Yonsei Med J.
2016 Jul;57(4):1034-1037. 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.4.1034.
In Vitro Activity of Tigecycline Against Orientia tsutsugamushi
- Affiliations
-
- 1Translation Research Center, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. ljinsoo@inha.ac.kr
- 3Department of Social & Preventive Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Microbiology, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Hanmaeum Hospital, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2374140
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.4.1034
Abstract
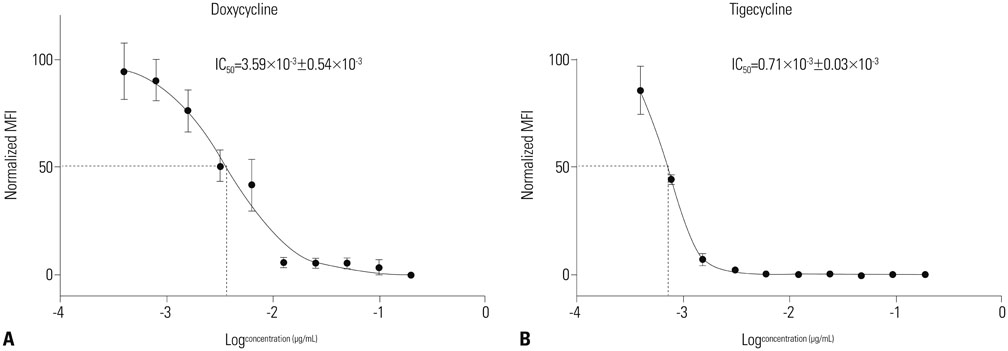
- Scrub typhus is a zoonosis caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi (O. tsutsugamushi) occurring mainly in autumn in Korea. The need of new antibiotics has arisen with a report on strains resistant to antibiotics and chronic infection. This study aims to identify susceptibility of tigecycline in-vitro as a new therapeutic option for O. tsutsugamushi. Antibacterial activity of tigecycline against the O. tsutsugamushi was compared with doxycycline using flow cytometry assay. The inhibitory concentration 50 (IC50) was 3.59×10(-3) µg/mL in doxycycline-treated group. Whereas in 0.71×10(-3) µg/mL tigecycline-treated group. These findings indicate that tigecycline may be a therapeutic option for the treatment of scrub typhus.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
History of Tsutsugamushi Disease in Korea
Moon-Hyun Chung, Jae-Seung Kang
Infect Chemother. 2019;51(2):196-209. doi: 10.3947/ic.2019.51.2.196.
Reference
-
1. Smadel JE, Woodward TE, Ley HL, Lewthwaite R. Chloramphenicol (chloromycetin) in the treatment of tsutsugamushi disease (scrub typhus). J Clin Invest. 1949; 28(5 Pt 2):1196–1215.
Article2. Prezyna AP, Chang TL, Wang TL, Dougherty WJ, Bond HB. Treatment of scrub typhus in the Pescadores Islands with chloramphenicol, aureomycin and terramycin. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1954; 3:608–614.
Article3. Watt G, Kantipong P, Jongsakul K, Watcharapichat P, Phulsuksombati D. Azithromycin activities against Orientia tsutsugamushi strains isolated in cases of scrub typhus in Northern Thailand. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999; 43:2817–2818.
Article4. Watt G, Chouriyagune C, Ruangweerayud R, Watcharapichat P, Phulsuksombati D, Jongsakul K, et al. Scrub typhus infections poorly responsive to antibiotics in northern Thailand. Lancet. 1996; 348:86–89.
Article5. Corwin A, Soderquist R, Suwanabun N, Sattabongkot J, Martin L, Kelly D, et al. Scrub typhus and military operations in Indochina. Clin Infect Dis. 1999; 29:940–941.
Article6. Chung MH, Lee JS, Baek JH, Kim M, Kang JS. Persistence of Orientia tsutsugamushi in humans. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:231–235.7. Chung MH, Han SW, Choi MG, Chang WH, Pai HJ, Shin HS, et al. Comparison of 3-day course of azithromycin with doxycycline for the treatment of scrub typhus. Korean J Infect Dis. 2000; 32:433–438.8. Olson MW, Ruzin A, Feyfant E, Rush TS 3rd, O'Connell J, Bradford PA. Functional, biophysical, and structural bases for antibacterial activity of tigecycline. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006; 50:2156–2166.
Article9. Noskin GA. Tigecycline: a new glycylcycline for treatment of serious infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 41:Suppl 5. S303–S314.
Article10. Spyridaki I, Psaroulaki A, Vranakis I, Tselentis Y, Gikas A. Bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities of tigecycline against Coxiella burnetii and comparison with those of six other antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 53:2690–2692.
Article11. Dessus-Babus S, Belloc F, Bébéar CM, Poutiers F, Lacombe F, Bébéar C, et al. Antibiotic susceptibility testing for Chlamydia trachomatis using flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1998; 31:37–44.
Article12. Kim MJ, Kim MK, Kang JS. Improved antibiotic susceptibility test of Orientia tsutsugamushi by flow cytometry using monoclonal antibody. J Korean Med Sci. 2007; 22:1–6.
Article13. Kim MJ, Lee SM, Kil SH, Kang JS. Cleavage of p65 Subunit of NF-κB by Orientia tsutsugamushi. J Bacteriol Virol. 2010; 40:151–157.
Article14. Chung MH, Kang JS. Treatment of tsutsugamushi disease. Korean J Med. 2002; 63:234–238.15. Maurin M, Benoliel AM, Bongrand P, Raoult D. Phagolysosomal alkalinization and the bactericidal effect of antibiotics: the Coxiella burnetii paradigm. J Infect Dis. 1992; 166:1097–1102.
Article16. Babinchak T, Ellis-Grosse E, Dartois N, Rose GM, Loh E. Tigecycline 301 Study Group. Tigecycline 306 Study Group. The efficacy and safety of tigecycline for the treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections: analysis of pooled clinical trial data. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 41:Suppl 5. S354–S367.
Article17. Barbour A, Schmidt S, Ma B, Schiefelbein L, Rand KH, Burkhardt O, et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of tigecycline. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009; 48:575–584.
Article18. Edelstein PH, Weiss WJ, Edelstein MA. Activities of tigecycline (GAR-936) against Legionella pneumophila in vitro and in guinea pigs with L. pneumophila pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003; 47:533–540.
Article19. Rose WE, Rybak MJ. Tigecycline: first of a new class of antimicrobial agents. Pharmacotherapy. 2006; 26:1099–1110.
Article20. Tang HJ, Ko WC, Chen CC, Chen PL, Toh HS, Weng TC, et al. In vitro and in vivo intracellular killing effects of tigecycline against clinical nontyphoid Salmonella isolates using ceftriaxone as a comparator. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011; 55:2755–2759.
Article21. Conte JE Jr, Golden JA, Kelly MG, Zurlinden E. Steady-state serum and intrapulmonary pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of tigecycline. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2005; 25:523–529.
Article22. Ong CT, Babalola CP, Nightingale CH, Nicolau DP. Penetration, efflux and intracellular activity of tigecycline in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs). J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005; 56:498–501.
Article23. Poole K. Efflux-mediated antimicrobial resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005; 56:20–51.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis Associated with Orientia tsutsugamushi Infection: A Report of Two Cases
- Genetic Heterogeneity in 56 kDa gene of Orientia tsutsugamushi Genotype Karp
- Proliferation of ECV304 cells Infected Persistently with Orientia tsutsugamushi
- Seropositive rate of Orientia tsutsugamushi in Tamias sibiricus from Korea
- In vitro Synergism between Chloroquine and Antibiotics against Orientia tsutsugamushi