Ann Dermatol.
2016 Dec;28(6):697-703. 10.5021/ad.2016.28.6.697.
Clinicopathological Features and Immunohistochemical Alterations of Keratinocyte Proliferation, Melanocyte Density, Smooth Muscle Hyperplasia and Nerve Fiber Distribution in Becker's Nevus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Guangdong, China. ymfan1963@163.com
- 2Department of Dermatology, Gaobu Hospital of Dongguan, Guangdong, China.
- KMID: 2368119
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2016.28.6.697
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Although Becker's nevus (BN) is a relatively common disease, the systematic studies of clinicopathological and immunohistochemical results are poorly reported.
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the clinicopathological features and immunohistochemical alterations of keratinocyte proliferation, melanocyte density, smooth muscle hyperplasia and nerve fiber distribution in BN.
METHODS
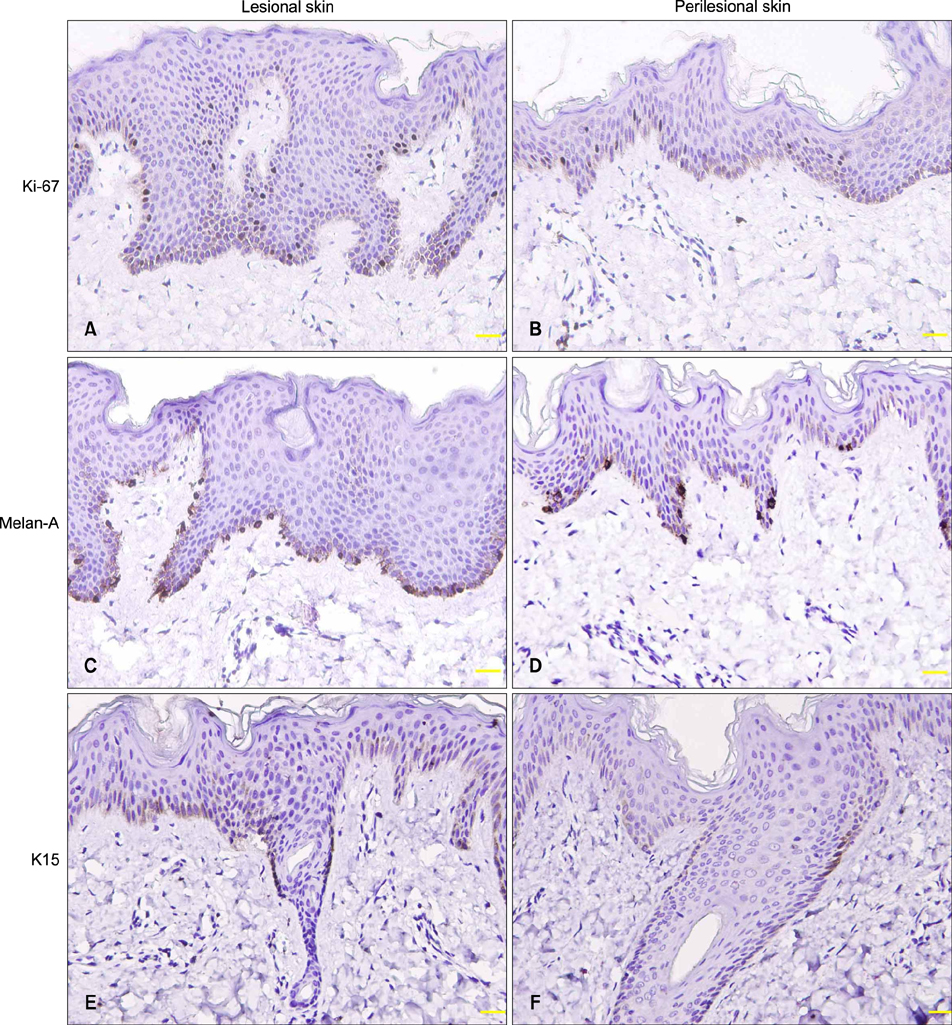
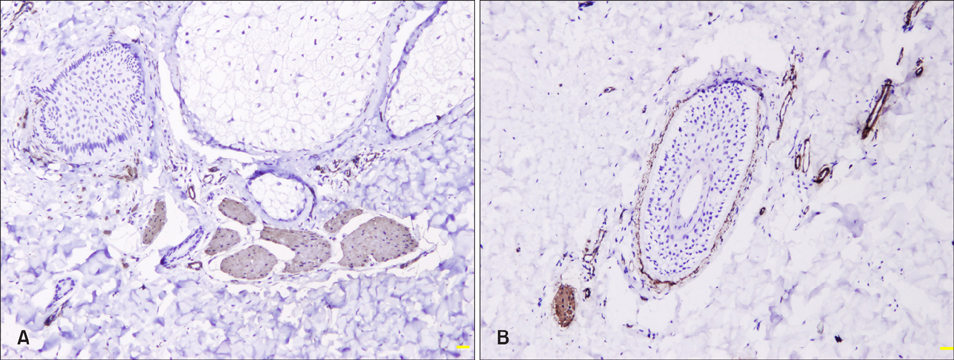
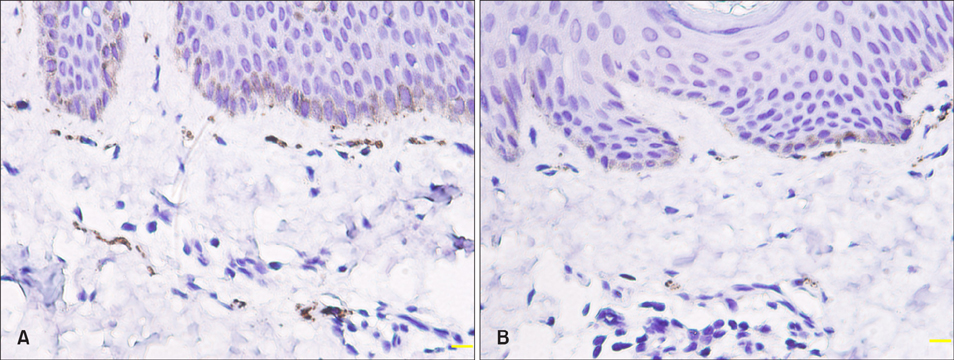
Clinical and pathological data were collected in 60 newly-diagnosed BN cases. Immunohistochemical stain of Ki-67, Melan-A, keratin 15, smooth muscle actin and protein gene product 9.5 was performed in 21 cases.
RESULTS
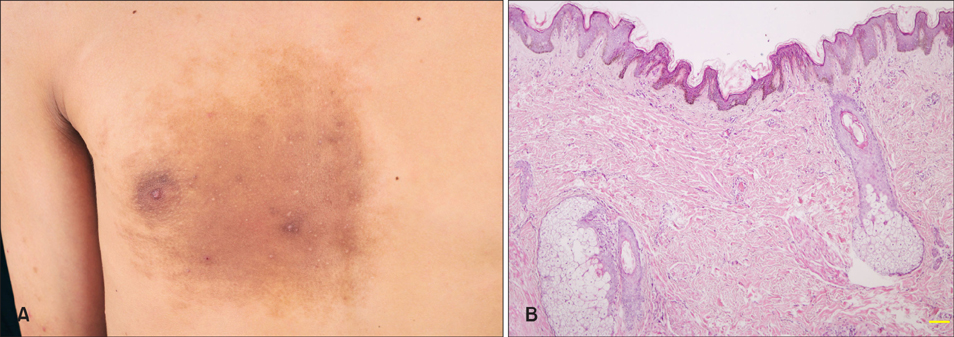
The median diagnostic and onset age was 17 and 12 years, respectively. Skin lesions usually appeared on the upper trunk and upper limbs. The pathological features included the rete ridge elongation and fusion and basal hyperpigmentation. Epidermal Ki-67, Melan-A and keratin 15 expression and dermal nerve fiber length were significantly higher in lesional and perilesional skin than in normal skin (p<0.05~0.01), while smooth muscle actin expression was upregulated only in skin lesion (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
Although the clinical diagnosis of BN is often straightforward, histopathology is helpful to differentiate from other pigmentary disorders. The hyperproliferation of keratinocytes, melanocytes, arrector pili muscle and dermal nerve fibers could be involved in the pathogenesis of BN.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Neuropeptides Profile and Increased Innervation in Becker's Nevus
Ji Seok Kim, Myeong Jin Park, Hye Young Kang, Seung Phil Hong, Byung Cheol Park, Myung Hwa Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2019;31(2):154-163. doi: 10.5021/ad.2019.31.2.154.
Reference
-
1. Patel P, Malik K, Khachemoune A. Sebaceus and Becker's nevus: overview of their presentation, pathogenesis, associations, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015; 16:197–204.
Article2. Kim YJ, Han JH, Kang HY, Lee ES, Kim YC. Androgen receptor overexpression in Becker nevus: histopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis. J Cutan Pathol. 2008; 35:1121–1126.
Article3. Rasi A, Berenji Ardestani H, Tabaie SM. Hypertrichosis is not so prevalent in Becker's nevus: analysis of 47 cases. ISRN Dermatol. 2014; 2014:953747.
Article4. Patrizi A, Medri M, Raone B, Bianchi F, Aprile S, Neri I. Clinical characteristics of Becker's nevus in children: report of 118 cases from Italy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012; 29:571–574.
Article5. Grande Sarpa H, Harris R, Hansen CD, Callis Duffin KP, Florell SR, Hadley ML. Androgen receptor expression patterns in Becker's nevi: an immunohistochemical study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008; 59:834–838.
Article6. Lauria G, Cazzato D, Porretta-Serapiglia C, Casanova-Molla J, Taiana M, Penza P, et al. Morphometry of dermal nerve fibers in human skin. Neurology. 2011; 77:242–249.
Article7. de Almeida HL Jr, Duquia RP, Souza PR, Breunig Jde A. Prevalence and characteristics of Becker nevus in Brazilian 18-year-old males. Int J Dermatol. 2010; 49:718–720.
Article8. Alfadley A, Hainau B, Al Robaee A, Banka N. Becker's melanosis: a report of 12 cases with atypical presentation. Int J Dermatol. 2005; 44:20–24.
Article9. Kar S, Preetha K, Yadav N, Madke B, Gangane N. Becker's nevus with neurofibromatosis type 1. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2015; 18:90–92.
Article10. AlGhamdi KM, AlKhalifah AI, AlSheikh AM, AlSaif FM. Clinicopathologic profile of Becker's melanosis with atypical features. J Drugs Dermatol. 2009; 8:745–748.11. Tate PR, Hodge SJ, Owen LG. A quantitative study of melanocytes in Becker's nevus. J Cutan Pathol. 1980; 7:404–409.
Article12. Tsujita-Kyutoku M, Kiuchi K, Danbara N, Yuri T, Senzaki H, Tsubura A. p63 expression in normal human epidermis and epidermal appendages and their tumors. J Cutan Pathol. 2003; 30:11–17.
Article13. Poblet E, Jiménez F, Godínez JM, Pascual-Martín A, Izeta A. The immunohistochemical expression of CD34 in human hair follicles: a comparative study with the bulge marker CK15. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006; 31:807–812.
Article14. Kanoh M, Amoh Y, Sato Y, Katsuoka K. Expression of the hair stem cell-specific marker nestin in epidermal and follicular tumors. Eur J Dermatol. 2008; 18:518–523.15. Abbas O, Richards JE, Yaar R, Mahalingam M. Stem cell markers (cytokeratin 15, cytokeratin 19 and p63) in in situ and invasive cutaneous epithelial lesions. Mod Pathol. 2011; 24:90–97.
Article16. Torkamani N, Rufaut NW, Jones L, Sinclair RD. Beyond goosebumps: does the arrector pili muscle have a role in hair loss? Int J Trichology. 2014; 6:88–94.
Article17. Fujiwara H, Ferreira M, Donati G, Marciano DK, Linton JM, Sato Y, et al. The basement membrane of hair follicle stem cells is a muscle cell niche. Cell. 2011; 144:577–589.
Article18. Thibaut S, Gaillard O, Bouhanna P, Cannell DW, Bernard BA. Human hair shape is programmed from the bulb. Br J Dermatol. 2005; 152:632–638.
Article19. Aneiros-Fernández J, Husein-ElAhmed H, Arias-Santiago S, Campos A, Carriel V, Sánchez-Montesinos I, et al. Expression of smoothelin and smooth muscle actin in the skin. Histol Histopathol. 2011; 26:673–678.20. Taneda K, Tominaga M, Negi O, Tengara S, Kamo A, Ogawa H, et al. Evaluation of epidermal nerve density and opioid receptor levels in psoriatic itch. Br J Dermatol. 2011; 165:277–284.
Article21. Melcangi RC, Ballabio M, Cavarretta I, Gonzalez LC, Leonelli E, Veiga S, et al. Effects of neuroactive steroids on myelin of peripheral nervous system. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003; 85:323–327.
Article22. Sato A, Toyoshima KE, Toki H, Ishibashi N, Asakawa K, Iwadate A, et al. Single follicular unit transplantation reconstructs arrector pili muscle and nerve connections and restores functional hair follicle piloerection. J Dermatol. 2012; 39:682–687.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Becker's Nevus Associated with Smooth Muscle Hamartoma
- A Case of Becker's Nevus with Smooth Muscle Harmatoma
- A Case of Aquired Smooth Muscle Hamartoma with Follicular Spotted Appearance
- Becker's Nevus with Underlying Neurofibroma
- A case of smooth muscle hamartoma associated with Becker's nevus