J Breast Cancer.
2013 Mar;16(1):122-126.
Prolonged Regression of Metastatic Leptomeningeal Breast Cancer That Has Failed Conventional Therapy: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, USA. mchan@wakehealth.edu
- 2Division on Hematology-Oncology, Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, USA.
Abstract
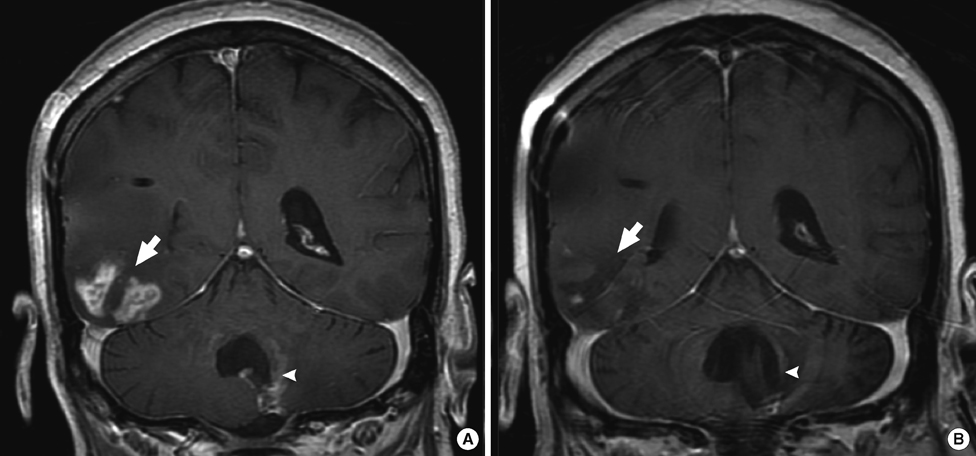
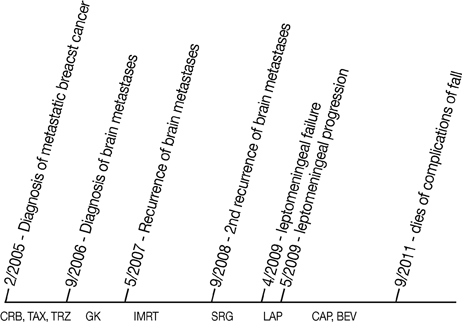
- Approximately 5% of breast cancer patients develop leptomeningeal metastases over the course of their disease. Though several treatments options are available for these patients, their prognosis is typically considered to be poor. We report a case of leptomeningeal failure after a patient underwent prior radiotherapy, radiosurgery, surgery, chemotherapy, and biologic therapy. This patient experienced a prolonged response after receiving bevacizumab and capecitabine. The literature currently contains several reports regarding the use of systemic therapy to manage leptomeningeal metastases from breast cancer, which we summarize. Finally, we review the relevant effects of the patient's treatment modalities and provide a rationale for the mechanism that led to her prolonged response.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tsukada Y, Fouad A, Pickren JW, Lane WW. Central nervous system metastasis from breast carcinoma. Autopsy study. Cancer. 1983. 52:2349–2354.
Article2. de la Monte SM, Hutchins GM, Moore GW. Estrogen and progesterone receptors in prediction of metastatic behavior of breast carcinoma. Am J Med. 1984. 76:11–17.
Article3. Jensen CA, Chan MD, McCoy TP, Bourland JD, deGuzman AF, Ellis TL, et al. Cavity-directed radiosurgery as adjuvant therapy after resection of a brain metastasis. J Neurosurg. 2011. 114:1585–1591.
Article4. Hermann B, Hültenschmidt B, Sautter-Bihl ML. Radiotherapy of the neuroaxis for palliative treatment of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Strahlenther Onkol. 2001. 177:195–199.
Article5. Wasserstrom WR, Glass JP, Posner JB. Diagnosis and treatment of leptomeningeal metastases from solid tumors: experience with 90 patients. Cancer. 1982. 49:759–772.
Article6. Peroukides S, Onyenadum A, Starakis I, Koutras A, Makatsoris T, Bouboukas G, et al. Prolonged survival of neoplastic meningitis from breast cancer with letrozole and intrathecal methotrexate: a case report. J Neurooncol. 2011. 101:509–511.
Article7. Ferrario C, Davidson A, Bouganim N, Aloyz R, Panasci LC. Intrathecal trastuzumab and thiotepa for leptomeningeal spread of breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2009. 20:792–795.
Article8. Stemmler HJ, Mengele K, Schmitt M, Harbeck N, Laessig D, Herrmann KA, et al. Intrathecal trastuzumab (Herceptin) and methotrexate for meningeal carcinomatosis in HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer: a case report. Anticancer Drugs. 2008. 19:832–836.
Article9. Clatot F, Philippin-Lauridant G, Ouvrier MJ, Nakry T, Laberge-Le-Couteulx S, Guillemet C, et al. Clinical improvement and survival in breast cancer leptomeningeal metastasis correlate with the cytologic response to intrathecal chemotherapy. J Neurooncol. 2009. 95:421–426.
Article10. Jaeckle KA, Phuphanich S, Bent MJ, Aiken R, Batchelor T, Campbell T, et al. Intrathecal treatment of neoplastic meningitis due to breast cancer with a slow-release formulation of cytarabine. Br J Cancer. 2001. 84:157–163.
Article11. Ekenel M, Hormigo AM, Peak S, Deangelis LM, Abrey LE. Capecitabine therapy of central nervous system metastases from breast cancer. J Neurooncol. 2007. 85:223–227.
Article12. Giglio P, Tremont-Lukats IW, Groves MD. Response of neoplastic meningitis from solid tumors to oral capecitabine. J Neurooncol. 2003. 65:167–172.
Article13. Rogers LR, Remer SE, Tejwani S. Durable response of breast cancer leptomeningeal metastasis to capecitabine monotherapy. Neuro Oncol. 2004. 6:63–64.
Article14. Tham YL, Hinckley L, Teh BS, Elledge R. Long-term clinical response in leptomeningeal metastases from breast cancer treated with capecitabine monotherapy: a case report. Clin Breast Cancer. 2006. 7:164–166.
Article15. Shigekawa T, Takeuchi H, Misumi M, Matsuura K, Sano H, Fujiuchi N, et al. Successful treatment of leptomeningeal metastases from breast cancer using the combination of trastuzumab and capecitabine: a case report. Breast Cancer. 2009. 16:88–92.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Determination of the Estrogen Receptor Status of Leptomeningeal Metastasis in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer Using [ 18 F]-FES PET/CT: a Case Report
- Metastatic Breast Cancer from Cervical Cancer
- Breast Cancer with Leptomeningeal Metastasis
- Intrathecal Trastuzumab Treatment in Patients with Breast Cancer and Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis
- A Case of Metastatic Carcinoma from the Breast Cancer to the Upper Ureter