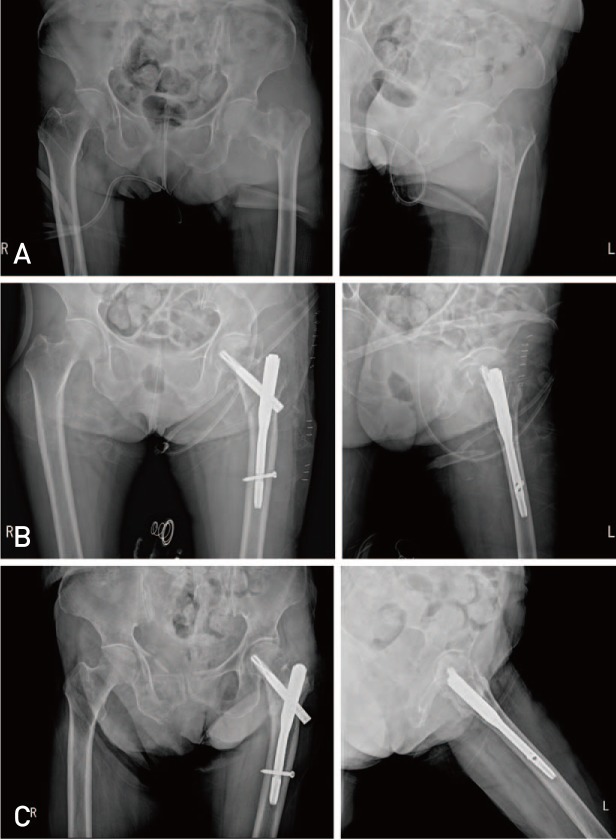
Hip Pelvis.
2017 Mar;29(1):54-61. 10.5371/hp.2017.29.1.54.
The Results of Proximal Femoral Nail for Intertrochanteric Fracture in Hemodialysis Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gwangmyeong Sungae Hospital, Gwangmyeong, Korea. osdr99@daum.net
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2371768
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2017.29.1.54
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Hip fractures in hemodialysis patients are accompanied by high rates of complications and morbidities. Previous studies have mainly reported on nonunion and avascular necrosis of femoral neck fractures in this patient group. In this study the complication and clinical results of hemodialysis patients with intertrochanteric fractures treated with proximal femoral intramedullary nailing have been investigated through comparison with patients with normal kidney function.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Forty-seven patients were included; the hemodialysis group (n=17) and the control group with normal kidney function (n=30). The medical history and clinical findings including preoperative and postoperative blood examinations, radiological examinations and ambulatory status (measured using the Koval score). The rate of complications and morbidities were also investigated and compared.
RESULTS
Preoperative hemoglobin/hematocrit was lower but a significant increase in partial thromboplastin time was observed in the hemodialysis group. The amount of bleeding/transfusions were higher and operative time was longer in the hemodialysis group. Upon radiologic examination, there was no significant difference in rate of unstable fracture and nonunion between the two groups. However the postoperative Koval score was significantly worse and the odds ratio of inability to walk after surgery was 13.5 times higher in the hemodialysis group.
CONCLUSION
There was no significant difference in radiological results, but the risk of inability to walk after surgery was 13.5 times higher in the hemodialysis group. Hemodialysis patients have more morbidities and are hemodynamically unstable therefore require special attention. Accurate reduction and firm fixation is required and attentive postoperative rehabilitation is needed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Influence of Renal Dialysis on All-Cause Mortality in Older Patients with Hip Fracture: a Korean Nationwide Cohort Study
Suk-Yong Jang, Yong-Chan Ha, Yonghan Cha, Kap Jung Kim, Wonsik Choy, Kyung-Hoi Koo
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(24):e190. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e190.
Reference
-
1. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002; 39(2 Suppl 1):S1–S266. PMID: 11904577.2. Stehman-Breen CO, Sherrard DJ, Alem AM, et al. Risk factors for hip fracture among patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2000; 58:2200–2205. PMID: 11044242.
Article3. Alem AM, Sherrard DJ, Gillen DL, et al. Increased risk of hip fracture among patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2000; 58:396–399. PMID: 10886587.
Article4. Karaeminogullari O, Demirors H, Sahin O, Ozalay M, Ozdemir N, Tandogan RN. Analysis of outcomes for surgically treated hip fractures in patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89:324–331. PMID: 17272447.
Article5. Tierney GS, Goulet JA, Greenfield ML, Port FK. Mortality after fracture of the hip in patients who have end-stage renal disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994; 76:709–712. PMID: 8175819.
Article6. Coco M, Rush H. Increased incidence of hip fractures in dialysis patients with low serum parathyroid hormone. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000; 36:1115–1121. PMID: 11096034.
Article7. Tosun B, Atmaca H, Gok U. Operative treatment of hip fractures in patients receiving hemodialysis. Musculoskelet Surg. 2010; 94:71–75. PMID: 20882378.
Article8. Kalra S, McBryde CW, Lawrence T. Intracapsular hip fractures in end-stage renal failure. Injury. 2006; 37:175–184. PMID: 16426611.
Article9. Lee JH, Kim YS, Hwang KT, Kim YH. Cementless bipolar hemiarthroplasty of hip fracture in patients on hemodialysis. Hip Pelvis. 2012; 24:200–205.
Article10. Protopsaltis TS, et al. Computed tomography for the classification of intertrochanteric fractures: correlation of fracture patterns and lag screw collapse with outcome scores. In : 69th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons; 2002 Feb 13-17; Dallas, TX, USA. Dallas: AAOS;2002.11. Koval KJ, Zuckerman JD. Intertrochanteric fractures. In : Bucholz RW, Heckman JD, editors. Rockwood and Green's fractures in adults. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2001. p. 1635–1663.12. Vidyadhara S, Rao SK. One and two femoral neck screws with intramedullary nails for unstable trochanteric fractures of femur in the elderly--randomised clinical trial. Injury. 2007; 38:806–814. PMID: 17049347.
Article13. Koval KJ, Skovron ML, Aharonoff GB, Meadows SE, Zuckerman JD. Ambulatory ability after hip fracture. A prospective study in geriatric patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995; (310):150–159.14. Chen CY, Chiu FY, Chen CM, Huang CK, Chen WM, Chen TH. Surgical treatment of basicervical fractures of femur--a prospective evaluation of 269 patients. J Trauma. 2008; 64:427–429. PMID: 18301209.
Article15. Kuo LT, Lin SJ, Hsu WH, Peng KT, Lin CL, Hsu RW. The effect of renal function on surgical outcomes of intracapsular hip fractures with osteosynthesis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014; 134:39–45. PMID: 24258682.
Article16. Stein MS, Packham DK, Ebeling PR, Wark JD, Becker GJ. Prevalence and risk factors for osteopenia in dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 1996; 28:515–522. PMID: 8840940.
Article17. Cunningham J, Sprague SM, Cannata-Andia J, et al. Osteoporosis in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004; 43:566–571. PMID: 14981616.
Article18. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for bone metabolism and disease in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003; 42(4 Suppl 3):S1–S201. PMID: 14520607.19. Martinez I, Saracho R, Montenegro J, Llach F. The importance of dietary calcium and phosphorous in the secondary hyperparathyroidism of patients with early renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997; 29:496–502. PMID: 9100037.
Article20. Buckwalter J, Marsh J, Gulotta L, Ranawat A, Lane J. Bone and joint healing. In : Buchholz RW, Heckman JD, Court-Brown CM, Tornetta P, editors. Rockwood and Green's fractures in adults. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2010.21. Ravikumar KJ, Marsh G. Internal fixation versus hemiarthroplasty versus total hip arthroplasty for displaced subcapital fractures of femur--13 year results of a prospective randomised study. Injury. 2000; 31:793–797. PMID: 11154750.22. Rogmark C, Carlsson A, Johnell O, Sernbo I. A prospective randomised trial of internal fixation versus arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the neck of the femur. Functional outcome for 450 patients at two years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84:183–188. PMID: 11922358.23. Lu-Yao GL, Keller RB, Littenberg B, Wennberg JE. Outcomes after displaced fractures of the femoral neck. A meta-analysis of one hundred and six published reports. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994; 76:15–25. PMID: 8288658.
Article24. Altner PC. Reasons for failure in treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. Orthop Rev. 1982; 11:117.25. Boyd HB, Lipinski SW. Nonunion of trochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1957; 104:463–470. PMID: 13422173.26. Kohlmeier M, Saupe J, Schaefer K, Asmus G. Bone fracture history and prospective bone fracture risk of hemodialysis patients are related to apolipoprotein E genotype. Calcif Tissue Int. 1998; 62:278–281. PMID: 9501964.
Article27. Piraino B, Chen T, Cooperstein L, Segre G, Puschett J. Fractures and vertebral bone mineral density in patients with renal osteodystrophy. Clin Nephrol. 1988; 30:57–62. PMID: 3180516.28. Schaab PC, Murphy G, Tzamaloukas AH, et al. Femoral neck fractures in patients receiving long-term dialysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; (260):224–231.
Article29. Klein DM, Tornetta P 3rd, Barbera C, Neuman D. Operative treatment of hip fractures in patients with renal failure. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; (350):174–178.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Femoral Intertrochanteric Fracture with Proximal Femoral Nail
- Excessive Sliding of the Helical Blade and the Femoral Neck Fracture after Insertion of Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-Rotation for Type A2 Intertrochanteric Fractures - A Case Report -
- Treatment of Intertrochanteric Fracture with Proximal Femoral Nail
- Comparative Study of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treated with the Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-Rotation and the Third Generation of Gamma Nail
- Treatment of Unstable Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture with the AO/ASIF Proximal Femoral Nail (PFN)