Prog Med Phys.
2016 Dec;27(4):236-240. 10.14316/pmp.2016.27.4.236.
Conceptual Study of Brain Dedicated PET Improving Sensitivity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Engineering and Research Institute of Biomedical Engineering, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Electronic Engineering, Sogang University, Seoul, Korea. ychoi@sogang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2376558
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2016.27.4.236
Abstract
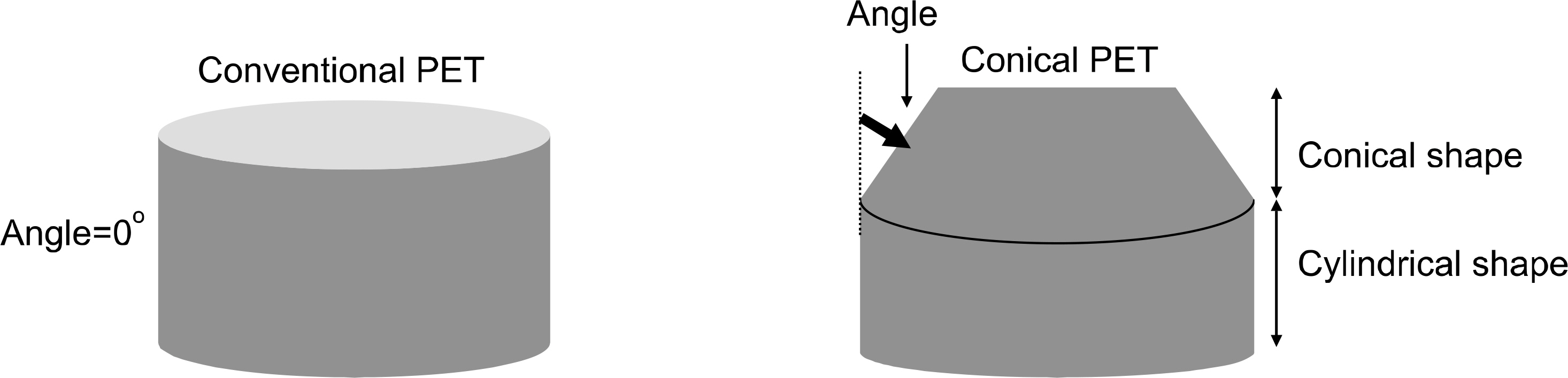
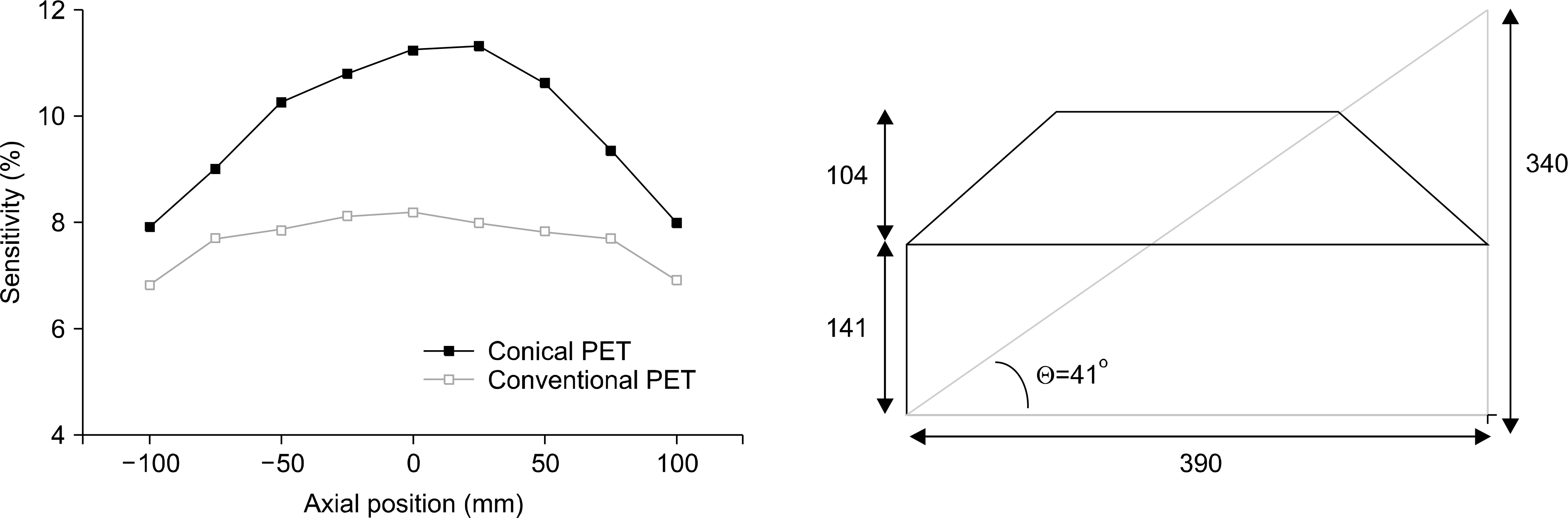
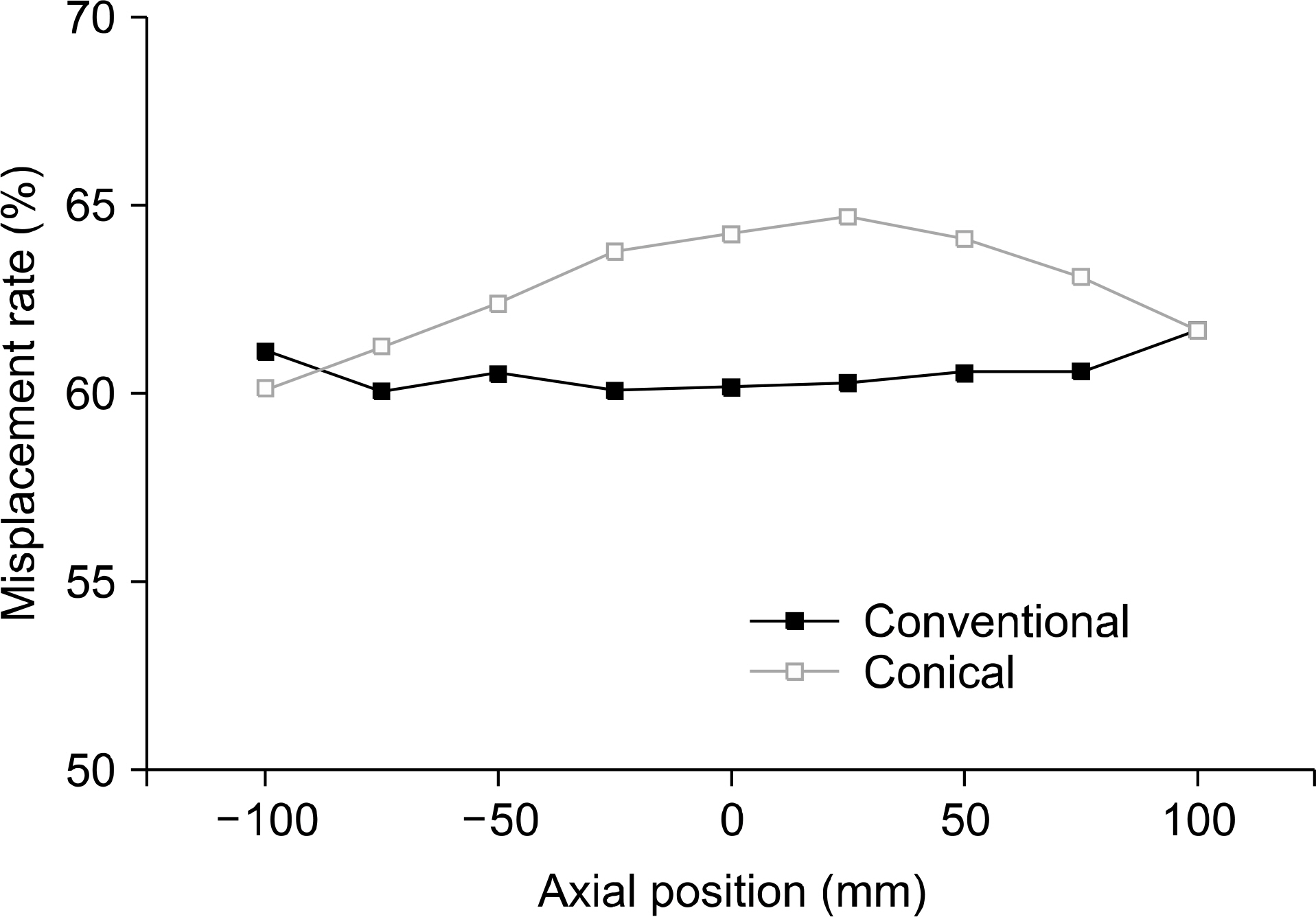
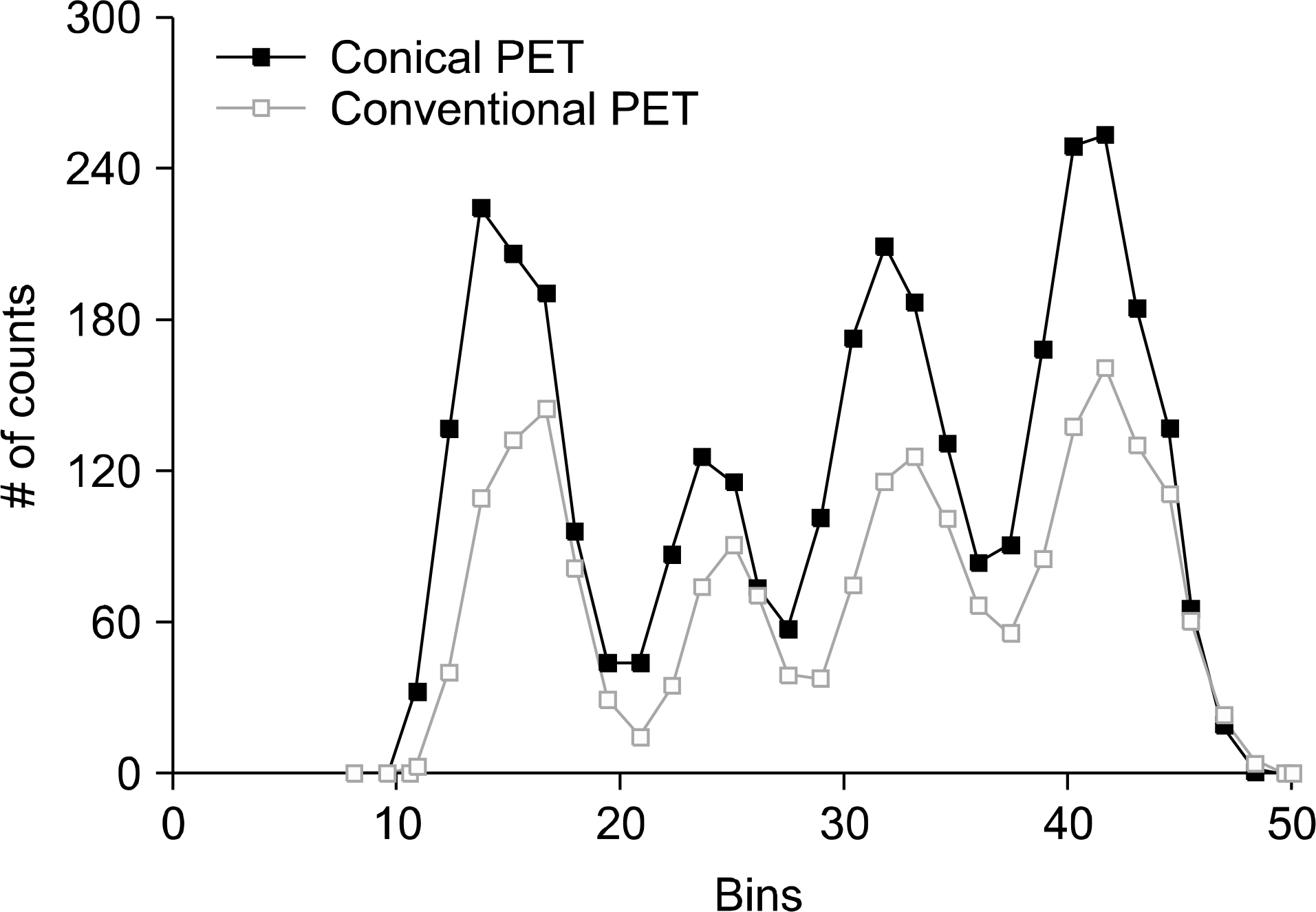
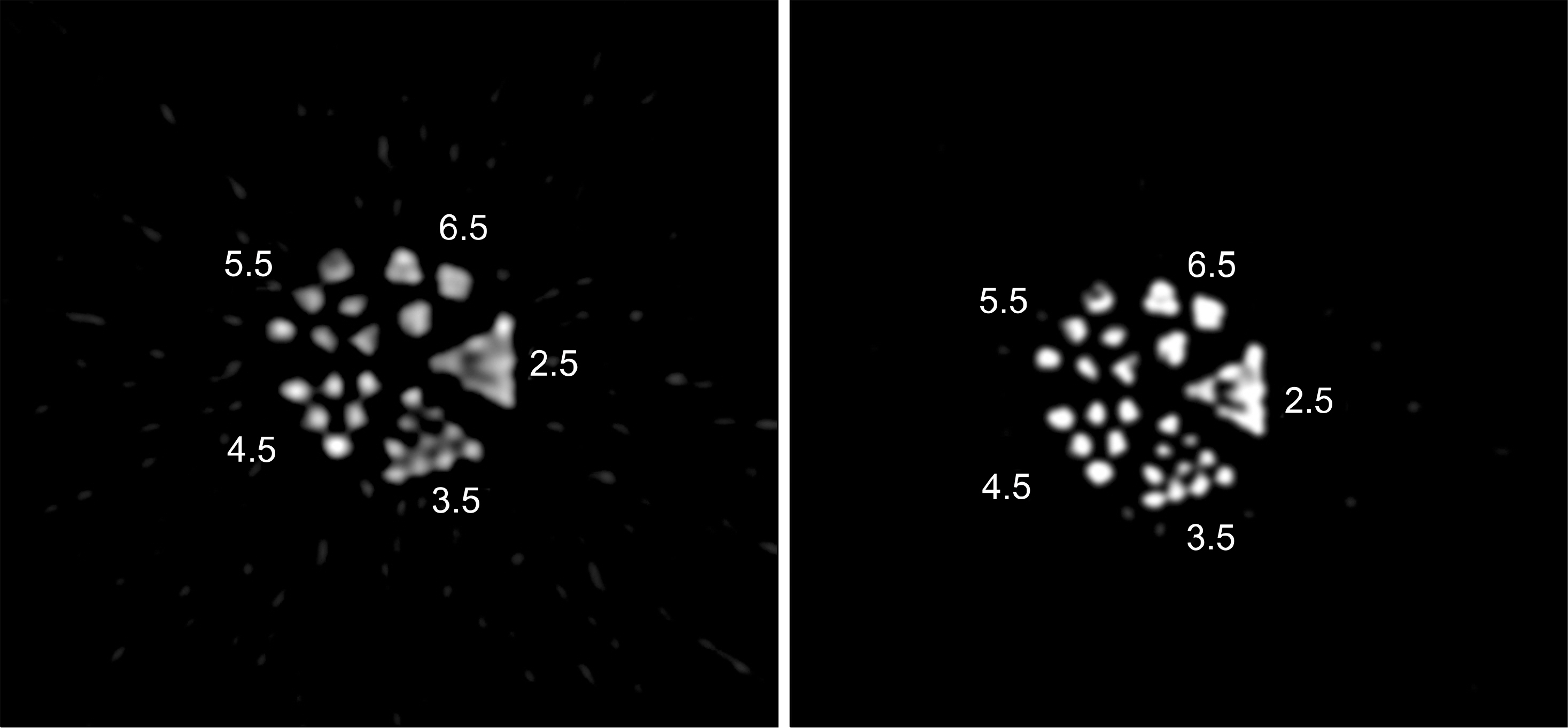
- The purpose of this study is to propose a novel high sensitivity neuro-PET design. The improvement of sensitivity in neuro-PET is important because it can reduce scan time and/or radiation dose. In this study, we proposed a novel PET detector design that combined conical shape detector with cylindrical one to obtain high sensitivity. The sensitivity as a function of the oblique angle and the ratio of the conical to cylindrical portion was estimated to optimize the design of brain PET using Monte Carlo simulation tool, GATE. An axial sensitivity and misplacement rate by penetration of γ rays were also estimated to evaluate the performance of the proposed PET. The sensitivity was improved by 36% at the center of axial FOV. This value was similar to the calculated value. The misplacement rate of conical shaped PET was about 5% higher than the conventional PET. The results of this study demonstrated the conical detector proposed in this study could provide subsequent improvement in sensitivity which could allow to design high sensitivity PET for brain imaging.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Karp J. S., Surti S., Daube-Witherspoon E., et al. Performance of a Brain PET Camera Based on Anger-Logic Gadolinium Oxyorthosilicate Detectors. J Nucl Med. 44:1340–1349. 2003.2. Hoffman E. J., E Phelps M., C Huang S., et al. Performance evaluation of a positron tomograph designed for brain imaing. J Nucl Med. 24:245–257. 1983.3. Knoess C., Siegel S., et al. Performance evaluation of the micro PET R4 PET scanner for rodents. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 30:737–747. 2003.4. Jan S., Santin G., Strul D., et al. GATE: a simulation toolkit for PET and SPECT. Phys. Med. Biol. 49:4543. 2004.5. Shao Y., Cherry S. R., Siegel S., et al. A study of inter-crystal scatter in small scintillator arrays designed for high resoultion PET imaging, IEEE Trans. Nuc. Sci. 43:1938–1944. 1996.6. Buvat I., Lazaro D.Monte Carlo simulations in emission tomography and GATE: an overview. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. 569:323–329. 2006.
Article7. Cherry S. R., Sorenson J. A., Phelps M. E.Physics in Nuclear Medicine 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders. 2004.8. Bailey D.L., Meikle S. R.A convolution-subtraction scatter correction method for 3D PET. Phys Med Biol. 39:411. 1994.
Article9. Moehrs S., Del Guerra A., Herbert D. J., Mandelkern M. A.A detector head design for small-animal PET with silicon photomultipliers (SiPM). Phys Med Biol. 51:1113–1127. 2006.
Article10. Bartoli A., Belcari N., Del Guerra A., Fabbri S.Simultaneous PET/SPECT imaging with the small animal scanner YAP-(S) PET. IEEE Nucl Sci Symp Conf Rec. 5:3408–13. 2007.11. Yao R., Beaudoin J. F., Deng X., Cadorette J., et al. Imaging performance of a PET/SPECT dual modality animal system. IEEE Nucl Sci Symp Conf Rec 2418-21. 2011.12. Tai Y. C., Ruangma A., Rowland D., et al. Performance evaluation of the microPET focus: a third-generation microPET scanner dedicated to animal imaing. J Nucl Med. 46:455–463. 2005.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnostic Efficacy of PET/CT Plus Brain MR Imaging for Detection of Extrathoracic Metastases in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma
- A Review of Machine Learning Approaches for Brain Positron Emission Tomography Data Analysis
- Marchiafava-Bignami Disease with Abnormal PET Findings: Case Report
- Classification of Aβ State From Brain Amyloid PET Images Using Machine Learning Algorithm
- The Proper Use of PET/CT in Tumoring Imaging