Investig Clin Urol.
2017 Mar;58(2):82-89. 10.4111/icu.2017.58.2.82.
Efficacy of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors for the treatment of distal ureteral calculi: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Universidad del Valle, Cali, Colombia. medihelp65@gmail.com
- KMID: 2368472
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2017.58.2.82
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To determine the efficacy of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5i) as medical expulsive therapy (MET) for the treatment of distal ureteral calculi.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A search strategy was conducted in the MEDLINE, CENTRAL, and Embase databases. Searches were also conducted in other databases and unpublished literature. Clinical trials were included without language restrictions. The risk of bias was evaluated with the Cochrane Collaboration's tool. An analysis of random effects due to statistical heterogeneity was conducted. The primary outcome was the expulsion rate of the distal ureteral calculus in 28 days. The secondary outcomes were the time to expulsion, side effects of treatment, and amount (mg) of nonopioid analgesia. The measure of the effect was the risk difference (RD) with a 95% confidence interval (CI). The planned interventions were PDE5i vs. placebo, tadalafil vs. placebo, and tadalafil vs. tamsulosin.
RESULTS
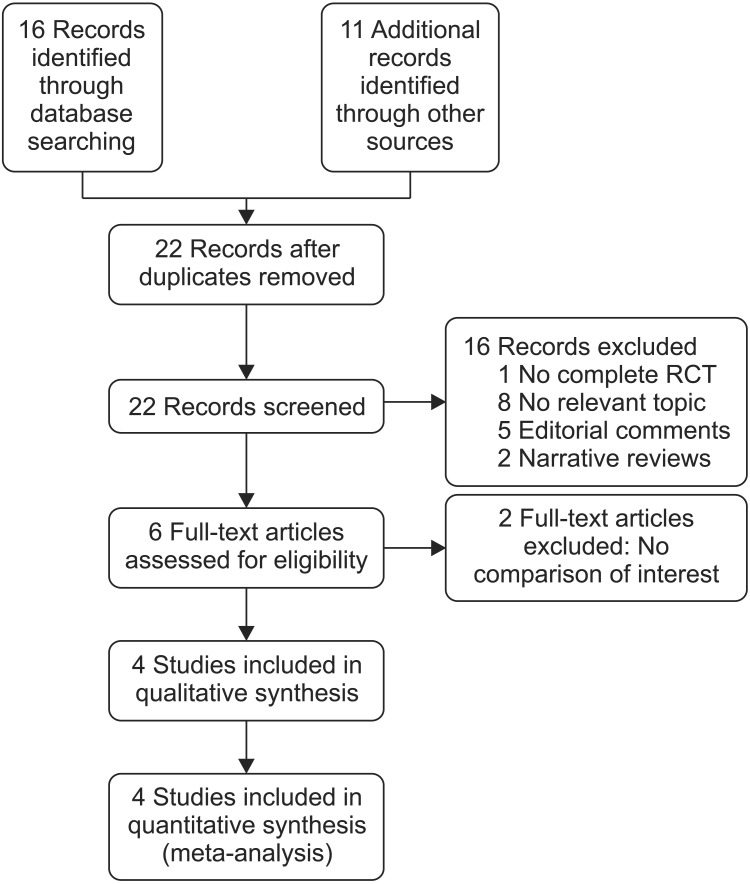
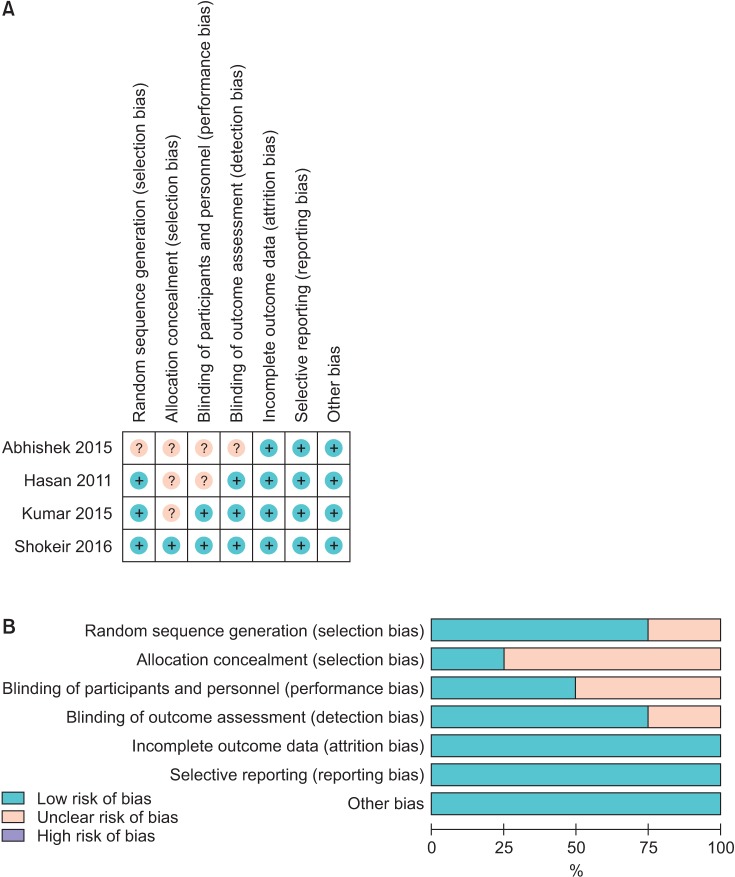
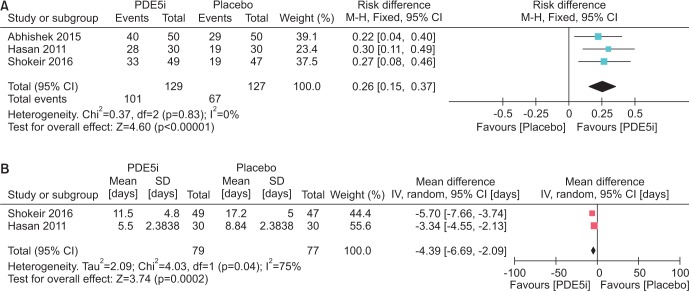
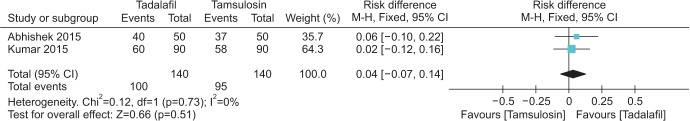
Four articles were included in the qualitative and quantitative analysis. Records of 580 patients were found among the four studies. A low risk of bias was shown for the majority of the study items. The calculi expulsion rate had an RD of 0.26 (95% CI, 0.15-0.37) and a less prolonged expulsion as a secondary outcome with a mean difference of -4.39 days (95% CI, -6.69 to -2.09) in favor of PDE5i compared with the placebo. No significant difference was found for these outcomes when comparing tadalafil with tamsulosin.
CONCLUSIONS
Compared with a placebo, PDE5i could be effective as MET for the treatment of distal ureter calculi.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Colella J, Kochis E, Galli B, Munver R. Urolithiasis/nephrolithiasis: what's it all about? Urol Nurs. 2005; 25:427–428. 475449PMID: 16438249.2. Trinchieri A. Epidemiology of urolithiasis: an update. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2008; 5:101–106. PMID: 22460989.3. Wooldridge AA, Seahorn TL, Williams J, Taylor HW, Oliver JL, Kim DY, et al. Chronic renal failure associated with nephrolithiasis, ureterolithiasis, and renal dysplasia in a 2-year-old quarter horse gelding. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 1999; 40:361–364. PMID: 10463829.
Article4. Miller OF, Kane CJ. Time to stone passage for observed ureteral calculi: a guide for patient education. J Urol. 1999; 162(3 Pt 1):688–690. PMID: 10458343.
Article5. Dellabella M, Milanese G, Muzzonigro G. Randomized trial of the efficacy of tamsulosin, nifedipine and phloroglucinol in medical expulsive therapy for distal ureteral calculi. J Urol. 2005; 174:167–172. PMID: 15947613.
Article6. Gratzke C, Uckert S, Kedia G, Reich O, Schlenker B, Seitz M, et al. In vitro effects of PDE5 inhibitors sildenafil, vardenafil and tadalafil on isolated human ureteral smooth muscle: a basic research approach. Urol Res. 2007; 35:49–54. PMID: 17102958.
Article7. Al-Aown A, Kyriazis I, Kallidonis P, Sakellaropoulos G, Vrettos T, Perimenis P, et al. Vardenafil effect on ureteric smooth muscle: in vitro study in porcine model. J Endourol. 2011; 25:505–509. PMID: 21401398.
Article8. Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration;2011. updated 2011 Mar. cited 2016 Nov 5. Available from: http://handbook.cochrane.org.9. DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986; 7:177–188. PMID: 3802833.
Article10. Shokeir AA, Tharwat MA, Abolazm AE, Harraz A. Sildenafil citrate as a medical expulsive therapy for distal ureteric stones: A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled study. Arab J Urol. 2016; 14:1–6. PMID: 26966585.
Article11. Hasan HF, Jaffal WN, Al-Hossona HA. The role of tadalafil in lower ureteric stone expulsion. Iraqi Postgrad Med J. 2011; 10:24–32.12. Abhishek L, Shashikant N, Arvind G, Ravindra S, Mahesh D. Comparison of tadalafil and tamsulosin in medical expulsive therapy for ureteric calculus: prospective, randomized, placebo controlled study [abstract]. Indian J Urol. 2015; 31(Suppl 1):S39. Abstract No. CKP 03.13. Kumar S, Jayant K, Agrawal MM, Singh SK, Agrawal S, Parmar KM. Role of tamsulosin, tadalafil, and silodosin as the medical expulsive therapy in lower ureteric stone: a randomized trial (a pilot study). Urology. 2015; 85:59–63. PMID: 25530364.
Article14. Pickard R, Starr K, MacLennan G, Lam T, Thomas R, Burr J, et al. Medical expulsive therapy in adults with ureteric colic: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2015; 386:341–349. PMID: 25998582.
Article15. Sur RL, Shore N, L'Esperance J, Knudsen B, Gupta M, Olsen S, et al. Silodosin to facilitate passage of ureteral stones: a multi-institutional, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Urol. 2015; 67:959–964. PMID: 25465978.
Article16. Taher A, Schulz-Knappe P, Meyer M, Truss M, Forssmann WG, Stief CG, et al. Characterization of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzymes in the human ureter and their functional role in vitro. World J Urol. 1994; 12:286–291. PMID: 7866426.
Article17. Truss MC, Uckert S, Stief CG, Forssmann WG, Jonas U. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) isoenzymes in the human detrusor smooth muscle. II. Effect of various PDE inhibitors on smooth muscle tone and cyclic nucleotide levels in vitro. Urol Res. 1996; 24:129–134. PMID: 8839479.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ureteroscopic Manipulation of Distal Ureteral Calculi
- Ureteral calculi: treatment options under advanced technology
- An Introduction of the Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Experience of Ureteroscopic Removal of Ureteral Stone in 35 Cases
- Distal Ureteral Calculi: The Usefulness of Transrectal Ultrasound and Comparision with Intravenous Urography