Cancer Res Treat.
2017 Jan;49(1):213-218. 10.4143/crt.2016.195.
Clinicopathological Features of Low-Grade Thyroid-like Nasopharyngeal Papillary Adenocarcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Shaoxing People’s Hospital, Shaoxing Hospital of Zhejiang University, Shaoxing, China. jiangling817@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2367519
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2016.195
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Primary low-grade thyroid-like papillary adenocarcinomas are extremely rare neoplasms that generally originate in the nasopharynx. Here, we describe a novel case of a 15-year-old Chinese girl who was diagnosed with low-grade thyroid-like papillary adenocarcinoma, including a brief review of the literature to reveal the clinicopathological features of low-grade thyroid-like nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Immunohistochemistry was used to evaluate the expression of pan-cytokeratin (CKpan), cytokeratin (CK) 7, thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1), vimentin, epithelial membrane antigen (EMA), thyroglobulin, CD15, S100, P40, CK20, CDX-2, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and Ki-67. Additionally, in situ hybridization investigation was utilized to identify the presence of small Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded RNA.
RESULTS
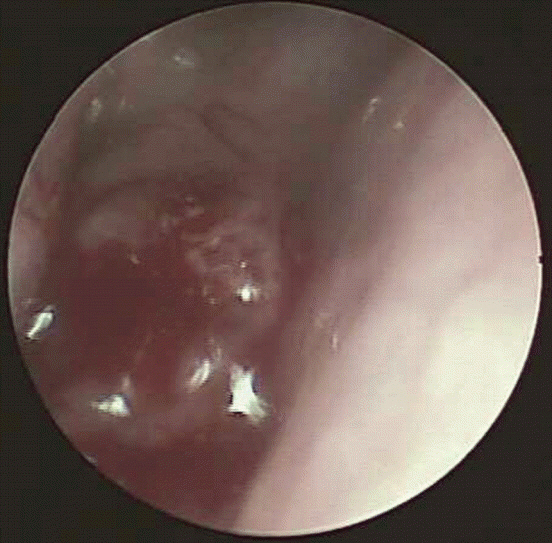
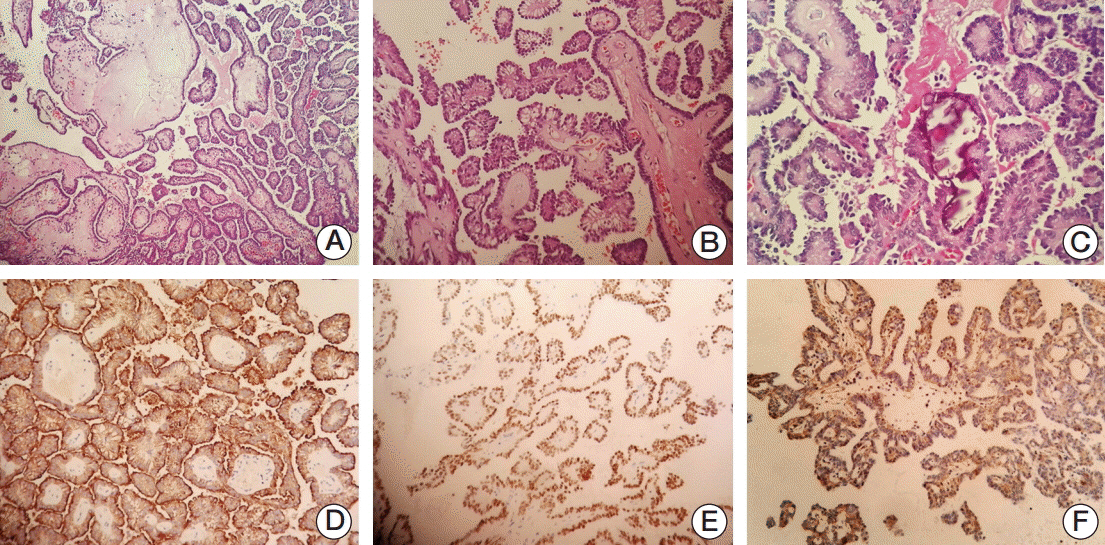
Histopathological analysis revealed florid proliferation of papillary structures lined by columnar epithelial cells with fibrovascular cores. Immunohistochemically, the neoplastic cells were positive for CKpan, CK7, TTF-1, vimentin, and EMA, but negative for thyroglobulin, CD15, S100, P40, CK20, CDX-2, and GFAP. The Ki-67-labeling index reached 5% in the most concentrated spot. In situ hybridization for EBV was negative.
CONCLUSION
Due to the distinct rarity of low-grade thyroid-like papillary adenocarcinomaswith a favorable clinical outcome, a nationwide effort to raise public awareness of this neoplasm is required.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma, Papillary*
Adolescent
Asian Continental Ancestry Group
Epithelial Cells
Female
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein
Herpesvirus 4, Human
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
In Situ Hybridization
Keratins
Mucin-1
Nasopharynx
RNA
Thyroglobulin
Thyroid Gland
Transcription Factors
Vimentin
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein
Keratins
Mucin-1
RNA
Thyroglobulin
Transcription Factors
Vimentin
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. He JH, Zong YS, Luo RZ, Liang XM, Wu QL, Liang YJ. Clinicopathological characteristics of primary nasopharyngeal adenocarcinoma. Ai Zheng. 2003; 22:753–7.2. McGuire LJ, Lee JC. The histopathologic diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ear Nose Throat J. 1990; 69:229–36.3. Carrizo F, Luna MA. Thyroid transcription factor-1 expression in thyroid-like nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma: report of 2 cases. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2005; 9:189–92.
Article4. Wu PY, Huang CC, Chen HK, Chien CY. Adult thyroid-like low-grade nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma with thyroid transcription factor-1 expression. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 137:837–8.
Article5. Fu CH, Chang KP, Ueng SH, Wu CC, Hao SP. Primary thyroid-like papillary adenocarcinoma of the nasopharynx. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2008; 35:579–82.
Article6. Bansal A, Pradeep KE, Gumparthy KP. An unusual case of low-grade tubulopapillary adenocarcinoma of the sinonasal tract. World J Surg Oncol. 2008; 6:54.
Article7. Ohe C, Sakaida N, Tadokoro C, Fukui H, Asako M, Tomoda K, et al. Thyroid-like low-grade nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma: report of two cases. Pathol Int. 2010; 60:107–11.
Article8. Sillings CN, Weathers DR, Delgaudio JM. Thyroid-like papillary adenocarcinoma of the nasopharynx: a case report in a 19-year-old male. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010; 110:e25.
Article9. Petersson F, Pang B, Loke D, Hao L, Yan B. Biphasic low-grade nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma with a prominent spindle cell component: report of a case localized to the posterior nasal septum. Head Neck Pathol. 2011; 5:306–13.
Article10. Huang CH, Chang YL, Wang CP, Wu HP. Positive immunostaining of thyroid transcription factor-1 in primary nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma. J Formos Med Assoc. 2015; 114:473–4.
Article11. Ozer S, Kayahan B, Cabbarzade C, Bugdayci M, Kosemehmetoglu K, Yucel OT. Thyroid-like papillary adenocarcinoma of the nasopharynx with focal thyroglobulin expression. Pathology. 2013; 45:622–4.
Article12. Oishi N, Kondo T, Nakazawa T, Mochizuki K, Kasai K, Inoue T, et al. Thyroid-like low-grade nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma: case report and literature review. Pathol Res Pract. 2014; 210:1142–5.
Article13. Ozturk K, Midilli R, Veral A, Ertan Y, Karci B. Primary thyroid-like papillary adenocarcinoma of the nasal septum: a case report. Ear Nose Throat J. 2015; 94:E19–21.
Article14. Wu R, Liu H. Clinicopathological features of low-grade nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2014; 43:613–7.15. Zhang X, Xu X, Qian K, Liu Y, Wang L, Li M, et al. Low-grade thyroid-like papillary of the nasopharynx with squamous differentiation: report of a case. Lin Chuang Yu Shi Yan Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2015; 31:1199–200.16. Kang Z, Ou Y, Yao L, Qu L, Zheng Z, Yu Y. Low-grade nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma: report of two cases and literature review. Lin Chuang Yu Shi Yan Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2015; 31:1165–7.17. Li JF, Ye Q, Hong B, Gao X, Xu KL. Thyroid-like low-grade nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma: report of a case. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2011; 40:638–9.18. Han S, Yang F, Yuan C, Zhang R. Clinicopathological observation of 1 cases of low grade nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma. Lin Chuang Yu Shi Yan Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2013; 29:328–30.19. Chen Z, Zhuo M, Zheng X. Thyroid-like low-grade nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma: one case report. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014; 28:1266–7.20. Wenig BM, Hyams VJ, Heffner DK. Nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma: a clinicopathologic study of a low-grade carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988; 12:946–53.21. Thompson L. World Health Organization classification of tumours: pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours. Ear Nose Throat J. 2006; 85:74.
Article22. Bingle CD. Thyroid transcription factor-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997; 29:1471–3.
Article23. Katoh R, Kawaoi A, Miyagi E, Li X, Suzuki K, Nakamura Y, et al. Thyroid transcription factor-1 in normal, hyperplastic, and neoplastic follicular thyroid cells examined by immunohistochemistry and nonradioactive in situ hybridization. Mod Pathol. 2000; 13:570–6.
Article24. Ordonez NG. Value of thyroid transcription factor-1 immunostaining in tumor diagnosis: a review and update. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2012; 20:429–44.25. Imamura Y. CD15 (C3D-1) immunoreactivity in normal, benign and malignant thyroid lesions. Appl Immunohistochem. 1998; 6:181–6.
Article26. Ortiz-Rey JA, Alvarez C, San Miguel P, Iglesias B, Anton I. Expression of CDX2, cytokeratins 7 and 20 in sinonasal intestinal-type adenocarcinoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2005; 13:142–6.
Article27. Wang CP, Chang YL, Chen CT, Yang TH, Lou PJ. Photodynamic therapy with topical 5-aminolevulinic acid as a post-operative adjuvant therapy for an incompletely resected primary nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma: a case report. Lasers Surg Med. 2006; 38:435–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Low-grade Papillary Adenocarcinoma of the Nasopharynx
- A Case of Nasopharyngeal Papillary Adenocarcinoma: Nasal Endoscopic Approach
- Exclusive Endoscopic Resection of Nasopharyngeal Papillary Adenocarcinoma via Combined Transnasal and Transoral Approach
- A Case of Thyroid Hemiagenesis with Papillary Adenocarcinoma
- Papillary Adenocarcinoma