J Adv Prosthodont.
2016 Jun;8(3):214-218. 10.4047/jap.2016.8.3.214.
Repeatability and reproducibility of individual abutment impression, assessed with a blue light scanner
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dental Technology, Medical campus, KyungDong University, Wonju, Republic of Korea.
- 2Department of Dental Laboratory Science and Engineering, College of Health Science, Korea University, Seoul, Republic of Korea. kuc2842@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2376846
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2016.8.3.214
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We assessed the repeatability and reproducibility of abutment teeth dental impressions, digitized with a blue light scanner, by comparing the discrepancies in repeatability and reproducibility values for different types of abutment teeth.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
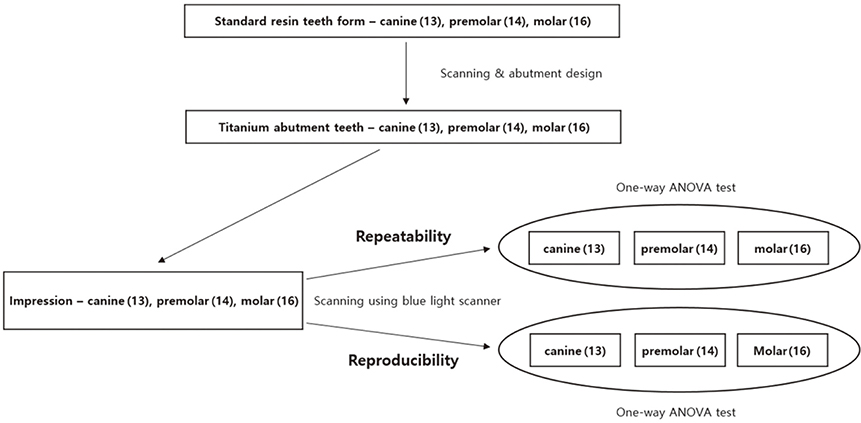
To evaluate repeatability, impressions of the canine, first premolar, and first molar, prepared for ceramic crowns, were repeatedly scanned to acquire 5 sets of 3-dimensional data via stereolithography (STL) files. Point clouds were compared and the error sizes were measured (n=10, per type). To evaluate reproducibility, the impressions were rotated by 10-20° on the table and scanned. These data were compared to the first STL data and the error sizes were measured (n=5, per type). One-way analysis of variance was used to assess the repeatability and reproducibility of the 3 types of teeth, and Tukey honest significant differences (HSD) multiple comparison test was used for post hoc comparisons (α=.05).
RESULTS
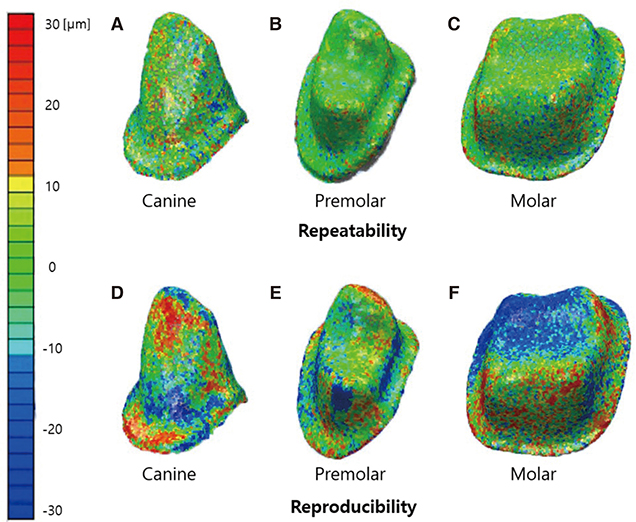
The differences with regard to repeatability were 4.5, 2.7, and 3.1 µm for the canine, premolar, and molar, indicating the poorest repeatability for the canine (P<.001). For reproducibility, the differences were 6.6, 5.8, and 11.0 µm indicating the poorest reproducibility for the molar (P=.007).
CONCLUSION
Our results indicated that impressions of individual abutment teeth, digitized with a blue light scanner, had good repeatability and reproducibility.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Trueness and precision of scanning abutment impressions and stone models according to dental CAD/CAM evaluation standards
Jin-Hun Jeon, Seong-Sig Hwang, Ji-Hwan Kim, Woong-Chul Kim
J Adv Prosthodont. 2018;10(5):335-339. doi: 10.4047/jap.2018.10.5.335.Evaluation of the reproducibility of various abutments using a blue light model scanner
Dong-Yeon Kim, Kyung-Eun Lee, Jin-Hun Jeon, Ji-Hwan Kim, Woong-Chul Kim
J Adv Prosthodont. 2018;10(4):328-334. doi: 10.4047/jap.2018.10.4.328.
Reference
-
1. Nedelcu RG, Persson AS. Scanning accuracy and precision in 4 intraoral scanners: an in vitro comparison based on 3-dimensional analysis. J Prosthet Dent. 2014; 112:1461–1471.2. Persson A, Andersson M, Oden A, Sandborgh-Englund G. A three-dimensional evaluation of a laser scanner and a touch-probe scanner. J Prosthet Dent. 2006; 95:194–200.3. Jeon JH, Kim HY, Kim JH, Kim WC. Accuracy of 3D white light scanning of abutment teeth impressions: evaluation of trueness and precision. J Adv Prosthodont. 2014; 6:468–473.4. Quaas S, Rudolph H, Luthardt RG. Direct mechanical data acquisition of dental impressions for the manufacturing of CAD/CAM restorations. J Dent. 2007; 35:903–908.5. Jeon JH, Lee KT, Kim HY, Kim JH, Kim WC. White light scanner-based repeatability of 3-dimensional digitizing of silicon rubber abutment teeth impressions. J Adv Prosthodont. 2013; 5:452–456.6. Jeon JH, Choi BY, Kim CM, Kim JH, Kim HY, Kim WC. Three-dimensional evaluation of the repeatability of scanned conventional impressions of prepared teeth generated with white- and blue-light scanners. J Prosthet Dent. 2015; 114:549–553.7. Jeon JH, Jung ID, Kim JH, Kim HY, Kim WC. Three-dimensional evaluation of the repeatability of scans of stone models and impressions using a blue LED scanner. Dent Mater J. 2015; 34:686–691.8. Luthardt RG, Loos R, Quaas S. Accuracy of intraoral data acquisition in comparison to the conventional impression. Int J Comput Dent. 2005; 8:283–294.9. Ender A, Mehl A. Accuracy of complete-arch dental impressions: a new method of measuring trueness and precision. J Prosthet Dent. 2013; 109:121–128.10. Persson AS, Andersson M, Odén A, Sandborgh-Englund G. Computer aided analysis of digitized dental stone replicas by dental CAD/CAM technology. Dent Mater. 2008; 24:1123–1130.11. Bernal C, de Agustina B, Marin MM, Camacho AM. Performance evaluation of optical scanner based on blue LED structured light. Procedia Eng. 2013; 63:591–598.12. ISO-12836. Dentistry - Digitizing devices for CAD/CAM systems for indirect dental restorations-test methods for assessing accuracy. Geneva; Switzerland: ISO;2015. Accessed March 2, 2016. Available from: http://www.iso.org/iso/store.html.13. Hoyos A, Soderholm KJ. Influence of tray rigidity and impression technique on accuracy of polyvinyl siloxane impressions. Int J Prosthodont. 2011; 24:49–54.14. Wöstmann B, Rehmann P, Balkenhol M. Accuracy of impressions obtained with dual-arch trays. Int J Prosthodont. 2009; 22:158–160.15. Ziegler M. Digital impression taking with reproducibly high precision. Int J Comput Dent. 2009; 12:159–163.16. Chandran DT, Jagger DC, Jagger RG, Barbour ME. Two- and three-dimensional accuracy of dental impression materials: effects of storage time and moisture contamination. Biomed Mater Eng. 2010; 20:243–249.17. Logozzo S, Zanetti EM, Franceschini G, Kilpelä A, Mäkynen A. Recent advances in dental optics – Part I: 3D intraoral scanners for restorative dentistry. Opt Lasers Eng. 2014; 54:203–221.18. Martorelli M, Ausiello P, Morrone R. A new method to assess the accuracy of a Cone Beam Computed Tomography scanner by using a non-contact reverse engineering technique. J Dent. 2014; 42:460–465.19. Persson M, Andersson M, Bergman B. The accuracy of a high-precision digitizer for CAD/CAM of crowns. J Prosthet Dent. 1995; 74:223–229.20. Naidu D, Freer TJ. Validity, reliability, and reproducibility of the iOC intraoral scanner: a comparison of tooth widths and Bolton ratios. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2013; 144:304–310.21. Flügge TV, Schlager S, Nelson K, Nahles S, Metzger MC. Precision of intraoral digital dental impressions with iTero and extraoral digitization with the iTero and a model scanner. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2013; 144:471–478.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of the effect of abutment preparation angles on the repeatability and reproducibility using a blue light model scanner
- Evaluation of the reproducibility of various abutments using a blue light model scanner
- White light scanner-based repeatability of 3-dimensional digitizing of silicon rubber abutment teeth impressions
- Posterior single implant prosthesis using scannable healing abutment
- Influence of individual tooth tray on the teeth with undercut in impression taking