J Korean Med Sci.
2016 May;31(5):750-756. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.5.750.
Daily Mean Temperature Affects Urolithiasis Presentation in Seoul: a Time-series Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Seonam University College of Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, KEPCO Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Health promotion, Severance Check-up, Health Promotion Center, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, Severance Hospital, Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Urology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. caucih@cau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2373673
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.5.750
Abstract
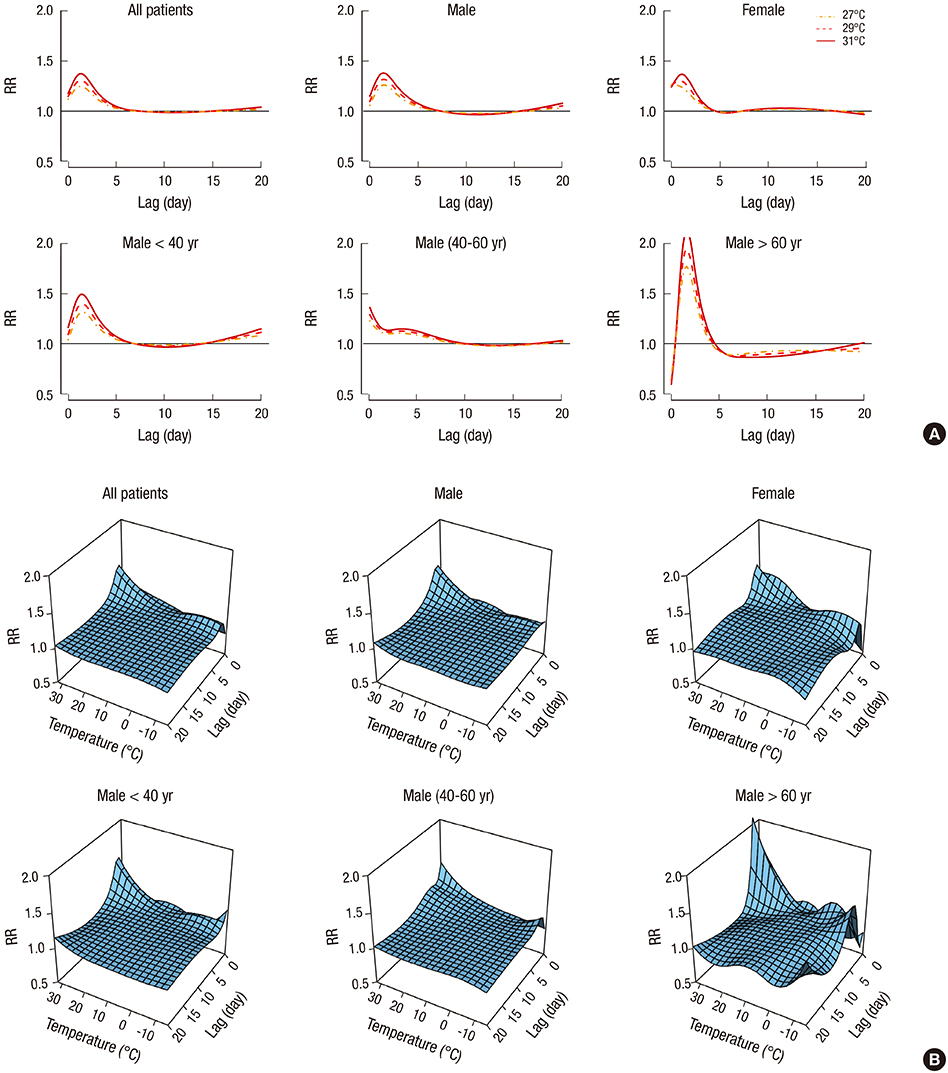
- This study aimed to investigate the overall cumulative exposure-response and the lag response relationships between daily temperature and urolithiasis presentation in Seoul. Using a time-series design and distributing lag nonlinear methods, we estimated the relative risk (RR) of urolithiasis presentation associated with mean daily temperature, including the cumulative RR for a 20 days period, and RR for individual daily lag through 20 days. We analyzed data from 14,518 patients of 4 hospitals emergency department who sought medical evaluation or treatment of urolithiasis from 2005-2013 in Seoul. RR was estimated according to sex and age. Associations between mean daily temperature and urolithiasis presentation were not monotonic. Furthermore, there was variation in the exposure-response curve shapes and the strength of association at different temperatures, although in most cases RRs increased for temperatures above the 13℃ reference value. The RRs for urolothiasis at 29℃ vs. 13℃ were 2.54 in all patients (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.67-3.87), 2.59 in male (95% CI, 1.56-4.32), 2.42 in female (95% CI, 1.15-5.07), 3.83 in male less than 40 years old (95% CI, 1.78-8.26), and 2.47 in male between 40 and 60 years old (95% CI, 1.15-5.34). Consistent trends of increasing RR of urolithiasis presentation were observed within 5 days of high temperatures across all groups. Urolithiasis presentation increased with high temperature with higher daily mean temperatures, with the strongest associations estimated for lags of only a few days, in Seoul, a metropolitan city in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sirohi M, Katz BF, Moreira DM, Dinlenc C. Monthly variations in urolithiasis presentations and their association with meteorologic factors in New York city. J Endourol. 2014; 28:599–604.2. Lo SS, Johnston R, Al Sameraaii A, Metcalf PA, Rice ML, Masters JG. Seasonal variation in the acute presentation of urinary calculi over 8 years in Auckland, New Zealand. BJU Int. 2010; 106:96–101.3. Cervellin G, Comelli I, Comelli D, Meschi T, Lippi G, Borghi L. Mean temperature and humidity variations, along with patient age, predict the number of visits for renal colic in a large urban Emergency Department: results of a 9-year survey. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2012; 2:31–38.4. Chen YK, Lin HC, Chen CS, Yeh SD. Seasonal variations in urinary calculi attacks and their association with climate: a population based study. J Urol. 2008; 179:564–569.5. Park HK, Bae SR, Kim SE, Choi WS, Paick SH, Ho K, Kim HG, Lho YS. The effect of climate variability on urinary stone attacks: increased incidence associated with temperature over 18 °C: a population-based study. Urolithiasis. 2015; 43:89–94.6. Tasian GE, Pulido JE, Gasparrini A, Saigal CS, Horton BP, Landis JR, Madison R, Keren R; Urologic Diseases in America Project. Daily mean temperature and clinical kidney stone presentation in five U.S. metropolitan areas: a time-series analysis. Environ Health Perspect. 2014; 122:1081–1087.7. Borissova A, Goltz GE, Kavanagh JP, Wilkins TA. Reverse engineering the kidney: modelling calcium oxalate monohydrate crystallization in the nephron. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2010; 48:649–659.8. Costa-Bauzá A, Perelló J, Isern B, Grases F. An experimental study on residual lithiasis after shock wave lithotripsy. Urol Res. 2005; 33:51–56.9. Egawa M, Oguri M, Kuwahara T, Takahashi M. Effect of exposure of human skin to a dry environment. Skin Res Technol. 2002; 8:212–218.10. Chou TC, Lin KH, Wang SM, Lee CW, Su SB, Shih TS, Chang HY. Transepidermal water loss and skin capacitance alterations among workers in an ultra-low humidity environment. Arch Dermatol Res. 2005; 296:489–495.11. Cravello B, Ferri A. Relationships between skin properties and environmental parameters. Skin Res Technol. 2008; 14:180–186.12. Taylor EN, Stampfer MJ, Curhan GC. Dietary factors and the risk of incident kidney stones in men: new insights after 14 years of follow-up. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004; 15:3225–3232.13. Curhan GC, Willett WC, Knight EL, Stampfer MJ. Dietary factors and the risk of incident kidney stones in younger women: Nurses’ Health Study II. Arch Intern Med. 2004; 164:885–891.14. Choi T, Yoo KH, Choi SK, Kim DS, Lee DG, Min GE, Jeon SH, Lee HL, Jeong IK. Analysis of factors affecting spontaneous expulsion of ureteral stones that may predict unfavorable outcomes during watchful waiting periods: What is the influence of diabetes mellitus on the ureter? Korean J Urol. 2015; 56:455–460.15. Jung HS, Chang IH, Kim KD, Moon YT, Kim TH, Myung SC, Kim YS, Lee JY. Possible relationship between metabolic syndrome traits and nephrolithiasis: incidence for 15 years according to gender. Korean J Urol. 2011; 52:548–553.16. Chang IH, Lee YT, Lee DM, Kim TH, Myung SC, Kim YS, Ahn SH. Metabolic syndrome, urine pH, and time-dependent risk of nephrolithiasis in Korean men without hypertension and diabetes. Urology. 2011; 78:753–758.17. Chiriboga DE, Ma Y, Li W, Stanek EJ 3rd, Hébert JR, Merriam PA, Rawson ES, Ockene IS. Seasonal and sex variation of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in healthy adults: a longitudinal study. Clin Chem. 2009; 55:313–321.18. Ockene IS, Chiriboga DE, Stanek EJ 3rd, Harmatz MG, Nicolosi R, Saperia G, Well AD, Freedson P, Merriam PA, Reed G, et al. Seasonal variation in serum cholesterol levels: treatment implications and possible mechanisms. Arch Intern Med. 2004; 164:863–870.19. Fletcher BA, Lin S, Fitzgerald EF, Hwang SA. Association of summer temperatures with hospital admissions for renal diseases in New York State: a case-crossover study. Am J Epidemiol. 2012; 175:907–916.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Daily Mean Temperature and Urolithiasis Presentation in Six Cities in Korea: Time-Series Analysis
- Clinical Review of Pediatric Urolithiasis: Etiology and Treatment
- Risk factors for urinary stone
- Improving Causal Inference in Observational Studies: Interrupted Time Series Design
- Numbers of Stroke Patients and Stroke Subtypes According to Highest and Lowest Daily Temperatures in Seoul