J Rheum Dis.
2017 Feb;24(1):27-34. 10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.27.
Cost-effectiveness of Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Adjusting for Upper and Lower Gastrointestinal Toxicities in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mcpark@yuhs.ac
- 2School of Pharmacy, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2371675
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.27
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
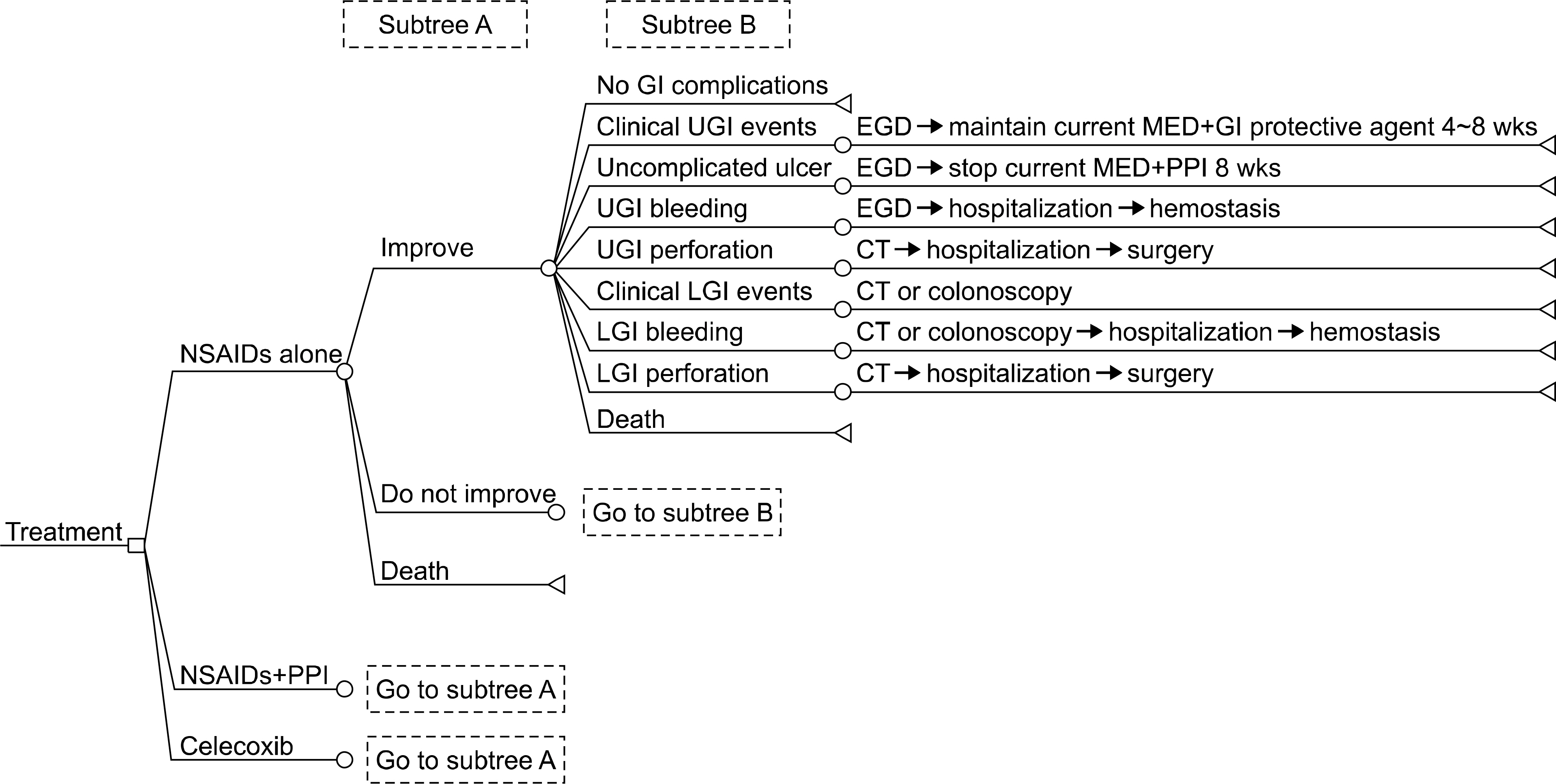
This study was performed to assess the cost-effectiveness of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2)-selective inhibitor, non-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and non-selective NSAID with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) while considering upper and lower gastrointestinal (GI) safety in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
METHODS
A Markov model was used to estimate the costs and effectiveness. Estimates of therapeutic efficacy and upper/lower GI safety were based on results from large randomized controlled trials. The main outcome measure was cost effectiveness, based on the quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) gained. Safety parameters included clinical upper GI symptoms, uncomplicated ulcer, upper GI bleeding, upper GI perforation, clinical lower GI symptoms, lower GI bleeding, and lower GI perforation. Cost data were obtained from patients treated in a tertiary referral center in Korea.
RESULTS
The expected three year cost was 3,052,800 Korean won (KRW) for COX2-selective inhibitor, 3,170,800 KRW for nonselective NSAID, and 3,325,900 KRW for non-selective NSAID with PPI. QALYs were 2.87446, 2.85320, and 2.85815, respectively. The total cost for COX2-selective inhibitor use was lower than non-selective NSAID, but QALY was higher, indicating that the incremental cost effectiveness ratio of COX2-selective inhibitor is superior.
CONCLUSION
COX2-selective inhibitor has reasonable cost-effectiveness adjusted for upper and lower GI toxicity for patients with RA in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wolfe F, Zhao S, Lane N. Preference for nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs over acetaminophen by rheumatic disease patients: a survey of 1,799 patients with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 43:378–85.
Article2. Hochberg MC, Altman RD, April KT, Benkhalti M, Guyatt G, McGowan J, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2012 recommendations for the use of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies in osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012; 64:465–74.
Article3. Patrono C. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Hochberg MC, editor. Rheumatology. Madrid: Mosby;2008. p. 403–10.
Article4. Scheiman JM, Fendrick AM. Summing the risk of NSAID therapy. Lancet. 2007; 369:1580–1.
Article5. Singh G, Ramey DR, Morfeld D, Shi H, Hatoum HT, Fries JF. Gastrointestinal tract complications of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. A prospective observational cohort study. Arch Intern Med. 1996; 156:1530–6.
Article6. Wolfe MM, Lichtenstein DR, Singh G. Gastrointestinal toxicity of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. N Engl J Med. 1999; 340:1888–99.
Article7. Lai KC, Lam SK, Chu KM, Wong BC, Hui WM, Hu WH, et al. Lansoprazole for the prevention of recurrences of ulcer complications from long-term low-dose aspirin use. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:2033–8.
Article8. Cullen D, Bardhan KD, Eisner M, Kogut DG, Peacock RA, Thomson JM, et al. Primary gastroduodenal prophylaxis with omeprazole for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug users. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1998; 12:135–40.
Article9. Chan FK, Hung LC, Suen BY, Wu JC, Lee KC, Leung VK, et al. Celecoxib versus diclofenac and omeprazole in reducing the risk of recurrent ulcer bleeding in patients with arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:2104–10.
Article10. Lai KC, Chu KM, Hui WM, Wong BC, Hu WH, Wong WM, et al. Celecoxib compared with lansoprazole and naproxen to prevent gastrointestinal ulcer complications. Am J Med. 2005; 118:1271–8.
Article11. Goldstein JL, Silverstein FE, Agrawal NM, Hubbard RC, Kaiser J, Maurath CJ, et al. Reduced risk of upper gastrointestinal ulcer complications with celecoxib, a novel COX-2 inhibitor. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000; 95:1681–90.
Article12. Schnitzer TJ, Burmester GR, Mysler E, Hochberg MC, Doherty M, Ehrsam E, et al. Comparison of lumiracoxib with naproxen and ibuprofen in the Therapeutic Arthritis Research and Gastrointestinal Event Trial (TARGET), reduction in ulcer complications: randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2004; 364:665–74.
Article13. Bombardier C, Laine L, Reicin A, Shapiro D, Burgos-Vargas R, Davis B, et al. Comparison of upper gastrointestinal toxicity of rofecoxib and naproxen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. VIGOR Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343:1520–8.14. Cho SK, Sung YK, Choi CB, Kwon JM, Lee EK, Bae SC. Development of an algorithm for identifying rheumatoid arthritis in the Korean National Health Insurance claims database. Rheumatol Int. 2013; 33:2985–92.
Article15. Lanas A, Sekar MC, Hirschowitz BI. Objective evidence of aspirin use in both ulcer and nonulcer upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastroenterology. 1992; 103:862–9.
Article16. Laine L, Smith R, Min K, Chen C, Dubois RW. Systematic review: the lower gastrointestinal adverse effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 24:751–67.
Article17. Laine L, Curtis SP, Langman M, Jensen DM, Cryer B, Kaur A, et al. Lower gastrointestinal events in a double-blind trial of the cyclo-oxygenase-2 selective inhibitor etoricoxib and the traditional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac. Gastroenterology. 2008; 135:1517–25.
Article18. Laine L, Connors LG, Reicin A, Hawkey CJ, Burgos-Vargas R, Schnitzer TJ, et al. Serious lower gastrointestinal clinical events with nonselective NSAID or coxib use. Gastroenterology. 2003; 124:288–92.
Article19. Silverstein FE, Faich G, Goldstein JL, Simon LS, Pincus T, Whelton A, et al. Gastrointestinal toxicity with celecoxib vs nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: the CLASS study: A randomized controlled trial. Celecoxib Long-term Arthritis Safety Study. JAMA. 2000; 284:1247–55.20. Wilcox CM, Alexander LN, Cotsonis GA, Clark WS. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs are associated with both upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Dig Dis Sci. 1997; 42:990–7.21. Feldman M, Friedman LS, Sleisenger MH. Sleisenger and Fordtran's gastrointestinal and liver disease. 7th ed.Vol. 1. Philadelphia: Saunders;2002. p. 211–42.22. Sonnenberg FA, Beck JR. Markov models in medical decision making: a practical guide. Med Decis Making. 1993; 13:322–38.23. Chan FK, Lanas A, Scheiman J, Berger MF, Nguyen H, Goldstein JL. Celecoxib versus omeprazole and diclofenac in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis (CONDOR): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2010; 376:173–9.
Article24. Rascati KL. Essentials of pharmacoeconomics. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2009. p. 9–23.25. Maetzel A, Krahn M, Naglie G. The cost effectiveness of rofecoxib and celecoxib in patients with osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 49:283–92.
Article26. Latimer N, Lord J, Grant RL, O'Mahony R, Dickson J, Conaghan PG. Cost effectiveness of COX 2 selective inhibitors and traditional NSAIDs alone or in combination with a proton pump inhibitor for people with osteoarthritis. BMJ. 2009; 339:b2538.
Article27. Reuter BK, Davies NM, Wallace JL. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug enteropathy in rats: role of permeability, bacteria, and enterohepatic circulation. Gastroenterology. 1997; 112:109–17.
Article28. Price AB. Pathology of drug-associated gastrointestinal disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2003; 56:477–82.
Article29. Lanas A, García-Rodríguez LA, Polo-Tomás M, Ponce M, Alonso-Abreu I, Perez-Aisa MA, et al. Time trends and impact of upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation in clinical practice. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009; 104:1633–41.
Article30. Graham DY, Opekun AR, Willingham FF, Qureshi WA. Visible small-intestinal mucosal injury in chronic NSAID users. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 3:55–9.
Article31. Maiden L, Thjodleifsson B, Theodors A, Gonzalez J, Bjarnason I. A quantitative analysis of NSAID-induced small bowel pathology by capsule enteroscopy. Gastroenterology. 2005; 128:1172–8.
Article32. Fujimori S, Gudis K, Takahashi Y, Seo T, Yamada Y, Ehara A, et al. Distribution of small intestinal mucosal injuries as a result of NSAID administration. Eur J Clin Invest. 2010; 40:504–10.
Article33. Goldstein JL, Eisen GM, Lewis B, Gralnek IM, Zlotnick S, Fort JG. Investigators. Video capsule endoscopy to prospectively assess small bowel injury with celecoxib, naproxen plus omeprazole, and placebo. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 3:133–41.
Article34. Goldstein JL, Eisen GM, Lewis B, Gralnek IM, Aisenberg J, Bhadra P, et al. Small bowel mucosal injury is reduced in healthy subjects treated with celecoxib compared with ibuprofen plus omeprazole, as assessed by video capsule endoscopy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007; 25:1211–22.
Article35. Svarvar P, Aly A. Use of the ACCES model to predict the health economic impact of celecoxib in patients with osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis in Norway. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000; 39(Suppl 2):43–50.
Article36. Haglund U, Svarvar P. The Swedish ACCES model: predicting the health economic impact of celecoxib in patients with osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000; 39(Suppl 2):51–6.37. Kristiansen IS, Kvien TK. Cost-effectiveness of replacing NSAIDs with coxibs: diclofenac and celecoxib in rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2002; 2:229–41.
Article38. Spiegel BM, Targownik L, Dulai GS, Gralnek IM. The cost-effectiveness of cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors in the management of chronic arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2003; 138:795–806.
Article39. Lee KK, You JH, Ho JT, Suen BY, Yung MY, Lau WH, et al. Economic analysis of celecoxib versus diclofenac plus omeprazole for the treatment of arthritis in patients at risk of ulcer disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003; 18:217–22.
Article40. Al MJ, Maniadakis N, Grijseels EW, Janssen M. Costs and effects of various analgesic treatments for patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis in the Netherlands. Value Health. 2008; 11:589–99.
Article41. Solomon SD, McMurray JJ, Pfeffer MA, Wittes J, Fowler R, Finn P, et al. Cardiovascular risk associated with celecoxib in a clinical trial for colorectal adenoma prevention. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:1071–80.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Medical treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (I): Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, disease modifying antirheumatic drugs and glucocorticoids
- Treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs and Helicobacter pylori in Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Current Guidelines for Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug-Induced Enteropathy