Blood Res.
2017 Mar;52(1):62-64. 10.5045/br.2017.52.1.62.
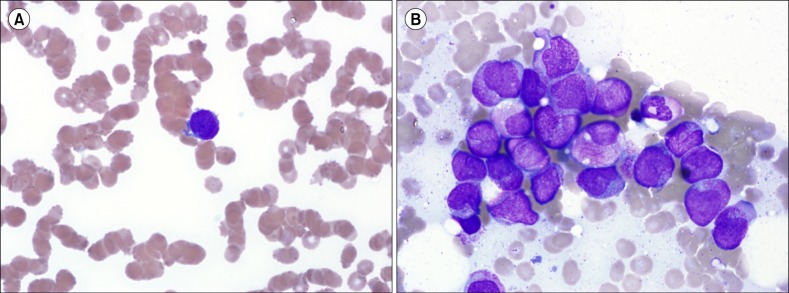
Therapy-related acute promyelocytic leukemia in plasma cell myeloma treated with melphalan: a case report and literature review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. 153jesus@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Hematology-Oncology, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2375206
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2017.52.1.62
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pulsoni A, Pagano L, Lo Coco F, et al. Clinicobiological features and outcome of acute promyelocytic leukemia occurring as a second tumor: the GIMEMA experience. Blood. 2002; 100:1972–1976. PMID: 12200354.
Article2. Beaumont M, Sanz M, Carli PM, et al. Therapy-related acute promyelocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:2123–2137. PMID: 12775738.
Article3. Dunkley S, Gibson J, Iland H, Li C, Joshua D. Acute promyelocytic leukaemia complicating multiple myeloma: evidence of different cell lineages. Leuk Lymphoma. 1999; 35:623–626. PMID: 10609802.
Article4. Invernizzi R, Bergamaschi G, Cazzola M. Acute promyelocytic leukemia complicating chemo-radiotherapy for multiple myeloma. Haematologica. 1996; 81:483. PMID: 8952165.5. Murakawa Y, Yokoyama A, Murata K, Yosioka T, Kanamaru R. A case of multiple myeloma terminating in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Ann Cancer Res Ther. 1998; 6:81–84.
Article6. Joannides M, Mays AN, Mistry AR, et al. Molecular pathogenesis of secondary acute promyelocytic leukemia. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2011; 3:e2011045. PMID: 22110895.
Article7. Lo-Coco F, Hasan SK, Montesinos P, Sanz MA. Biology and management of therapy-related acute promyelocytic leukemia. Curr Opin Oncol. 2013; 25:695–700. PMID: 24076582.
Article8. Mistry AR, Felix CA, Whitmarsh RJ, et al. DNA topoisomerase II in therapy-related acute promyelocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:1529–1538. PMID: 15829534.
Article9. Pedersen-Bjergaard J. Insights into leukemogenesis from therapy-related leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:1591–1594. PMID: 15829541.
Article10. Ravandi F. Therapy-related acute promyelocytic leukemia: further insights into the molecular basis of the disease and showing the way forward in therapy. Leuk Lymphoma. 2009; 50:1073–1074. PMID: 19557628.
Article11. Landgren O, Mailankody S. Update on second primary malignancies in multiple myeloma: a focused review. Leukemia. 2014; 28:1423–1426. PMID: 24418993.
Article12. Thomas A, Mailankody S, Korde N, Kristinsson SY, Turesson I, Landgren O. Second malignancies after multiple myeloma: from 1960s to 2010s. Blood. 2012; 119:2731–2737. PMID: 22310913.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Promyelocytic sarcoma of the sternum: a case report and review of the literature
- A Case of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Concomitant with Plasma Cell Myeloma
- SOLITARY PLASMA CELL MYELOMA ON ANTERIOR MAXILLA: A CASE REPORT
- Simultaneous presentation of plasma cell myeloma and hairy cell leukemia
- Cutaneous Plasmacytoma Associated with Multiple Myeloma