J Korean Soc Radiol.
2017 Mar;76(3):165-172. 10.3348/jksr.2017.76.3.165.
Central Image Archiving and Management System for Multicenter Clinical Studies: Lessons from Low-dose CT for Appendicitis Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Program in Biomedical Radiation Sciences, Department of Transdisciplinary Studies, Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology, Seoul National University, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, The Armed Forces Capital Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. icofjea@gmail.com
- 4Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Radiology, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 6Department of Radiology, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Radiology, Kangwon National University Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 8Department of Radiology, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2371681
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2017.76.3.165
Abstract
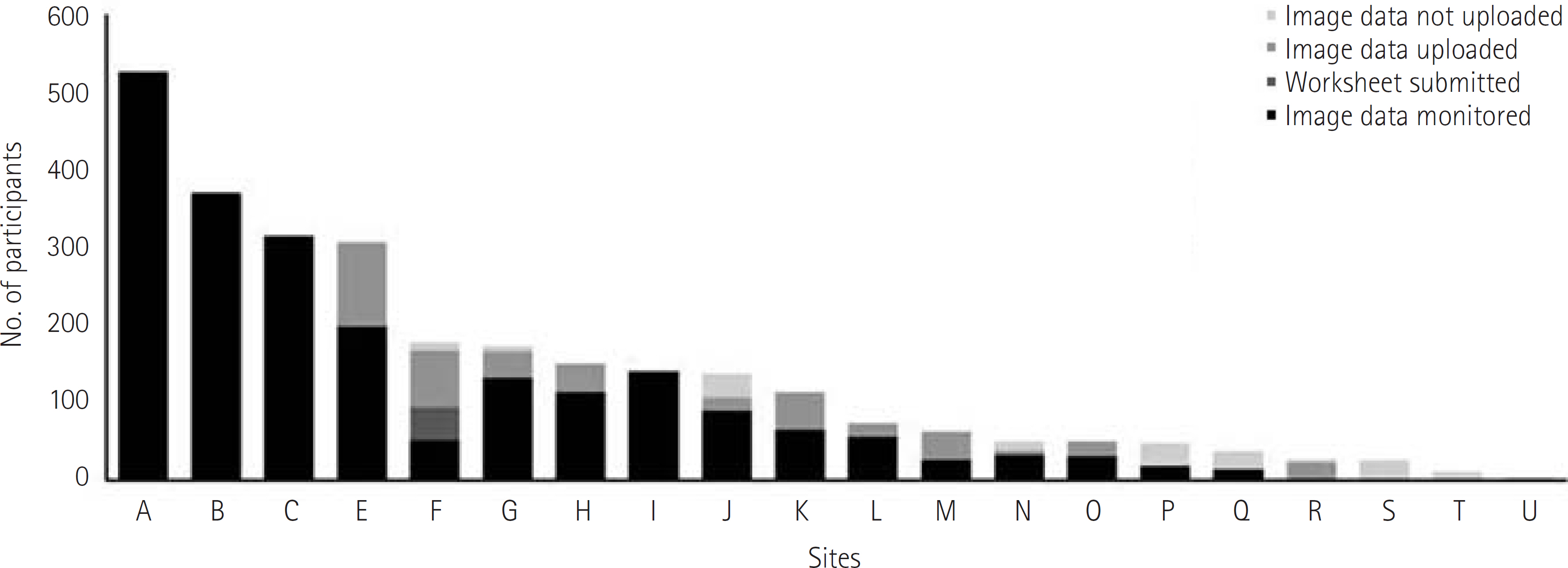
- This special report aimed to document our experiences in implementing the Central Imaging Archiving and Management System (CIAMS) for a multicenter clinical trial, Low-dose CT for Appendicitis Trial (LOCAT), supported by the Korean Society of Radiology and Radiology Imaging Network of Korea for Clinical Research. LOCAT was a randomized controlled trial to determine whether low-dose CT is non-inferior to standard-dose CT with respect to the negative appendectomy rate in patients aged from 15 to 44 years. Site investigators downloaded the CT images from the site picture archiving and communication system servers, and uploaded the anonymized images to the primary server. CIAMS administrators inspected the images routed to the secondary server by a cross-check against image submission worksheets provided by the site investigators. The secondary server was automatically synchronized to the tertiary backup server. Up to June 2016, 2715 patients from 20 sites participated in LOCAT for 30 months. A total of 2539 patients' images (93.5%, 2539/2715) were uploaded to the primary server, 2193 patients' worksheets (80.8%, 2193/2715) were submitted, and 2163 patients' data (79.7%, 2163/2715) were finally monitored. No data error occurred.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pisano ED, Gatsonis C, Hendrick E, Yaffe M, Baum JK, Acha-ryya S, et al. Diagnostic performance of digital versus film mammography for breast-cancer screening. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:1773–1783.
Article2. National Lung Screening Trial Research Team. Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, Black WC, Clapp JD, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomo-graphic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365:395–409.
Article3. Yoon SH, Lee KH, Goo JM, Kim SJ, Kim EK, Baek JH, et al. First step for clinical trial in the Korean Society of Radiology: a panel discussion. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2013; 68:157–168.
Article4. Ahn S. LOCAT group. LOCAT (low-dose computed tomography for appendicitis trial) comparing clinical outcomes fol-lowing low- vs standard-dose computed tomography as the first-line imaging test in adolescents and young adults with suspected acute appendicitis: study protocol for a random-ized controlled trial. Trials. 2014; 15:28.
Article5. Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER). Clinical Trial Imaging Endpoint Process Standards. Web site.http://www.fda. gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInfor-mation/Guidances/UCM268555.pdf. Accessed Feb 6,. 2016.6. Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Can-cer. 2009; 45:228–247.
Article7. Park JH. LOCAT Group. Diagnostic imaging utilization in cases of acute appendicitis: multicenter experience. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29:1308–1316.
Article8. Kim K, Kim YH, Kim SY, Kim S, Lee YJ, Kim KP, et al. Low-dose abdominal CT for evaluating suspected appendicitis. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:1596–1605.
Article9. Lee YJ, Kim B, Ko Y, Cho KE, Hong SS, Kim DH, et al. Low-Dose (2-mSv) CT in adolescents and young adults with suspected appendicitis: advantages of additional review of thin sections using multiplanar sliding-slab averaging technique. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015; 205:W485–W491.
Article10. Lee KH, Kim YH, Hahn S, Lee KW, Kim TJ, Kang SB, et al. Computed tomography diagnosis of acute appendicitis: advantages of reviewing thin-section datasets using slid-ing slab average intensity projection technique. Invest Radiol. 2006; 41:579–585.11. Park JH, Kim B, Kim MS, Kim HJ, Ko Y, Ahn S, et al. Compari-son of filtered back projection and iterative reconstruction in diagnosing appendicitis at 2-mSv CT. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2016; 41:1227–1236.
Article12. American College of Radiology Imaging Network. ACRIN. Web site. https://www.acrin.org. Accessed Jan 8. 2016.13. Radiology. ACo. Windows Client Installation and User Guide. Web site.http://triadhelp.acr.org/. Published 2015. Accessed Dec 4,. 2015.14. Yang HK, Woo H, Jo J, Lee MH, Kim B, Seo J, et al. development of an online radiology case review system featuring interactive navigation of volumetric image datasets using advanced visualization techniques. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2015; 73:312–322.
Article15. Yang HK, Ko Y, Lee MH, Woo H, Ahn S, Kim B, et al. Initial performance of radiologists and radiology residents in in-terpreting low-dose (2-mSv) appendiceal CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015; 205:W594–W611.
Article16. Bierer BE, Li R, Barnes M, Sim I. A Global, neutral platform for sharing trial data. N Engl J Med. 2016; 374:2411–2413.
Article17. Drazen JM. Data sharing and the journal. N Engl J Med. 2016; 374:e24.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Low-Dose Abdominal CT for Evaluating Suspected Appendicitis in Adolescents and Young Adults: Review of Evidence
- CT Findings of Acute Appendicitis in Children
- Dose and Image Evaluations of Imaging for Radiotherapy
- Evaluation of the effective dose and image quality of low-dose multi-detector CT for orthodontic treatment planning
- Necessity and conduct of multicenter clinical trials