therapy for refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. J Infect. 2008; 57:223–8.
Article9. Chan ED, Welsh CH. Fulminant Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. West J Med. 1995; 162:133–42.10. Mahler DA, Wells CK. Evaluation of clinical methods for rating dyspnea. Chest. 1988; 93:580–6.
Article11. Lee SH, Noh SM, Lee KY, Lee HS, Hong JH, Lee MH, et al. Clinico-epi-demiologic Study of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia (1993 through 2003). Korean J Pediatr. 2005; 48:154–7.12. Eun BW, Kim NH, Choi EH, Lee HJ. Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Korean children: the epidemiology of pneumonia over an 18-year period. J Infect. 2008; 56:326–31.
Article13. Kang KS, Woo HO. Pattern of occurrence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia in admitted children: Southern Central Korea, from 1989 to 2002. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2003; 46:474–9.14. Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet J, Falke K, Hudson L, et al. Report of the American-European consensus conference on ARDS: defi-nitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes and clinical trial coordination. The Consensus Committee. Intensive Care Med. 1994; 20:225–32.15. Kim CK, Chung CY, Kim JS, Kim WS, Park Y, Koh YY. Late abnormal findings on high-resolution computed tomography after Mycoplasma pneumonia. Pediatrics. 2000; 105:372–8.
Article16. Tomikawa SO, Adde FV, da Silva Filho LV, Leone C, Rodrigues JC. Follow-up on pediatric patients with bronchiolitis obliterans treated with corticosteroid pulse therapy. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014; 9:128.
Article17. Morozumi M, Takahashi T, Ubukata K. Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae: characteristics of isolates and clinical aspects of communi-ty-acquired pneumonia. J Infect Chemother. 2010; 16:78–86.
Article18. Hsieh YC, Tsao KC, Huang CG, Tong S, Winchell JM, Huang YC, et al. Life-threatening pneumonia caused by macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012; 31:208–9.
Article19. Morozumi M, Iwata S, Hasegawa K, Chiba N, Takayanagi R, Matsubara K, et al. Increased macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in pediatric patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008; 52:348–50.20. Tagliabue C, Salvatore CM, Techasaensiri C, Mejias A, Torres JP, Katz K, et al. The impact of steroids given with macrolide therapy on experimental Mycoplasma pneumoniae respiratory infection. J Infect Dis. 2008; 198:1180–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children
- A case mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- A Case of Cerebral Infarction Complicated by Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia
- A Case of Bilateral Spontaneous Tension Pneumothorax Associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection
- A clinical study on mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia