Perinatology.
2017 Mar;28(1):11-19. 10.14734/PN.2017.28.1.11.
A Survey on the Awareness of Human Milk Bank in Korean Female Health Care Providers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Soon Chun Hyang University, Korea.
- 2Department of Biostatistics, Soonchunhyang Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Nursing, Konkuk University, Chungju, Korea. nmkang03@kku.ac.kr
- 4Department of Nursing, College of Nursing, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
- 5Department of Political Sciences, Faculty of Social Sciences, University of Antwerp, Belgium.
- KMID: 2376572
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/PN.2017.28.1.11
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Human milk bank is known as best alternative option for sick infants. However, only two human milk banks (HMBs) are working in Korea. In the present study, we evaluated the awareness on the HMB in female health care provider to find out the issues that would help facilitating HMB establishment in Korea.
METHODS
The survey questionnaire was developed by a team composed with neonatologists, obstetricians, nurses, nutritionists, and health care specialists. The survey was performed for female health care workers in Soon Chun Hyang Cheonan Hospital between March and June in 2016. Eighty-eight of 110 questionnaires were collected and the results were analyzed.
RESULTS
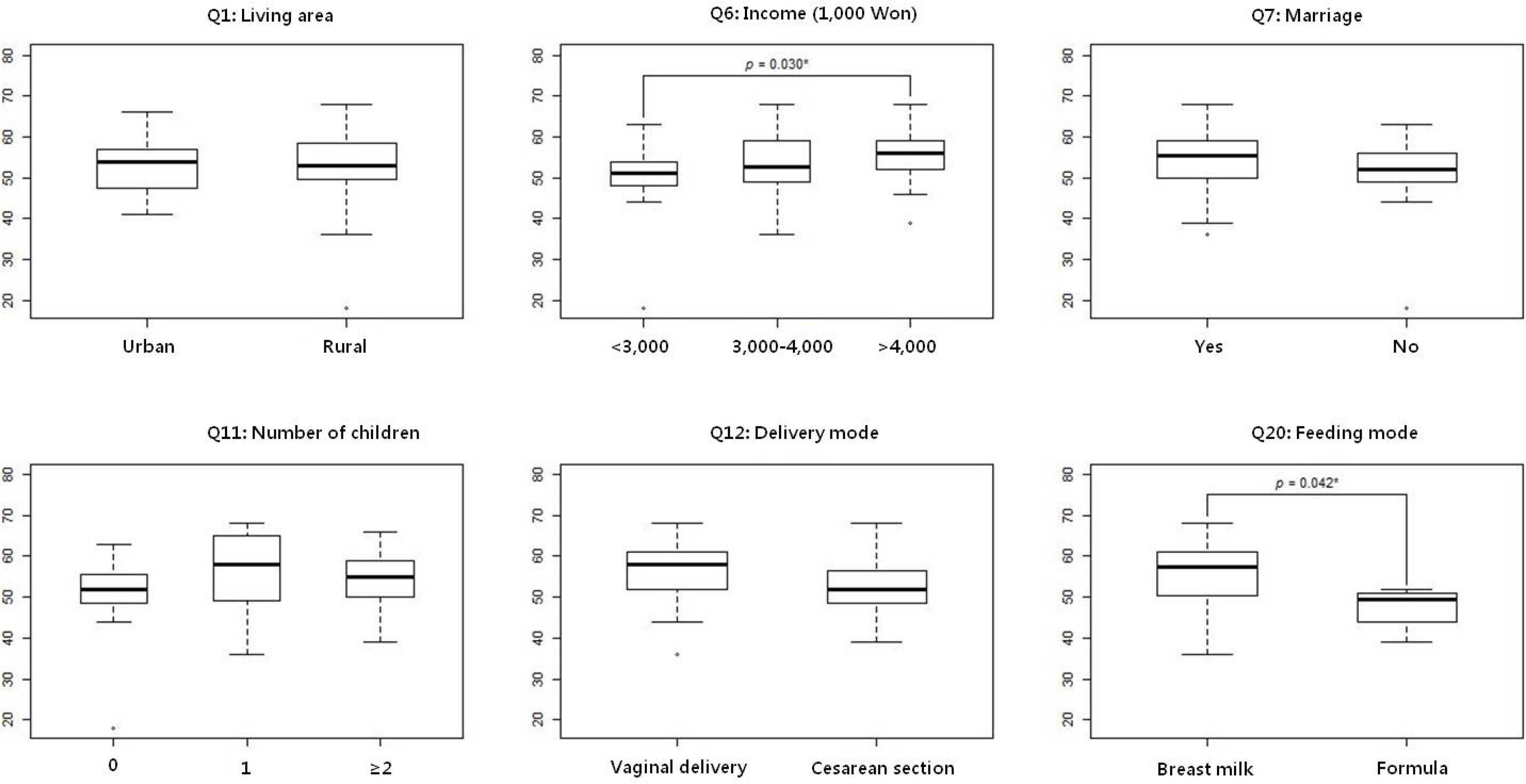
Most of subjects were found to have correct knowledge on the breast milk feeding. However, only 49% of subjects had awareness of the presence of HMB. Unfortunately, less than half of them could get information about HMB by official way including mass media. In addition, 76% of subjects were found not to want to use HMB. Most important reason was found as a concern on the safety of donor milk including life style of donors, infection controls, and possible nutritional loss of banked milk.
CONCLUSION
The purpose and function of HMB was not widely educated and it seems to be one of most important reasons why women have negative concept about HMB in Korea. Thus, further study is warranted with more numbers of subjects after active public education about the HMB.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Das BK., Mishra RN., Mishra OP., Bhargava V., Prakash A. Comparative outcome of low birth weight babies. Indian Pediatr. 1993. 30:15–21.2). Arslanoglu S., Moro GE., Bellu R., Turoli D., De Nisi G., Tonetto P, et al. Presence of human milk bank is associated with elevated rate of exclusive breastfeeding in VLBW infants. J Perinat Med. 2013. 41:129–31.
Article3). Bharati P., Pal M., Bandyopadhyay M., Bhakta A., Chakraborty S., Bharati P. Prevalence and causes of low birth weight in India. Malays J Nutr. 2011. 17:301–13.4). Cristofalo EA., Schanler RJ., Blanco CL., Sullivan S., Trawoeger R., Kiechl-Kohlendorfer U, et al. Randomized trial of exclusive human milk versus preterm formula diets in extremely premature infants. J Pediatr. 2013. 163:1592–5.
Article5). De Nisi G., Berti M., De Nisi M., Bertino E. Early enteral feeding with human milk for VLBW infants. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2012. 26:69–73.6). Israel-Ballard K., Donovan R., Chantry C., Coutsoudis A., Sheppard H., Sibeko L, et al. Flash-heat inactivation of HIV-1 in human milk: a potential method to reduce postnatal transmission in developing countries. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007. 45:318–23.7). Bharadva K., Tiwari S., Mishra S., Mukhopadhyay K., Yadav B., Agarwal RK, et al. Human milk banking guidelines. Indian Pediatr. 2014. 51:469–74.
Article8). Arslanoglu S., Bertino E., Tonetto P., De Nisi G., Ambruzzi AM., Biasini A, et al. Guidelines for the establishment and operation of a donor human milk bank. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010. 23(Suppl 2):1–20.
Article9). Song KH., Lee YM., Chang JY., Park EY., Park SA., Cho NK, et al. A report on operating a nationwide human milk bank in Korea. Korean J Pediatr. 2010. 53:488–94.
Article10). Karadag A., Ozdemir R., Ak M., Ozer A., Dogan DG., Elkiran O. Human milk banking and milk kinship: Perspectives of mothers in a Muslim country. J Trop Pediatr. 2015. 61:188–96.
Article11). Escuder-Vieco D., Garcia-Algar Ó., Pichini S., Pacifici R., García-Lara NR., Pallás-Alonso CR. Validation of a screening questionnaire for a human milk bank to determine the presence of illegal drugs, nicotine, and caffeine. J Pediatr. 2014. 164:811–4.
Article12). Mizuno K., Sakurai M., Itabashi K. Necessity of human milk banking in Japan: Questionnaire survey of neonatologists. Pediatr Int. 2015. 57:639–44.
Article13). Kim HJ., Kim KY., Hwangbo JY. Brestfeeding rate and its related factors in rural area. J Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Soc. 2014. 15:1671–80.
Article14). Kim JE., Park DY. A study on the experience of breastfeeding education for women with children 24 months of age and younger. Korean J Community Living Sci. 2012. 23:523–35.
Article15). Lee HS., Suh SR., Kim KY., Kim HJ. Breastfeeding rate and its related factors in Gumi. J Korean Soc Matern Child Health. 2013. 17:129–42.16). Seo JW., Kim YJ., Lee KH., Kim JY., Sim JG., Kim HS, et al. A survey on the understanding of breast-feeding in pregnant woman. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2002. 45:575–87.17). Sung YA., Ahn JY., Lee HY., Kim JY., Ahn DH., Hong YJ. A survey of breastfeeding. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1998. 41:444–50.18). Byun SJ. A study on performance of breast feeding by employed mother. Korean J Women Health Nursing. 1995. 1:137–52.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Web-based Health Information Survey for Korean Human Milk Bank and Current Issues
- Research on the Perceptions of Low Vision Rehabilitation
- Women Infant and Children program participants' beliefs and consumption of soy milk : Application of the Theory of Planned Behavior
- A report on operating a nationwide human milk bank in Korea
- The Experience of Human Milk Banking for 8 Years: Korean Perspective