Clin Orthop Surg.
2016 Sep;8(3):310-315. 10.4055/cios.2016.8.3.310.
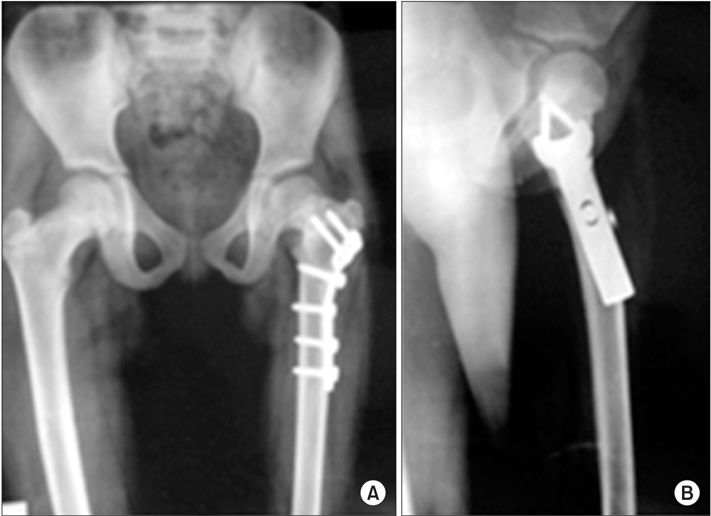
Fixation of Intertrochanteric Valgus Osteotomy with T Plate in Treatment of Developmental Coxa Vara
- Affiliations
-
- 1Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University Hospitals, Sharkia, Egypt. elzohairy.me@gmail.com
- KMID: 2374278
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.3.310
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Although the valgus subtrochanteric osteotomy is considered as a standard surgical treatment for coxa vara, there is no consensus on the optimal method of fixation and osteotomy technique. Fixation of the osteotomy has been achieved by various methods including external fixation and internal fixation with pins and cerclage and a variety of plates. The aim of this study is the evaluation of the results of developmental coxa treated by Y intertrochanteric valgus osteotomy fixed with a T-buttress plate compared with other methods of fixation in the literature.
METHODS
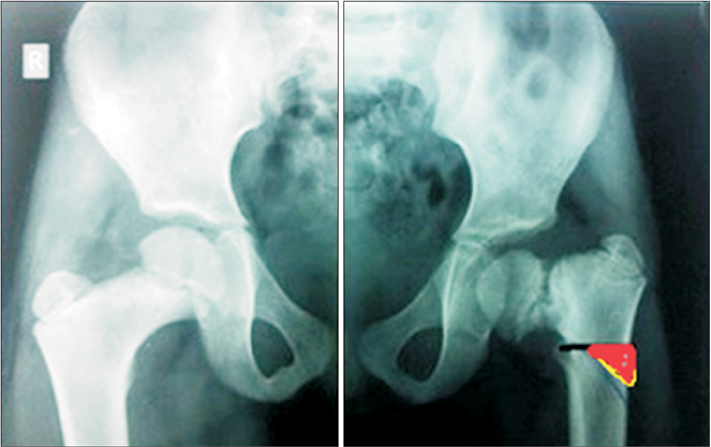
Eighteen corrective valgus intertrochanteric femoral osteotomies were performed in 18 patients (18 hips) for treatment of unilateral developmental coxa vara deformity and fixed with a T plate. There were 12 males and 6 females. The right hip was affected in 10 patients and the left hip in 8 patients. Clinically, patients were evaluated by Larson hip score. Radiographically, anteroposterior view of the pelvis and frog leg lateral views of the affected hip were taken preoperatively and compared with the findings at the final follow-up.
RESULTS
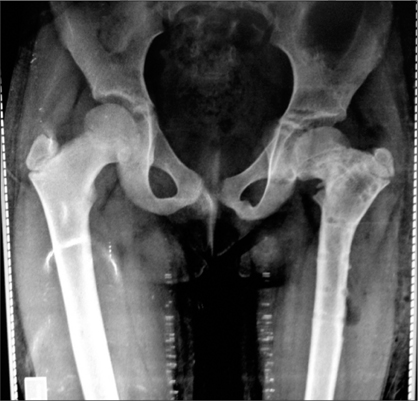
The average follow-up was 29 months (range, 24 to 36 months). Clinical results showed improvement of the mean Larson hip score from 57.8 to 97.0 (p < 0.001). Radiological results showed that all osteotomies were completely united in 2.4 months (range, 2 to 3 months) with the achievement of the planned correction angle. The average correction of Hilgenreiner's epiphyseal angle improved from 78.2° to 27.8° (p < 0.001) at the final follow-up. The femoral neck shaft angle was improved from 93.7° to 129.9° (p < 0.001) at the final follow-up. Shortening of the affected limb was corrected from 2.8 cm to 1.3 cm (p < 0.001) at the last follow-up. No major serious complications were recorded in the present study.
CONCLUSIONS
Intertrochanteric valgus osteotomy of the proximal femur fixed with a T plate may be efficient for treatment of developmental coxa vara. With careful planning, it can result in a low complication rate and insignificant or minimal recurrence rate.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Herring JA. Tachdjian's pediatric orthopaedics: from the Texas Scottish Rite Hospital for children. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Company;2002. p. 193–195.2. Hefny H, Elmoatasem EM, Nassar W. Valgus osteotomy by external fixation for treatment for developmental coxa vara. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2013; 8(3):161–167.
Article3. Dobbs MB, Morcuende JA. Other condition of the hip: coxa vara. In : Morrissy RT, Weinstein SL, editors. Lovell and Winter's pediatric orthopaedics. 6th ed. New York, NY: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2005. p. 1126–1134.4. El-Sobky T. Subtrochanteric valgus osteotomy in developmental coxa vara. Indian J Orthop. 2011; 45(4):320–323.
Article5. Larson CB. Rating scale for hip disabilities. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1963; 31:85–93.
Article6. Galante VN, Caiaffa V, Franchin F, Colasuonno R. The treatment of infantile coxa vara with the external circular fixator. Ital J Orthop Traumatol. 1990; 16(4):491–500.7. Carroll K, Coleman S, Stevens PM. Coxa vara: surgical outcomes of valgus osteotomies. J Pediatr Orthop. 1997; 17(2):220–224.
Article8. Cordes S, Dickens DR, Cole WG. Correction of coxa vara in childhood: the use of Pauwels' Y-shaped osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73(1):3–6.
Article9. Amstutz HC. Developmental (infantile) coxa vara: a distinct entity. Report of two patients with previously normal roentgenograms. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1970; 72:242–247.10. Muller ME, Allgower M, Schneider R, Willenegger H. Manual of internal fixation: techniques recommened by the AOASIF group. 3rd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag;1991. p. 210–213.11. Pauwels F. Biomechanics of the normal and diseased hip: theoretical foundation, technique and results of treatment. Berlin: Springer-Verlag;1976.12. Behrens FF, Sabharwal S. Deformity correction and reconstructive procedures using percutaneous techniques. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000; (375):133–139.
Article13. Sabharwal S, Mittal R, Cox G. Percutaneous triplanar femoral osteotomy correction for developmental coxa vara: a new technique. J Pediatr Orthop. 2005; 25(1):28–33.
Article14. Amstutz HC, Freiberger RH. Coxa vara in children. Clin Orthop. 1962; 22:73–92.15. Amstutz HC, Wilson PD Jr. Dysgenesis of the proximal femur (coxa vara) and its surgical management. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1962; 44(1):1–24.
Article16. Dhar SA, Dar TA, Sultan A, Malik AR, Mir MR. The reciprocal ledge closing wedge osteotomy for post traumatic coxa vara. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2011; 6(3):155–158.
Article17. Bartonicek J, Vavra J. Valgus intertrochanteric osteotomy for coxa vara of Bucholz-Ogden Types II and III in patients older than 30 years. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011; 131(9):1211–1217.
Article18. Gunther CM, Komm M, Jansson V, Heimkes B. Midterm results after subtrochanteric end-to-side valgization osteotomy in severe infantile coxa vara. J Pediatr Orthop. 2013; 33(4):353–360.
Article19. Joeris A, Audige L, Ziebarth K, Slongo T. The Locking Compression Paediatric Hip Plate: technical guide and critical analysis. Int Orthop. 2012; 36(11):2299–2306.
Article