Yonsei Med J.
2016 Jul;57(4):872-878. 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.4.872.
Estimation of Prognostic Marker Genes by Public Microarray Data in Patients with Ovarian Serous Cystadenocarcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Sciences, Seoul National University Graduate School, Seoul, Korea. jongil@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 3Center for Convergence Research of Advanced Technologies, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Genomic Medicine Institute, Medical Research Center, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2374117
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.4.872
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Lymphatic invasion (LI) is regarded as a predictor of the aggressiveness of ovarian cancer (OC). However, LI is not always the major determinant of long-term patient survival. To establish proper diagnosis and treatment for OC, we analyzed differentially expressed genes (DEGs) for patients with serous epithelial OC, with or without LI, who did or did not survive for 5 years.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
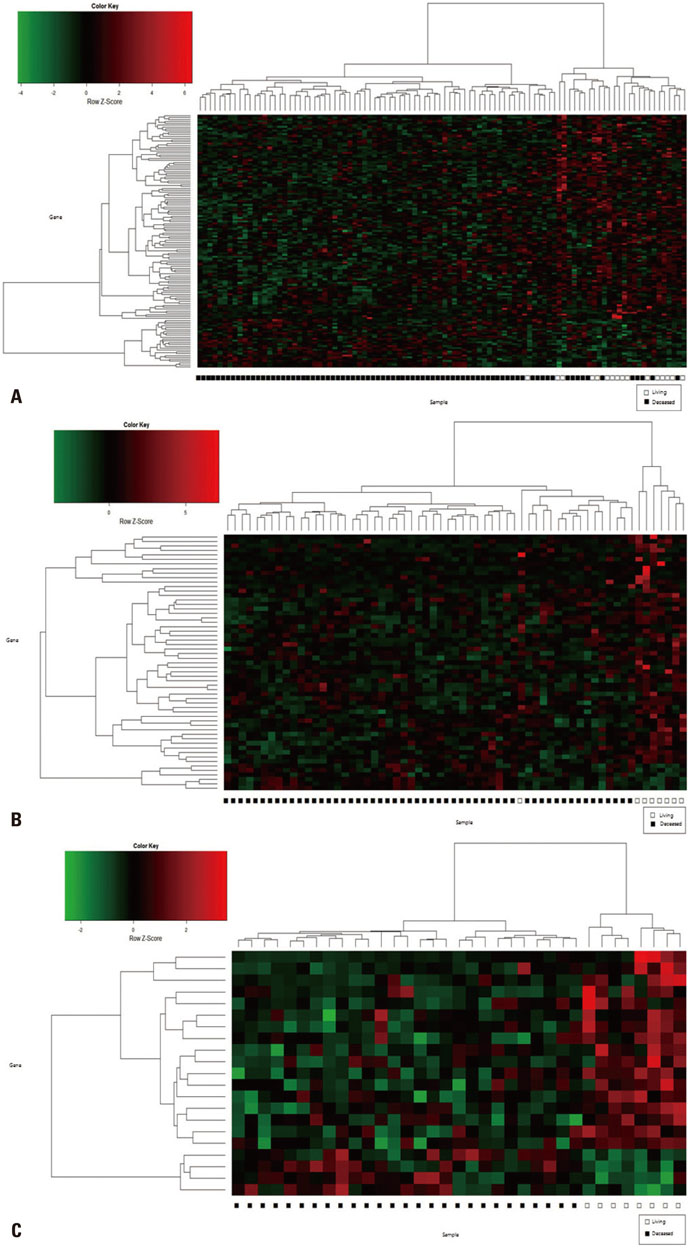
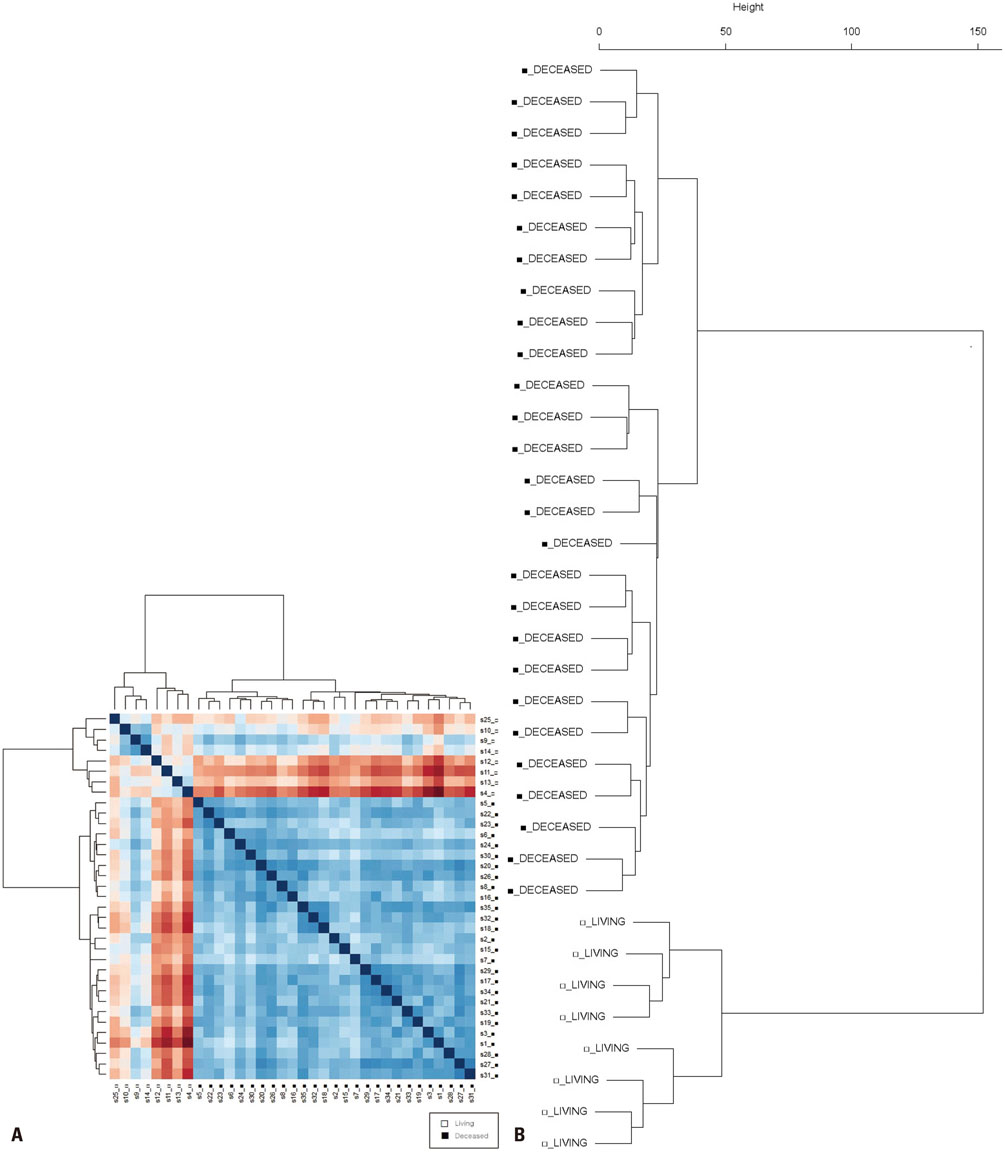
Gene expression data from 63 patients with OC and LI, and 35 patients with OC but without LI, were investigated using an Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Array and analyzed using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Among these 98 patients, 16 survived for 5 years or more. DEGs were identified using the Bioconductor R package, and their functions were analyzed using the DAVID web tool.
RESULTS
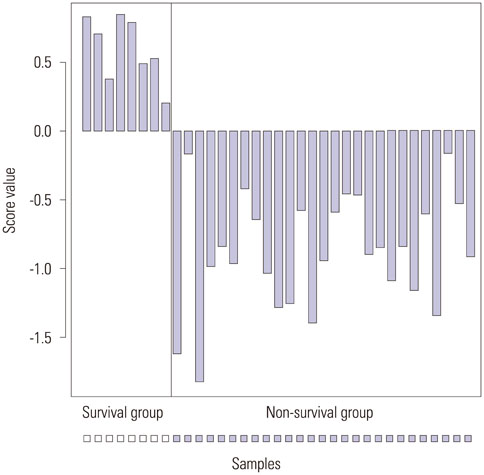
We found 55 significant DEGs (p<0.01) from the patients with LI and 20 highly significant DEGs (p<0.001) from those without it. Pathway analysis showed that DEGs associated with carbohydrate metabolism or with renal cell carcinoma pathways were enriched in the patients with and without LI, respectively. Using the top five prognostic marker genes, we generated survival scores that could be used to predict the 5-year survival of patients with OC without LI.
CONCLUSION
The DEGs identified in this study could be used to elucidate the mechanism of tumor progression and to guide the prognosis and treatment of patients with serous OC but without LI.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Cancer Institute. United States Cancer Statistics (USCS): 1999-2012 cancer incidence and mortality data. accessed on 2015 July 31. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/uscs.2. Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014; 64:9–29.
Article3. Bast RC Jr, Hennessy B, Mills GB. The biology of ovarian cancer: new opportunities for translation. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009; 9:415–428.
Article4. Holschneider CH, Berek JS. Ovarian cancer: epidemiology, biology, and prognostic factors. Semin Surg Oncol. 2000; 19:3–10.
Article5. Matsuo K, Yoshino K, Hiramatsu K, Banzai C, Hasegawa K, Yasuda M, et al. Effect of lymphovascular space invasion on survival of stage I epithelial ovarian cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2014; 123:957–965.
Article6. Matsuo K, Sheridan TB, Yoshino K, Miyake T, Hew KE, Im DD, et al. Significance of lymphovascular space invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Med. 2012; 1:156–164.
Article7. van‘t Veer LJ, Dai H, van de, He YD, Hart AA, Mao M, et al. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature. 2002; 415:530–536.
Article8. Setlur SR, Mertz KD, Hoshida Y, Demichelis F, Lupien M, Perner S, et al. Estrogen-dependent signaling in a molecularly distinct subclass of aggressive prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008; 100:815–825.
Article9. Mok SC, Chao J, Skates S, Wong K, Yiu GK, Muto MG, et al. Prostasin, a potential serum marker for ovarian cancer: identification through microarray technology. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001; 93:1458–1464.
Article10. Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature. 2011; 474:609–615.11. Dijkman B, Kooistra B, Bhandari M. Evidence-Based Surgery Working Group. How to work with a subgroup analysis. Can J Surg. 2009; 52:515–522.12. Kamai T, Tsujii T, Arai K, Takagi K, Asami H, Ito Y, et al. Significant association of Rho/ROCK pathway with invasion and metastasis of bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2003; 9:2632–2641.13. Reimers M, Carey VJ. Bioconductor: an open source framework for bioinformatics and computational biology. Methods Enzymol. 2006; 411:119–134.14. Suzuki R, Shimodaira H. Pvclust: an R package for assessing the uncertainty in hierarchical clustering. Bioinformatics. 2006; 22:1540–1542.
Article15. Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR, Alvord WG, Roayaei J, et al. The DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool: a novel biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large gene lists. Genome Biol. 2007; 8:R183.
Article16. Li H, Zeng J, Shen K. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway as a therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014; 290:1067–1078.
Article17. Eskander RN, Tewari KS. Exploiting the therapeutic potential of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway in enriched populations of gynecologic malignancies. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2014; 7:847–858.
Article18. Cai J, Xu L, Tang H, Yang Q, Yi X, Fang Y, et al. The role of the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway on prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis. Oncologist. 2014; 19:528–535.
Article19. Raspaglio G, Petrillo M, Martinelli E, Li Puma DD, Mariani M, De Donato M, et al. Sox9 and Hif-2α regulate TUBB3 gene expression and affect ovarian cancer aggressiveness. Gene. 2014; 542:173–181.
Article20. Seol HJ, Smith CA, Salhia B, Rutka JT. The guanine nucleotide exchange factor SWAP-70 modulates the migration and invasiveness of human malignant glioma cells. Transl Oncol. 2009; 2:300–309.
Article21. Kahn M. Can we safely target the WNT pathway? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014; 13:513–532.
Article22. Huang CL, Liu D, Nakano J, Ishikawa S, Kontani K, Yokomise H, et al. Wnt5a expression is associated with the tumor proliferation and the stromal vascular endothelial growth factor--an expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:8765–8773.
Article23. Syed Khaja AS, Helczynski L, Edsjö A, Ehrnström R, Lindgren A, Ulmert D, et al. Elevated level of Wnt5a protein in localized prostate cancer tissue is associated with better outcome. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e26539.
Article24. Dunlap SM, Celestino J, Wang H, Jiang R, Holland EC, Fuller GN, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 promotes glioma development and progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104:11736–11741.
Article25. Baxter RC. IGF binding proteins in cancer: mechanistic and clinical insights. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014; 14:329–341.
Article26. Probst-Hensch NM, Steiner JH, Schraml P, Varga Z, Zürrer-Härdi U, Storz M, et al. IGFBP2 and IGFBP3 protein expressions in human breast cancer: association with hormonal factors and obesity. Clin Cancer Res. 2010; 16:1025–1032.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of p27kip1 and Cyclin D1 in Serous Epithelial Ovarian Tumors
- A case report of Pseudo-Meigs' syndrome associated with ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma
- Differential Diagnosis of Ovarian Mucinous, Serous, and Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma in Peritoneal Washing Cytology
- A Case of Hinman Syndrome Complicated by Chronic Renal Failure
- A Case of Parovarian Serous Cystadenocarcinoma of Borderline Malignancy