Ann Lab Med.
2016 Mar;36(2):182-184. 10.3343/alm.2016.36.2.182.
Genetic Confirmation of Congenital Factor V Deficiency in Korean Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. heejinkim@skku.edu
- 2Korea Hemophilia Foundation, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2373522
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2016.36.2.182
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
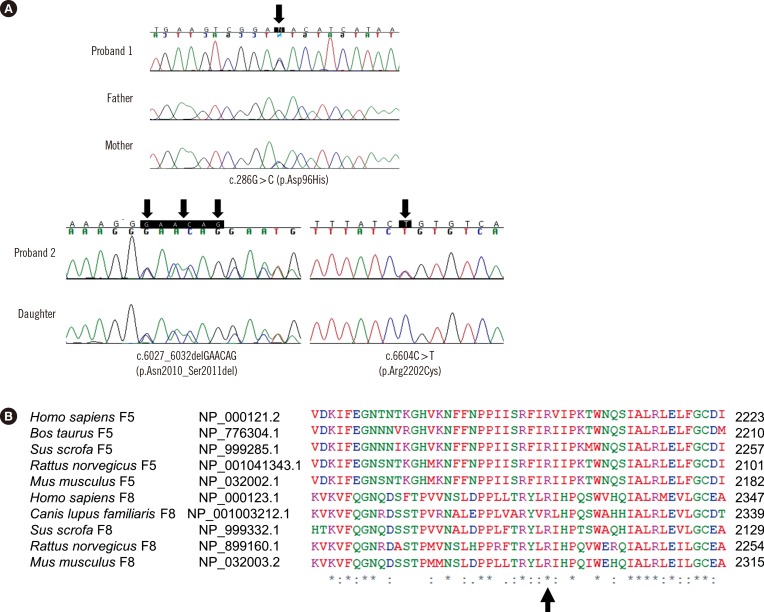
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
F5 유전자에서 새로운 변이를 포함한 복합 이형 접합 변이 1예 보고
Suji Park, Sung-Hyun Kim, Namhee Kim
Lab Med Online. 2024;14(2):147-150. doi: 10.47429/lmo.2024.14.2.147.
Reference
-
1. Liu HC, Shen MC, Eng HL, Wang CH, Lin TM. Asp68His mutation in the A1 domain of human factor V causes impaired secretion and ineffective translocation. Haemophilia. 2014; 20:e318–e326. PMID: 24893683.
Article2. Huang DD, Wang XF, Chen HY, Xu GQ, Zhang LW, Dai J, et al. Analysis of phenotype and genotype in four Chinese pedigrees with inherited coagulation factor V deficiency. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2010; 31:149–153. PMID: 20510101.3. Song J, Guella I, Kwon KY, Cho H, Park R, Asselta R, et al. A novel in-frame deletion in the factor V C1 domain associated with severe coagulation factor V deficiency in a Korean family. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2009; 20:150–156. PMID: 19786944.
Article4. Cao LJ, Wang ZY, Su YH, Yang HY, Zhao XJ, Zhang W, et al. Gene analysis of five inherited factor V deficiency cases. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2008; 29:145–148. PMID: 18788609.5. Thalji N, Camire RM. Parahemophilia: new insights into factor v deficiency. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2013; 39:607–612. PMID: 23893775.
Article6. Korea Hemophilia Foundation. 2013 Annual Report of Korea Hemophilia Foundation. Updated on April 25, 2014. http://www.kohem.org/_data/board_list_file/8/2014/1408121450071.pdf.7. Song JW, Um MR, Ahn HS, Hong CY. A case of congenital factor V deficiency. J Korean Med Sci. 1987; 2:179–182. PMID: 3268174.
Article8. Peyvandi F, Palla R, Menegatti M, Siboni SM, Halimeh S, Faeser B, et al. Coagulation factor activity and clinical bleeding severity in rare bleeding disorders: results from the European Network of Rare Bleeding Disorders. J Thromb Haemost. 2012; 10:615–621. PMID: 22321862.
Article9. James P, Salomon O, Mikovic D, Peyvandi F. Rare bleeding disorders-bleeding assessment tools, laboratory aspects and phenotype and therapy of FXI deficiency. Haemophilia. 2014; 20(Suppl 4):71–75. PMID: 24762279.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of congenital factor V deficiency
- A case of intracranial hemorrhage in a neonate with congenital factor VII deficiency
- A Case of Combined Congenital Deficiency of Factor V and Factor VIII
- A Case of Intractable Gastrointestinal Bleeding during Chemotherapy in Hereditary Coagulation Factor Deficiency
- A Case of Congenital Factor V Deficiency