Yonsei Med J.
2016 Sep;57(5):1260-1270. 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.5.1260.
Protocol-Based Resuscitation for Septic Shock: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials and Observational Studies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. nswksj@yuhs.ac
- 2Biostatistics Collaboration Unit, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Anesthesia and Pain Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2374174
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.5.1260
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Owing to the recommendations of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines, protocol-based resuscitation or goal-directed therapy (GDT) is broadly advocated for the treatment of septic shock. However, the most recently published trials showed no survival benefit from protocol-based resuscitation in septic shock patients. Hence, we aimed to assess the effect of GDT on clinical outcomes in such patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We performed a systematic review that included a meta-analysis. We used electronic search engines including PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane database to find studies comparing protocol-based GDT to common or standard care in patients with septic shock and severe sepsis.
RESULTS
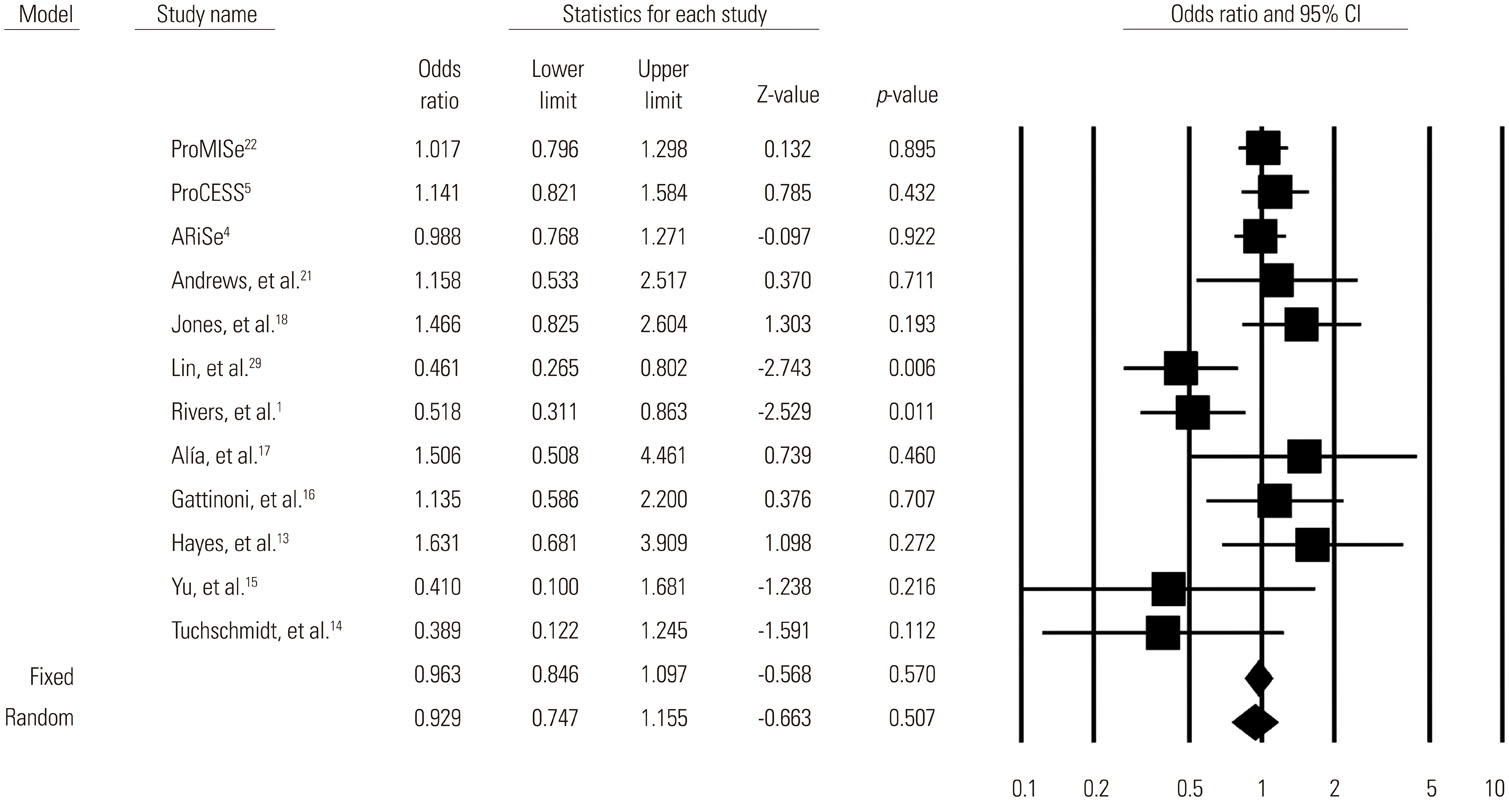
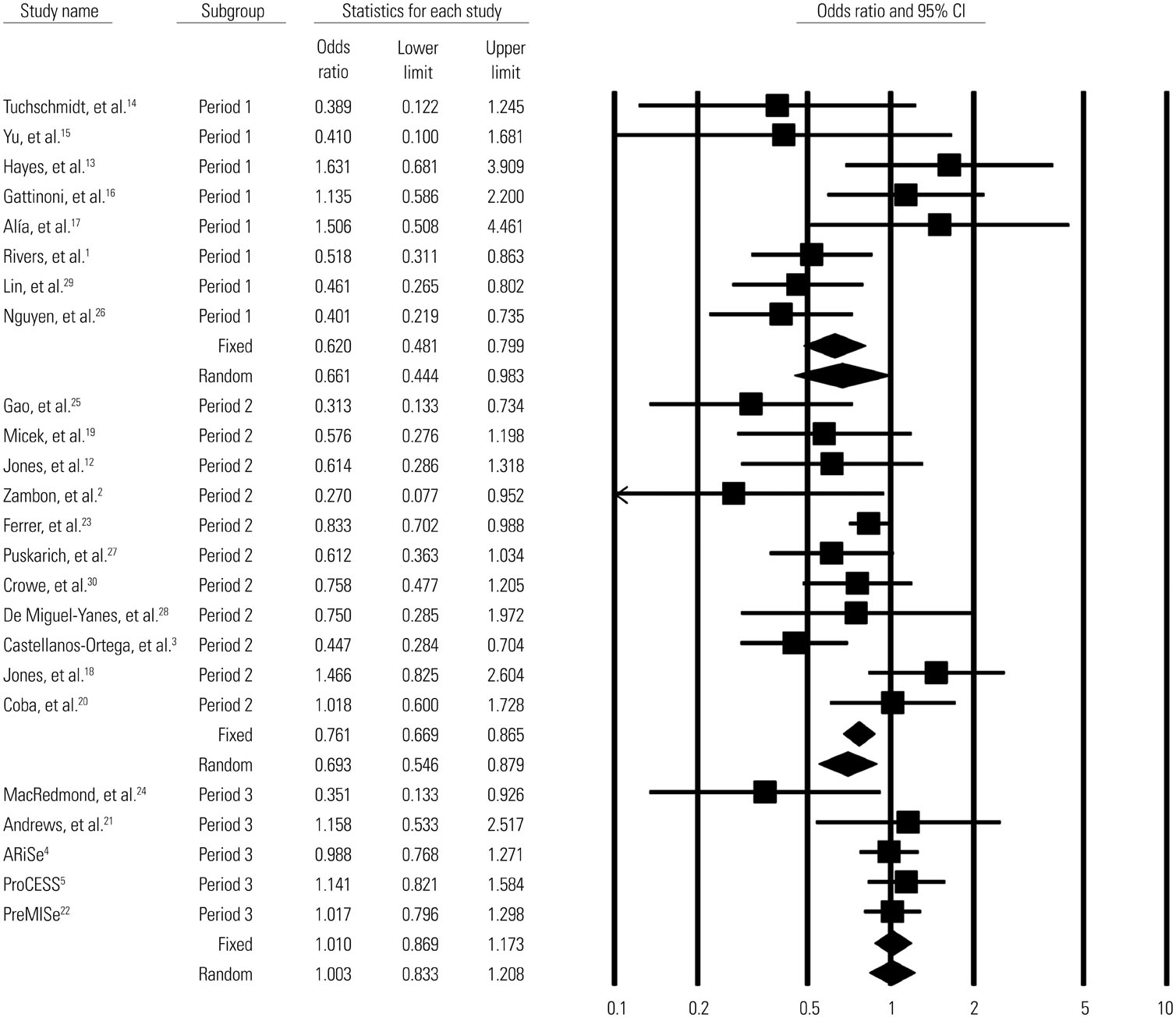
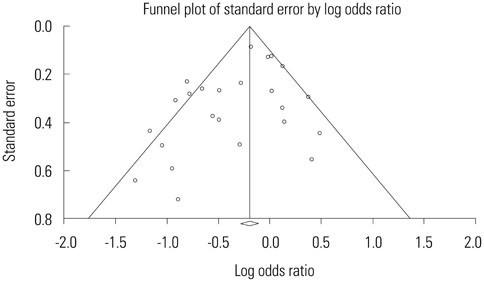
A total of 13269 septic shock patients in 24 studies were included [12 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and 12 observational studies]. The overall mortality odds ratio (OR) [95% confidence interval (CI)] for GDT versus conventional care was 0.746 (0.631-0.883). In RCTs only, the mortality OR (95% CI) for GDT versus conventional care in the meta-analysis was 0.93 (0.75-1.16). The beneficial effect of GDT decreased as more recent studies were added in an alternative, cumulative meta-analysis. No significant publication bias was found.
CONCLUSION
The result of this meta-analysis suggests that GDT reduces mortality in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. However, our cumulative meta-analysis revealed that the reduction of mortality risk was diminished as more recent studies were added.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, Knoblich B, et al. Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345:1368–1377.
Article2. Zambon M, Ceola M, Almeida-de-Castro R, Gullo A, Vincent JL. Implementation of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for severe sepsis and septic shock: we could go faster. J Crit Care. 2008; 23:455–460.
Article3. Castellanos-Ortega A, Suberviola B, García-Astudillo LA, Holanda MS, Ortiz F, Llorca J, et al. Impact of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign protocols on hospital length of stay and mortality in septic shock patients: results of a three-year follow-up quasi-experimental study. Crit Care Med. 2010; 38:1036–1043.
Article4. ARISE Investigators. ANZICS Clinical Trials Group. Peake SL, Delaney A, Bailey M, Bellomo R, et al. Goal-directed resuscitation for patients with early septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2014; 371:1496–1506.
Article5. ProCESS Investigators. Yealy DM, Kellum JA, Huang DT, Barnato AE, Weissfeld LA, et al. A randomized trial of protocol-based care for early septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370:1683–1693.
Article6. Gu WJ, Wang F, Bakker J, Tang L, Liu JC. The effect of goal-directed therapy on mortality in patients with sepsis - earlier is better: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Care. 2014; 18:570.
Article7. Zhang L, Zhu G, Han L, Fu P. Early goal-directed therapy in the management of severe sepsis or septic shock in adults: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Med. 2015; 13:71.
Article8. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009; 62:e1–e34.
Article9. Cochran WG. The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics. 1954; 10:101–129.
Article10. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315:629–634.
Article11. Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. 1994; 50:1088–1101.
Article12. Jones AE, Focht A, Horton JM, Kline JA. Prospective external validation of the clinical effectiveness of an emergency department-based early goal-directed therapy protocol for severe sepsis and septic shock. Chest. 2007; 132:425–432.
Article13. Hayes MA, Timmins AC, Yau EH, Palazzo M, Hinds CJ, Watson D. Elevation of systemic oxygen delivery in the treatment of critically ill patients. N Engl J Med. 1994; 330:1717–1722.
Article14. Tuchschmidt J, Fried J, Astiz M, Rackow E. Elevation of cardiac output and oxygen delivery improves outcome in septic shock. Chest. 1992; 102:216–220.
Article15. Yu M, Levy MM, Smith P, Takiguchi SA, Miyasaki A, Myers SA. Effect of maximizing oxygen delivery on morbidity and mortality rates in critically ill patients: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. Crit Care Med. 1993; 21:830–838.
Article16. Gattinoni L, Brazzi L, Pelosi P, Latini R, Tognoni G, Pesenti A, et al. A trial of goal-oriented hemodynamic therapy in critically ill patients. SvO2 Collaborative Group. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333:1025–1032.
Article17. Alía I, Esteban A, Gordo F, Lorente JA, Diaz C, Rodriguez JA, et al. A randomized and controlled trial of the effect of treatment aimed at maximizing oxygen delivery in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Chest. 1999; 115:453–461.
Article18. Jones AE, Shapiro NI, Trzeciak S, Arnold RC, Claremont HA, Kline JA, et al. Lactate clearance vs central venous oxygen saturation as goals of early sepsis therapy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2010; 303:739–746.
Article19. Micek ST, Roubinian N, Heuring T, Bode M, Williams J, Harrison C, et al. Before-after study of a standardized hospital order set for the management of septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2006; 34:2707–2713.
Article20. Coba V, Whitmill M, Mooney R, Horst HM, Brandt MM, Digiovine B, et al. Resuscitation bundle compliance in severe sepsis and septic shock: improves survival, is better late than never. J Intensive Care Med. 2011; 26:304–313.
Article21. Andrews B, Muchemwa L, Kelly P, Lakhi S, Heimburger DC, Bernard GR. Simplified severe sepsis protocol: a randomized controlled trial of modified early goal-directed therapy in Zambia. Crit Care Med. 2014; 42:2315–2324.22. Mouncey PR, Osborn TM, Power GS, Harrison DA, Sadique MZ, Grieve RD, et al. Trial of early, goal-directed resuscitation for septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372:1301–1311.
Article23. Ferrer R, Artigas A, Levy MM, Blanco J, González-Díaz G, Garnacho- Montero J, et al. Improvement in process of care and outcome after a multicenter severe sepsis educational program in Spain. JAMA. 2008; 299:2294–2303.
Article24. MacRedmond R, Hollohan K, Stenstrom R, Nebre R, Jaswal D, Dodek P. Introduction of a comprehensive management protocol for severe sepsis is associated with sustained improvements in timeliness of care and survival. Qual Saf Health Care. 2010; 19:e46.
Article25. Gao F, Melody T, Daniels DF, Giles S, Fox S. The impact of compliance with 6-hour and 24-hour sepsis bundles on hospital mortality in patients with severe sepsis: a prospective observational study. Crit Care. 2005; 9:R764–R770.26. Nguyen HB, Corbett SW, Steele R, Banta J, Clark RT, Hayes SR, et al. Implementation of a bundle of quality indicators for the early management of severe sepsis and septic shock is associated with decreased mortality. Crit Care Med. 2007; 35:1105–1112.
Article27. Puskarich MA, Marchick MR, Kline JA, Steuerwald MT, Jones AE. One year mortality of patients treated with an emergency department based early goal directed therapy protocol for severe sepsis and septic shock: a before and after study. Crit Care. 2009; 13:R167.
Article28. De Miguel-Yanes JM, Muñoz-González J, Andueza-Lillo JA, Moyano-Villaseca B, González-Ramallo VJ, Bustamante-Fermosel A. Implementation of a bundle of actions to improve adherence to the Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines at the ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2009; 27:668–674.
Article29. Lin SM, Huang CD, Lin HC, Liu CY, Wang CH, Kuo HP. A modified goal-directed protocol improves clinical outcomes in intensive care unit patients with septic shock: a randomized controlled trial. Shock. 2006; 26:551–557.
Article30. Crowe CA, Mistry CD, Rzechula K, Kulstad CE. Evaluation of a modified early goal-directed therapy protocol. Am J Emerg Med. 2010; 28:689–693.
Article