Ann Surg Treat Res.
2017 Feb;92(2):55-66. 10.4174/astr.2017.92.2.55.
A novel panel of serum miR-21/miR-155/miR-365 as a potential diagnostic biomarker for breast cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Breast Surgery, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China. 6-fu@163.com
- 2Department of Oncology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China.
- 3Institute of Cancer Prevention and Treatment, Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China.
- KMID: 2367917
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2017.92.2.55
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Insufficient sensitivity and specificity prevent the use of most existing biomarkers for early detection of breast cancer. Recently, it was reported that serum microRNAs (miRNAs) may be potential biomarkers in many cancer diseases. In this study, we investigated whether serum levels of 5 miRNAs including miR-21, miR-125b, miR-145, miR-155, and miR-365 could discriminate breast cancer patients and healthy controls.
METHODS
Serum levels of miRNAs were measured by using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in 99 breast cancer patients and 21 healthy controls. The abundance change of serum miRNAs were also evaluated following surgical resection in 20 breast cancer patients. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to assess the sensitivity and specificity of miRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers.
RESULTS
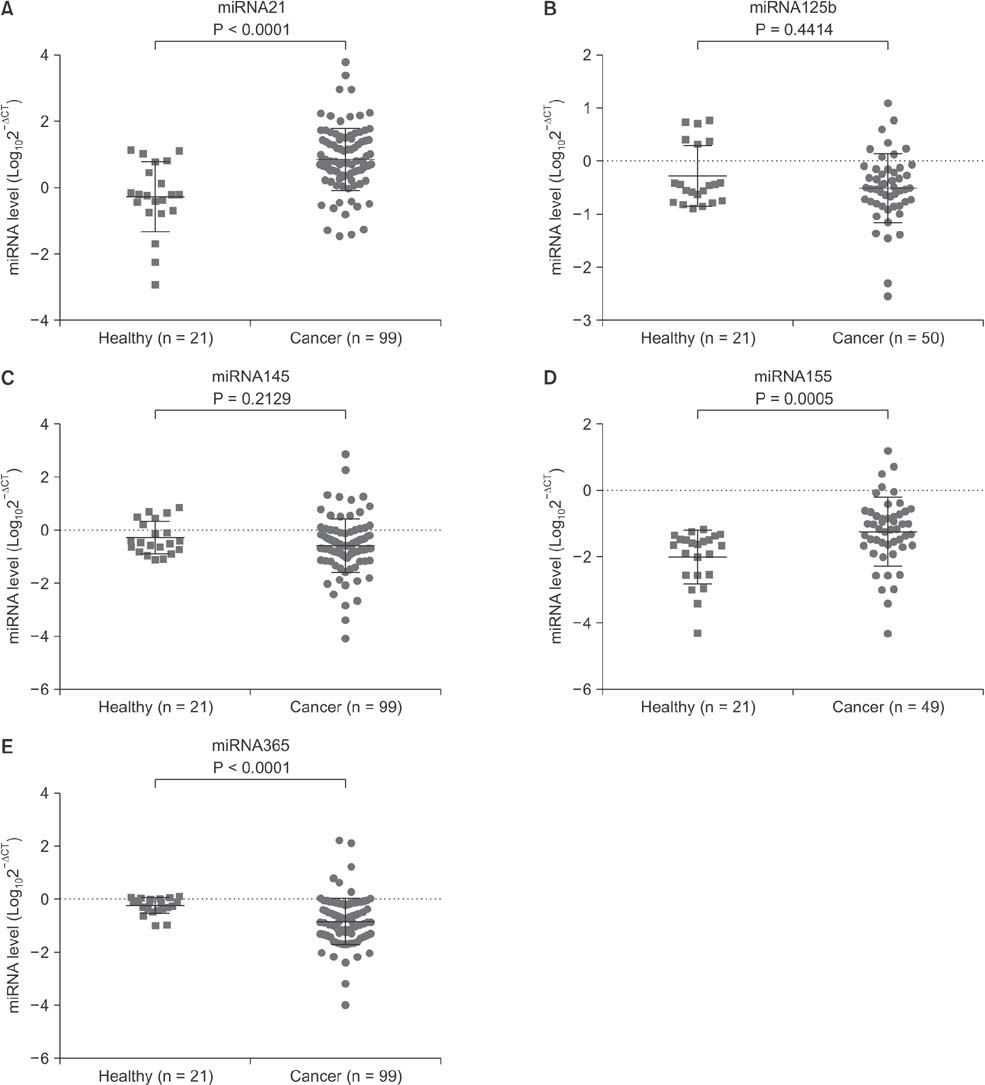
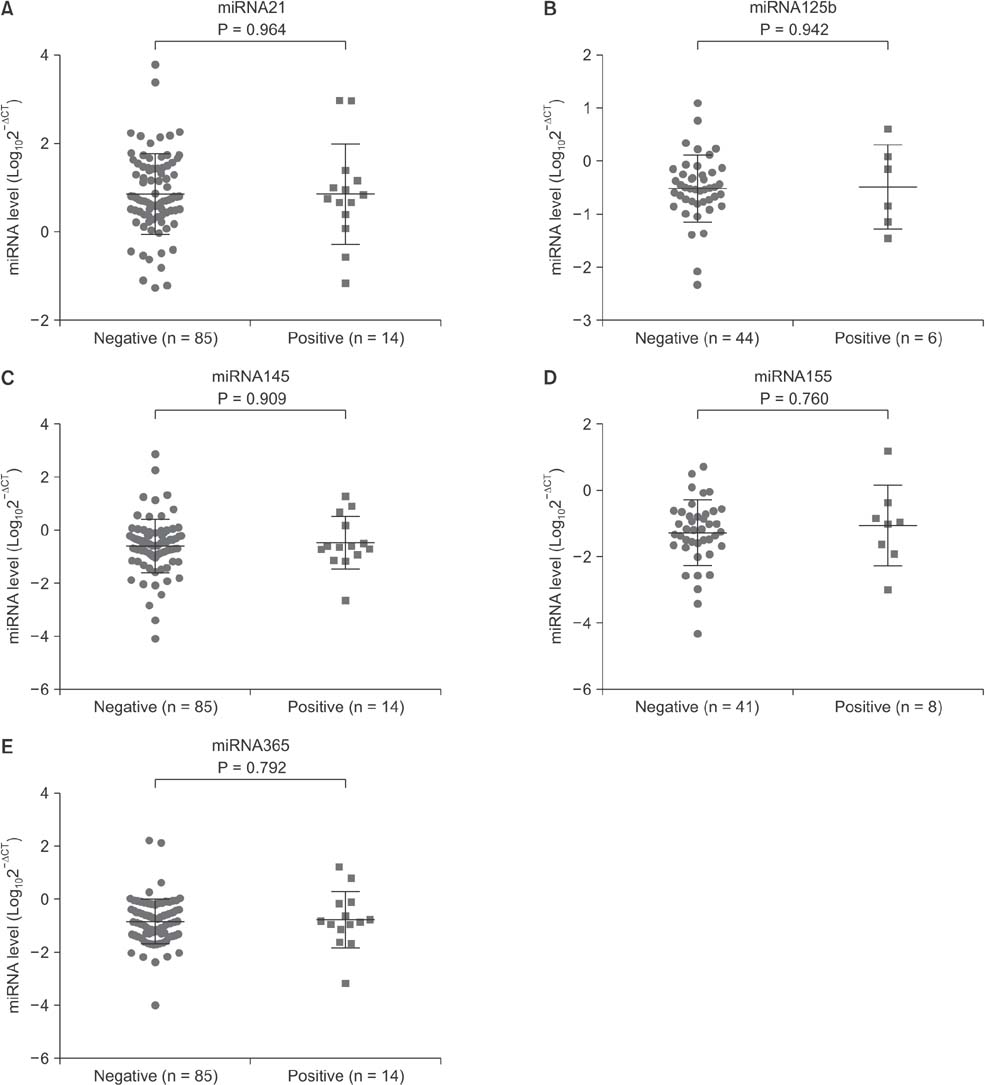
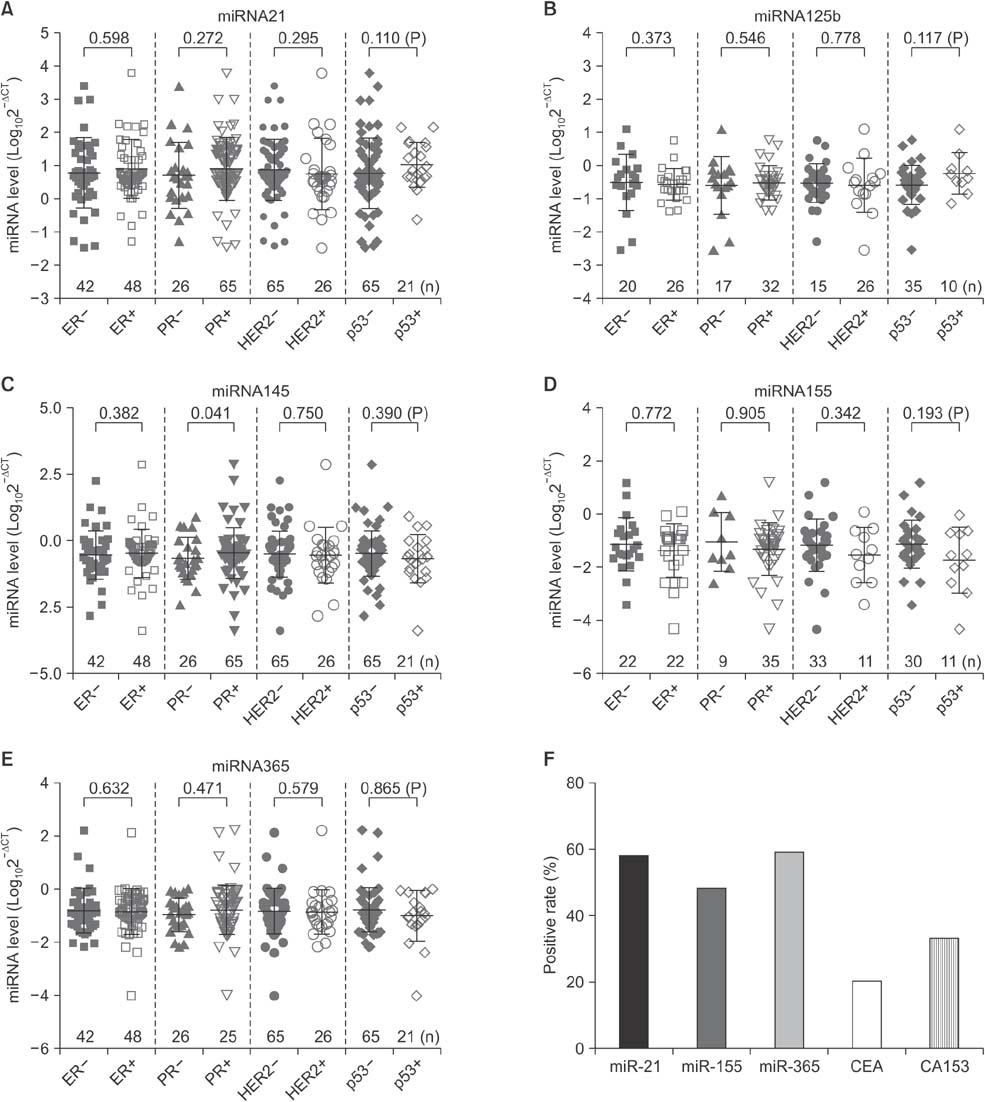
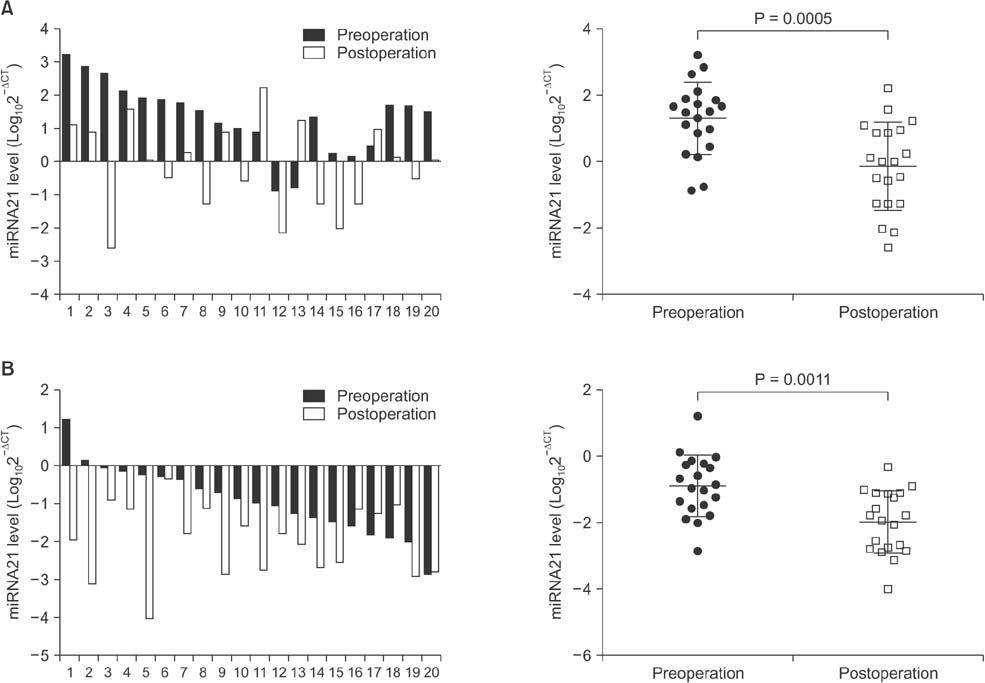
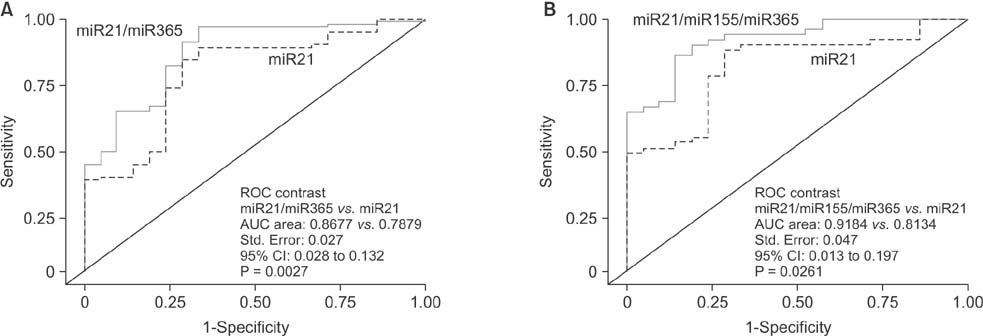
Serum levels of miR-21 and miR-155 was significantly higher, while miR-365 was significantly lower in breast cancer as compared with healthy controls. The serum levels of miR-21 and miR-155 significantly decreased following surgical resection. Additionally, the serum level of miR-155 at stages I and II was significantly higher compared to stage III. The serum miR-145 level was remarkably higher in progesterone receptor (PR)-positive patients than PR-negative. The positivity of miR-21, miR-155, and miR-365 was high compared to CA 153 and CEA in breast cancer. ROC curve analyses of a combination of miR-21, miR-155, and miR-365 yielded much higher area under curve and enhanced sensitivity and specificity in comparison to each miRNA alone.
CONCLUSION
The combination of serum miR-21/miR-155/miR-365 may potentially serve as a sensitive and specific biomarker that enables differentiation of breast cancer from healthy controls.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schettini F, Buono G, Cardalesi C, Desideri I, De Placido S, Del Mastro L. Hormone Receptor/Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-positive breast cancer: Where we are now and where we are going. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016; 46:20–26.2. Duffy MJ. Role of tumor markers in patients with solid cancers: a critical review. Eur J Intern Med. 2007; 18:175–184.3. Pileczki V, Cojocneanu-Petric R, Maralani M, Neagoe IB, Sandulescu R. MicroRNAs as regulators of apoptosis mechanisms in cancer. Clujul Med. 2016; 89:50–55.4. Solomides CC, Evans BJ, Navenot JM, Vadigepalli R, Peiper SC, Wang ZX. MicroRNA profiling in lung cancer reveals new molecular markers for diagnosis. Acta Cytol. 2012; 56:645–654.5. Markou A, Sourvinou I, Vorkas PA, Yousef GM, Lianidou E. Clinical evaluation of microRNA expression profiling in non small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2013; 81:388–396.6. Toiyama Y, Takahashi M, Hur K, Nagasaka T, Tanaka K, Inoue Y, et al. Serum miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013; 105:849–859.7. Liu R, Chen X, Du Y, Yao W, Shen L, Wang C, et al. Serum microRNA expression profile as a biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Clin Chem. 2012; 58:610–618.8. Mar-Aguilar F, Luna-Aguirre CM, Moreno-Rocha JC, Araiza-Chavez J, Trevino V, Rodriguez-Padilla C, et al. Differential expression of miR-21, miR-125b and miR-191 in breast cancer tissue. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2013; 9:53–59.9. Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng L, Wu QL, et al. MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA. 2008; 14:2348–2360.10. Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:7065–7070.11. Bertoli G, Cava C, Castiglioni I. MicroRNAs: new biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, therapy prediction and therapeutic tools for breast cancer. Theranostics. 2015; 5:1122–1143.12. Ravelli A, Reuben JM, Lanza F, Anfossi S, Cappelletti MR, Zanotti L, et al. Breast cancer circulating biomarkers: advantages, drawbacks, and new insights. Tumour Biol. 2015; 36:6653–6665.13. Al-Khanbashi M, Al-Moundhri M. Microribonucleic acid and carcinogenesis: breast cancer as an example. Oncol Rev. 2015; 9:279.14. Fatima S, Faridi N, Gill S. Breast cancer: steroid receptors and other prognostic indicators. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2005; 15:230–233.15. Stark AT, Claud S, Kapke A, Lu M, Linden M, Griggs J. Race modifies the association between breast carcinoma pathologic prognostic indicators and the positive status for HER-2/neu. Cancer. 2005; 104:2189–2196.16. Graveel CR, Calderone HM, Westerhuis JJ, Winn ME, Sempere LF. Critical analysis of the potential for microRNA biomarkers in breast cancer management. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2015; 7:59–79.17. Huang Y, Yang YB, Zhang XH, Yu XL, Wang ZB, Cheng XC. MicroRNA-21 gene and cancer. Med Oncol. 2013; 30:376.18. Savad S, Mehdipour P, Miryounesi M, Shirkoohi R, Fereidooni F, Mansouri F, et al. Expression analysis of MiR-21, MiR-205, and MiR-342 in breast cancer in Iran. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012; 13:873–877.19. Heneghan HM, Miller N, Lowery AJ, Sweeney KJ, Newell J, Kerin MJ. Circulating microRNAs as novel minimally invasive biomarkers for breast cancer. Ann Surg. 2010; 251:499–505.20. Sochor M, Basova P, Pesta M, Dusilkova N, Bartos J, Burda P, et al. Oncogenic microRNAs: miR-155, miR-19a, miR-181b, and miR-24 enable monitoring of early breast cancer in serum. BMC Cancer. 2014; 14:448.21. Mattiske S, Suetani RJ, Neilsen PM, Callen DF. The oncogenic role of miR-155 in breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2012; 21:1236–1243.22. Lyng MB, Lænkholm AV, Sokilde R, Gravgaard KH, Litman T, Ditzel HJ. Global microRNA expression profiling of high-risk ER+ breast cancers from patients receiving adjuvant tamoxifen monotherapy: a DBCG study. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e36170.23. Chen Z, Huang Z, Ye Q, Ming Y, Zhang S, Zhao Y, et al. Prognostic significance and anti-proliferation effect of microRNA-365 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8:1705–1711.24. Kang SM, Lee HJ, Cho JY. MicroRNA-365 regulates NKX2-1, a key mediator of lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013; 335:487–494.25. Kodahl AR, Lyng MB, Binder H, Cold S, Gravgaard K, Knoop AS, et al. Novel circulating microRNA signature as a potential non-invasive multi-marker test in ERpositive early-stage breast cancer: a case control study. Mol Oncol. 2014; 8:874–883.26. Mar-Aguilar F, Mendoza-Ramirez JA, Malagon-Santiago I, Espino-Silva PK, Santuario-Facio SK, Ruiz-Flores P, et al. Serum circulating microRNA profiling for identification of potential breast cancer biomarkers. Dis Markers. 2013; 34:163–169.27. Godfrey AC, Xu Z, Weinberg CR, Getts RC, Wade PA, DeRoo LA, et al. Serum microRNA expression as an early marker for breast cancer risk in prospectively collected samples from the Sister Study cohort. Breast Cancer Res. 2013; 15:R42.28. Polytarchou C, Iliopoulos D, Struhl K. An integrated transcriptional regulatory circuit that reinforces the breast cancer stem cell state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109:14470–14475.29. Zeng RC, Zhang W, Yan XQ, Ye ZQ, Chen ED, Huang DP, et al. Down-regulation of miRNA-30a in human plasma is a novel marker for breast cancer. Med Oncol. 2013; 30:477.30. Gao J, Zhang Q, Xu J, Guo L, Li X. Clinical significance of serum miR-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA. Chin J Cancer Res. 2013; 25:743–748.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- miR-205 and miR-200c: Predictive Micro RNAs for Lymph Node Metastasis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer
- Serum miR-3620-3p as a Novel Biomarker for Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Serum miR-329-3p as a potential biomarker for poor ovarian response in an in vitro fertilization
- Overexpression of miR-146a and miR-155 are Potentially Biomarkers and Predict Unfavorable Relationship between Gastric Cancer and Helicobacter pylori Infection
- Long Non-Coding RNA NORAD Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis by Regulating miR-155-5p/ SOCS1 Axis