J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Jul;31(7):1160-1163. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.7.1160.
Pralatrexate in Combination with Bortezomib for Relapsed or Refractory Peripheral T Cell Lymphoma in 5 Elderly Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hematology and Oncology, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea. drydh1685@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea.
- KMID: 2373738
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.7.1160
Abstract
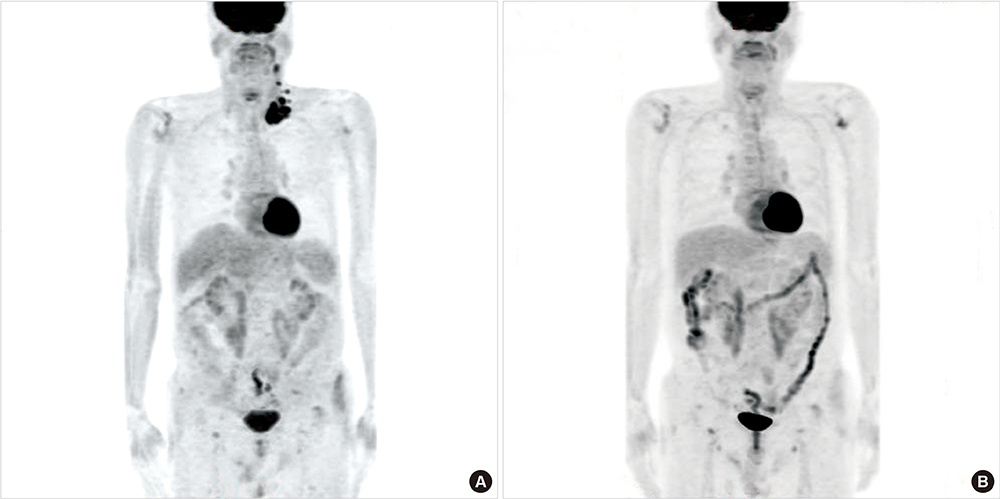
- Peripheral T cell lymphoma (PTCL) is a heterogeneous group of aggressive lymphomas with poor prognosis. Elderly (age ≥ 65years) patients generally have impaired bone marrow function, altered drug metabolism, comorbidities, and poor functional status. Thus, treatment of elderly patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL remains a challenge for clinicians. A recent study disclosed that pralatrexate has a synergistic effect in combination with bortezomib. Weekly pralatrexate and bortezomib were administered intravenously for 3 weeks in a 4-week cycle. Of 5 patients, one achieved complete response after 4 cycles which has lasted 12 months until now. Another patient attained partial response after 2 cycles. Only 1 patient experienced grade 3 thrombocytopenia and neutropenia. Two patients suffered from grade 3 mucositis. Combination therapy with pralatrexate and bortezomib may be used as a salvage therapy for relapsed or refractory PTCL in the elderly with a favorable safety profile.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Aminopterin/adverse effects/*analogs & derivatives/therapeutic use
Antineoplastic Agents/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Bortezomib/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Drug Administration Schedule
Drug Therapy, Combination
Humans
Lymphoma, T-Cell, Peripheral/diagnostic imaging/*drug therapy/pathology
Male
Neoplasm Recurrence, Local
Neutropenia/etiology
Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography
Aminopterin
Antineoplastic Agents
Bortezomib
Figure
Reference
-
1. A clinical evaluation of the International Lymphoma Study Group classification of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. Blood. 1997; 89:3909–3918.2. Hennessy BT, Hanrahan EO, Daly PA. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma: an update. Lancet Oncol. 2004; 5:341–353.3. Abouyabis AN, Shenoy PJ, Sinha R, Flowers CR, Lechowicz MJ. A systematic review and meta-analysis of front-line anthracycline-based chemotherapy regimens for peripheral T-cell lymphoma. ISRN hematol. 2011; 2011:623924.4. Coiffier B, Federico M, Caballero D, Dearden C, Morschhauser F, Jäger U, Trümper L, Zucca E, Gomes da Silva M, Pettengell R, et al. Therapeutic options in relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014; 40:1080–1088.5. O'Connor OA, Pro B, Pinter-Brown L, Bartlett N, Popplewell L, Coiffier B, Lechowicz MJ, Savage KJ, Shustov AR, Gisselbrecht C, et al. Pralatrexate in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma: results from the pivotal PROPEL study. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:1182–1189.6. Dondi A, Bari A, Pozzi S, Ferri P, Sacchi S. The potential of pralatrexate as a treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014; 23:711–718.7. Marchi E, Mangone M, Zullo K, O'Connor OA. Pralatrexate pharmacology and clinical development. Clin Cancer Res. 2013; 19:6657–6661.8. Robak T. Bortezomib in the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma. Future Oncol. 2015; 11:2807–2818.9. Marchi E, Paoluzzi L, Scotto L, Seshan VE, Zain JM, Zinzani PL, O'Connor OA. Pralatrexate is synergistic with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in in vitro and in vivo models of T-cell lymphoid malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2010; 16:3648–3658.10. Gallamini A, Stelitano C, Calvi R, Bellei M, Mattei D, Vitolo U, Morabito F, Martelli M, Brusamolino E, Iannitto E, et al. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma unspecified (PTCL-U): a new prognostic model from a retrospective multicentric clinical study. Blood. 2004; 103:2474–2479.11. Horwitz SM, Kim YH, Foss F, Zain JM, Myskowski PL, Lechowicz MJ, Fisher DC, Shustov AR, Bartlett NL, Delioukina ML, et al. Identification of an active, well-tolerated dose of pralatrexate in patients with relapsed or refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2012; 119:4115–4122.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Assessing the Efficacy of Bortezomib and Dexamethasone for Induction and Maintenance Therapy in Relapsed/Refractory Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma: A Phase II CISL1701/BIC Study
- Treatment of Relapsed Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Efficacy of bortezomib combined with Hyper‑CVAD in adults with relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia or positive measurable residual disease; effect of bortezomib in leukemia
- Combination treatment with 2-methoxyestradiol overcomes bortezomib resistance of multiple myeloma cells
- IMVP-16/Pd (Ifosfamide/Methotrexate/VP-16/Prednisone) Combination Chemotherapy for the Treatment of Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma