Chonnam Med J.
2017 May;53(2):95-102. 10.4068/cmj.2017.53.2.95.
Structure-Inherent Targeting of Near-Infrared Fluorophores for Image-Guided Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Sciences, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. hhyun@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2379281
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2017.53.2.95
Abstract
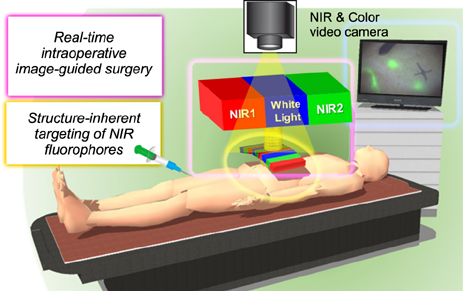
- Although various clinical imaging modalities have been developed to visualize internal body structures and detect abnormal tissues prior to surgical procedures, most medical imaging modalities do not provide disease-specific images in real-time. Optical imaging can provide the surgeon with real-time visualization of the surgical field for intraoperative image-guided surgery. Imaging in the near-infrared (NIR) window (650-900 nm), also known as the "therapeutic window" has high potential by offering low absorbance and scattering in tissues resulting in minimized background autofluorescence. Clinically, optical fluorescence imaging with the targeted contrast agents provides opportunities for significant advances in intraoperative image-guided surgery. There are only two clinically available NIR fluorophores, indocyanine green (ICG) and methylene blue (MB), that support the image-guided surgery. However, neither of them perform in vivo by providing optimum specificity and stability for targeted image guidance. Therefore, it is of paramount importance to develop targeted NIR fluorophores for unmet clinical needs. Using the right combination of an NIR fluorescence imaging system and a targeted fluorophore, the desired target tissues can be imaged to provide real-time fluorescence guidance without changing the field-of-view during surgery. Thus, in a clinical discipline, the development of NIR fluorophores for "˜structure-inherent targeting' is an unmet need for early phase diagnostics with accurate targeting.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Frangioni JV. In vivo near-infrared fluorescence imaging. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2003; 7:626–634.
Article2. Frangioni JV. New technologies for human cancer imaging. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:4012–4021.
Article3. Gioux S, Choi HS, Frangioni JV. Image-guided surgery using invisible near-infrared light: fundamentals of clinical translation. Mol Imaging. 2010; 9:237–255.
Article4. Vahrmeijer AL, Hutteman M, van der Vorst JR, van de Velde CJ, Frangioni JV. Image-guided cancer surgery using near-infrared fluorescence. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013; 10:507–518.
Article5. van Dam GM, Themelis G, Crane LM, Harlaar NJ, Pleijhuis RG, Kelder W, et al. Intraoperative tumor-specific fluorescence imaging in ovarian cancer by folate receptor-α targeting: first in-human results. Nat Med. 2011; 17:1315–1319.
Article6. Pierce MC, Javier DJ, Richards-Kortum R. Optical contrast agents and imaging systems for detection and diagnosis of cancer. Int J Cancer. 2008; 123:1979–1990.
Article7. Jang B, Park S, Kang SH, Kim JK, Kim SK, Kim IH, et al. Gold nanorods for target selective SPECT/CT imaging and photothermal therapy in vivo. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2012; 2:1–11.8. Kaneko OF, Willmann JK. Ultrasound for molecular imaging and therapy in cancer. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2012; 2:87–97.9. Li Y, Pang Y, Vigneron D, Glenn O, Xu D, Zhang X. Investigation of multichannel phased array performance for fetal MR imaging on 1.5T clinical MR system. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2011; 1:24–30.10. Pysz MA, Guracar I, Tian L, Willmann JK. Fast microbubble dwell-time based ultrasonic molecular imaging approach for quantification and monitoring of angiogenesis in cancer. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2012; 2:68–80.11. Yuan J, Mei CS, Panych LP, McDannold NJ, Madore B. Towards fast and accurate temperature mapping with proton resonance frequency-based MR thermometry. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2012; 2:21–32.12. Weissleder R, Tung CH, Mahmood U, Bogdanov A Jr. In vivo imaging of tumors with protease-activated near-infrared fluorescent probes. Nat Biotechnol. 1999; 17:375–378.
Article13. Hawrysz DJ, Sevick-Muraca EM. Developments toward diagnostic breast cancer imaging using near-infrared optical measurements and fluorescent contrast agents. Neoplasia. 2000; 2:388–417.
Article14. Weissleder R. A clearer vision for in vivo imaging. Nat Biotechnol. 2001; 19:316–317.
Article15. Keereweer S, Kerrebijn JD, van Driel PB, Xie B, Kaijzel EL, Snoeks TJ, et al. Optical image-guided surgery--where do we stand? Mol Imaging Biol. 2011; 13:199–207.
Article16. Gibbs SL. Near infrared fluorescence for image-guided surgery. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2012; 2:177–187.17. Kobayashi H, Ogawa M, Alford R, Choyke PL, Urano Y. New strategies for fluorescent probe design in medical diagnostic imaging. Chem Rev. 2010; 110:2620–2640.
Article18. Frangioni JV. The problem is background, not signal. Mol Imaging. 2009; 8:303–304.
Article19. Lee JH, Park G, Hong GH, Choi J, Choi HS. Design considerations for targeted optical contrast agents. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2012; 2:266–273.20. Ashitate Y, Tanaka E, Stockdale A, Choi HS, Frangioni JV. Near-infrared fluorescence imaging of thoracic duct anatomy and function in open surgery and video-assisted thoracic surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011; 142:31–38. 38.e1–38.e2.
Article21. Hutteman M, Choi HS, Mieog JS, van der Vorst JR, Ashitate Y, Kuppen PJ, et al. Clinical translation of ex vivo sentinel lymph node mapping for colorectal cancer using invisible near-infrared fluorescence light. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011; 18:1006–1014.
Article22. Ashitate Y, Stockdale A, Choi HS, Laurence RG, Frangioni JV. Real-time simultaneous near-infrared fluorescence imaging of bile duct and arterial anatomy. J Surg Res. 2012; 176:7–13.
Article23. Poellinger A. Near-infrared imaging of breast cancer using optical contrast agents. J Biophotonics. 2012; 5:815–826.
Article24. Hadjipanayis CG, Jiang H, Roberts DW, Yang L. Current and future clinical applications for optical imaging of cancer: from intraoperative surgical guidance to cancer screening. Semin Oncol. 2011; 38:109–118.
Article25. Kovar JL, Simpson MA, Schutz-Geschwender A, Olive DM. A systematic approach to the development of fluorescent contrast agents for optical imaging of mouse cancer models. Anal Biochem. 2007; 367:1–12.
Article26. Owens EA, Henary M, El Fakhri G, Choi HS. Tissue-specific near-infrared fluorescence imaging. Acc Chem Res. 2016; 49:1731–1740.
Article27. Choi HS, Frangioni JV. Nanoparticles for biomedical imaging: fundamentals of clinical translation. Mol Imaging. 2010; 9:291–310.
Article28. Choi HS, Liu W, Liu F, Nasr K, Misra P, Bawendi MG, et al. Design considerations for tumour-targeted nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol. 2010; 5:42–47.
Article29. Hellebust A, Richards-Kortum R. Advances in molecular imaging: targeted optical contrast agents for cancer diagnostics. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012; 7:429–445.
Article30. Owens EA, Lee S, Choi J, Henary M, Choi HS. NIR fluorescent small molecules for intraoperative imaging. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2015; 7:828–838.
Article31. Choi HS, Liu W, Misra P, Tanaka E, Zimmer JP, Itty Ipe B, et al. Renal clearance of quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol. 2007; 25:1165–1170.
Article32. Choi HS, Ipe BI, Misra P, Lee JH, Bawendi MG, Frangioni JV. Tissue- and organ-selective biodistribution of NIR fluorescent quantum dots. Nano Lett. 2009; 9:2354–2359.
Article33. Choi HS, Ashitate Y, Lee JH, Kim SH, Matsui A, Insin N, et al. Rapid translocation of nanoparticles from the lung airspaces to the body. Nat Biotechnol. 2010; 28:1300–1303.
Article34. Choi HS, Nasr K, Alyabyev S, Feith D, Lee JH, Kim SH, et al. Synthesis and in vivo fate of zwitterionic near-infrared fluorophores. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2011; 50:6258–6263.35. Hyun H, Bordo MW, Nasr K, Feith D, Lee JH, Kim SH, et al. cGMP-Compatible preparative scale synthesis of near-infrared fluorophores. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2012; 7:516–524.
Article36. Choi HS, Gibbs SL, Lee JH, Kim SH, Ashitate Y, Liu F, et al. Targeted zwitterionic near-infrared fluorophores for improved optical imaging. Nat Biotechnol. 2013; 31:148–153.
Article37. Ogawa M, Kosaka N, Choyke PL, Kobayashi H. In vivo molecular imaging of cancer with a quenching near-infrared fluorescent probe using conjugates of monoclonal antibodies and indocyanine green. Cancer Res. 2009; 69:1268–1272.
Article38. Schaafsma BE, Mieog JS, Hutteman M, van der Vorst JR, Kuppen PJ, Löwik CW, et al. The clinical use of indocyanine green as a near-infrared fluorescent contrast agent for image-guided oncologic surgery. J Surg Oncol. 2011; 104:323–332.
Article39. van der Vorst JR, Vahrmeijer AL, Hutteman M, Bosse T, Smit VT, van de Velde CJ, et al. Near-infrared fluorescence imaging of a solitary fibrous tumor of the pancreas using methylene blue. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2012; 4:180–184.
Article40. Hyun H, Park MH, Owens EA, Wada H, Henary M, Handgraaf HJ, et al. Structure-inherent targeting of near-infrared fluorophores for parathyroid and thyroid gland imaging. Nat Med. 2015; 21:192–197.
Article41. Josephson L, Mahmood U, Wunderbaldinger P, Tang Y, Weissleder R. Pan and sentinel lymph node visualization using a near-infrared fluorescent probe. Mol Imaging. 2003; 2:18–23.
Article42. Schaafsma BE, Verbeek FP, Elzevier HW, Tummers QR, van der Vorst JR, Frangioni JV, et al. Optimization of sentinel lymph node mapping in bladder cancer using near-infrared fluorescence imaging. J Surg Oncol. 2014; 110:845–850.
Article43. van der Vorst JR, Schaafsma BE, Verbeek FP, Swijnenburg RJ, Hutteman M, Liefers GJ, et al. Dose optimization for near-infrared fluorescence sentinel lymph node mapping in patients with melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 2013; 168:93–98.
Article44. Hutteman M, Mieog JS, van der Vorst JR, Liefers GJ, Putter H, Löwik CW, et al. Randomized, double-blind comparison of indocyanine green with or without albumin premixing for near-infrared fluorescence imaging of sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 127:163–170.
Article45. Mieog JS, Troyan SL, Hutteman M, Donohoe KJ, van der Vorst JR, Stockdale A, et al. Toward optimization of imaging system and lymphatic tracer for near-infrared fluorescent sentinel lymph node mapping in breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011; 18:2483–2491.
Article46. Troyan SL, Kianzad V, Gibbs-Strauss SL, Gioux S, Matsui A, Oketokoun R, et al. The FLARE intraoperative near-infrared fluorescence imaging system: a first-in-human clinical trial in breast cancer sentinel lymph node mapping. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009; 16:2943–2952.
Article47. Hutteman M, van der Vorst JR, Gaarenstroom KN, Peters AA, Mieog JS, Schaafsma BE, et al. Optimization of near-infrared fluorescent sentinel lymph node mapping for vulvar cancer. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2012; 206:89.e1–89.e5.
Article48. Ashitate Y, Hyun H, Kim SH, Lee JH, Henary M, Frangioni JV, et al. Simultaneous mapping of pan and sentinel lymph nodes for real-time image-guided surgery. Theranostics. 2014; 4:693–700.
Article49. Gibbs-Strauss SL, Nasr KA, Fish KM, Khullar O, Ashitate Y, Siclovan TM, et al. Nerve-highlighting fluorescent contrast agents for image-guided surgery. Mol Imaging. 2011; 10:91–101.
Article50. Whitney MA, Crisp JL, Nguyen LT, Friedman B, Gross LA, Steinbach P, et al. Fluorescent peptides highlight peripheral nerves during surgery in mice. Nat Biotechnol. 2011; 29:352–356.
Article51. Park MH, Hyun H, Ashitate Y, Wada H, Park G, Lee JH, et al. Prototype nerve-specific near-infrared fluorophores. Theranostics. 2014; 4:823–833.
Article52. Bao K, Nasr KA, Hyun H, Lee JH, Gravier J, Gibbs SL, et al. Charge and hydrophobicity effects of NIR fluorophores on bone-specific imaging. Theranostics. 2015; 5:609–617.
Article53. Zaheer A, Lenkinski RE, Mahmood A, Jones AG, Cantley LC, Frangioni JV. In vivo near-infrared fluorescence imaging of osteoblastic activity. Nat Biotechnol. 2001; 19:1148–1154.
Article54. Bhushan KR, Tanaka E, Frangioni JV. Synthesis of conjugatable bisphosphonates for molecular imaging of large animals. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2007; 46:7969–7971.
Article55. Bhushan KR, Misra P, Liu F, Mathur S, Lenkinski RE, Frangioni JV. Detection of breast cancer microcalcifications using a dual-modality SPECT/NIR fluorescent probe. J Am Chem Soc. 2008; 130:17648–17649.
Article56. Hyun H, Wada H, Bao K, Gravier J, Yadav Y, Laramie M, et al. Phosphonated near-infrared fluorophores for biomedical imaging of bone. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014; 53:10668–10672.
Article57. Hyun H, Owens EA, Wada H, Levitz A, Park G, Park MH, et al. Cartilage-specific near-infrared fluorophores for biomedical imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015; 54:8648–8652.
Article58. Owens EA, Hyun H, Tawney JG, Choi HS, Henary M. Correlating molecular character of NIR imaging agents with tissue-specific uptake. J Med Chem. 2015; 58:4348–4356.
Article59. Owens EA, Hyun H, Dost TL, Lee JH, Park G, Pham DH, et al. Near-infrared illumination of native tissues for image-guided surgery. J Med Chem. 2016; 59:5311–5323.
Article60. Ashitate Y, Levitz A, Park MH, Hyun H, Venugopal V, Park G, et al. Endocrine-specific NIR fluorophores for adrenal gland targeting. Chem Commun (Camb). 2016; 52:10305–10308.
Article61. Winer JH, Choi HS, Gibbs-Strauss SL, Ashitate Y, Colson YL, Frangioni JV. Intraoperative localization of insulinoma and normal pancreas using invisible near-infrared fluorescent light. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010; 17:1094–1100.
Article62. Wada H, Hyun H, Vargas C, Gravier J, Park G, Gioux S, et al. Pancreas-targeted NIR fluorophores for dual-channel image-guided abdominal surgery. Theranostics. 2015; 5:1–11.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Near-Infrared Contrast Agents for Bone-Targeted Imaging
- Assessment and Comparison of Three Dimensional Exoscopes for Near-Infrared Fluorescence-Guided Surgery Using Second-Window Indocyanine-Green
- Clinical Usefulness of Infrared image for Subretinal Structure in Chorioretinal Disease
- A Case of Image-Guided Surgery in Congenital Aural Atresia
- Real-Time Fluorescence Imaging in Thoracic Surgery