J Korean Fract Soc.
2013 Apr;26(2):151-155. 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.2.151.
Excessive Sliding of the Helical Blade and the Femoral Neck Fracture after Insertion of Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-Rotation for Type A2 Intertrochanteric Fractures - A Case Report -
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Gwangju Veterans Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. chm1228@naver.com
- KMID: 1496171
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.2.151
Abstract
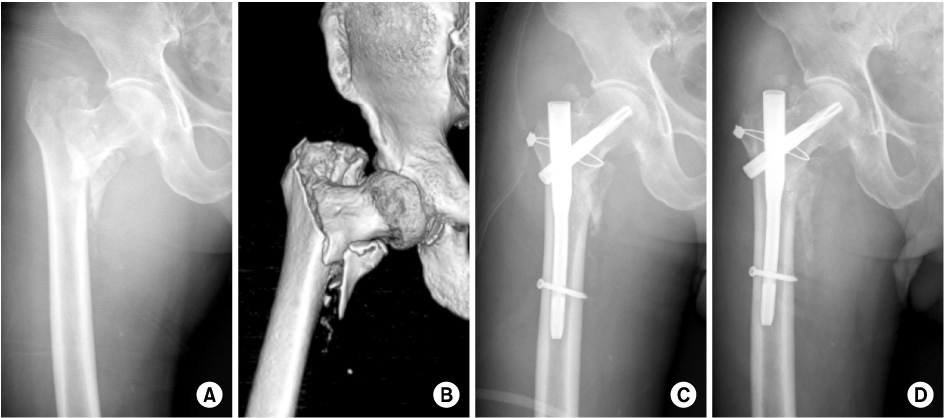
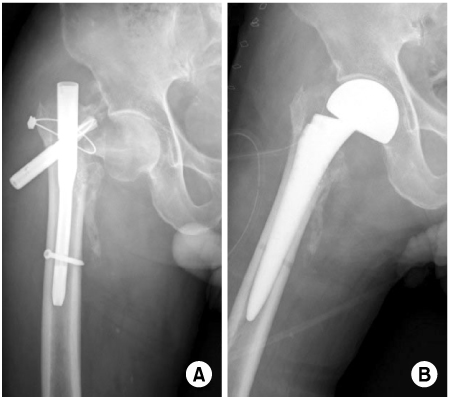
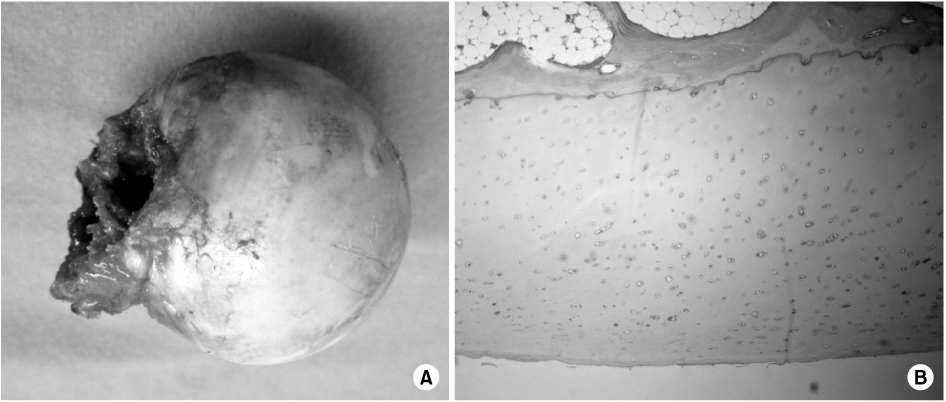
- Proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) with a lag screw that is shaped like a spiral blade shape is an orthopedic implant to fix trochanteric fractures of the proximal femur. In addition the reason of the biomechanical advantages, PFNA widely been used recently. We report an 83-year-old man with excessive sliding of the helical blade and a femoral neck fracture after AO/OTA type A2 intertrochanteric fracture, which was fixed with a PFNA.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brunner A, Jöckel JA, Babst R. The PFNA proximal femur nail in treatment of unstable proximal femur fractures--3 cases of postoperative perforation of the helical blade into the hip joint. J Orthop Trauma. 2008. 22:731–736.
Article2. Byun YS, Yoo CH, Nam JM, Cho YH, Shin DJ. Unstable trochanteric fractures of the femur treated with a condylar blade plate. J Korean Soc Fract. 2002. 15:320–327.
Article3. Jang SA, Cho YH, Byun YS, Cho HS, Choi S, Yoo HS. A case report of unique complications of PFNA penetration of the blade into the hip joint. J Korean Hip Soc. 2011. 23:318–322.
Article4. Mereddy P, Kamath S, Ramakrishnan M, Malik H, Donnachie N. The AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA): a new design for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures. Injury. 2009. 40:428–432.
Article5. Niikura T, Lee SY, Matsumoto T, et al. Backout of the helical blade of proximal femoral nail antirotation and accompanying fracture nonunion. Orthopedics. 2012. 35:e1264–e1266.
Article6. Park JH, Lee YS, Park JW, Wang JH, Kim JG. A comparative study of screw and helical proximal femoral nails for the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. Orthopedics. 2010. 33:81–85.
Article7. Simmermacher RK, Bosch AM, Van der Werken C. The AO/ASIF-proximal femoral nail (PFN): a new device for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures. Injury. 1999. 30:327–332.
Article8. Simmermacher RK, Ljungqvist J, Bail H, et al. AO - PFNA studygroup. The new proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in daily practice: results of a multicentre clinical study. Injury. 2008. 39:932–939.
Article9. Sommers MB, Roth C, Hall H, et al. A laboratory model to evaluate cutout resistance of implants for pertrochanteric fracture fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:361–368.
Article10. Takigami I, Ohnishi K, Ito Y, et al. Acetabular perforation after medial migration of the helical blade through the femoral head after treatment of an unstable trochanteric fracture with proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA): a case report. J Orthop Trauma. 2011. 25:e86–e89.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fixation Failure of Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-rotation in Femoral Intertrochanteric Fracture
- Comparative Study of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treated with the Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-Rotation and the Third Generation of Gamma Nail
- Helical Blade Locking Sleeve Disassembly Following Failed Femur Intertrochanter Fracture
- PFNA and PFN in Intertrochanteric Fractures: Comparison Study of Sliding
- Treatment of Intertrochanteric Fracture with Proximal Femoral Nail