Restor Dent Endod.
2017 Feb;42(1):1-8. 10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.1.
Effect of adhesive luting on the fracture resistance of zirconia compared to that of composite resin and lithium disilicate glass ceramic
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea. lkw@jbnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2367315
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.1
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of adhesive luting on the fracture resistance of zirconia compared to that of a composite resin and a lithium disilicate glass ceramic.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
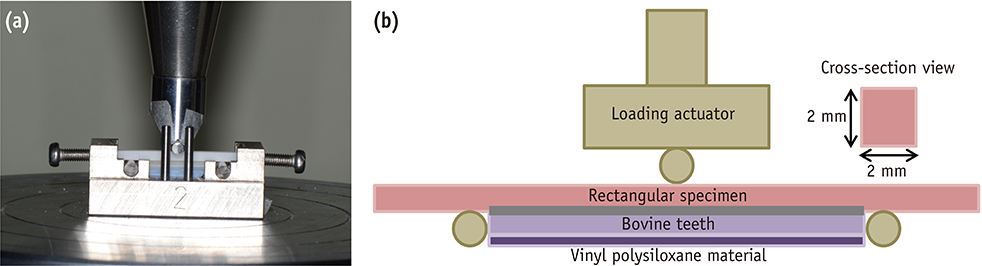
The specimens (dimension: 2 mm × 2 mm × 25 mm) of the composite resin, lithium disilicate glass ceramic, and yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP) were prepared. These were then divided into nine groups: three non-luting groups, three non-adhesive luting groups, and three adhesive luting groups, for each restorative material. In the non-luting groups, specimens were placed on the bovine tooth without any luting agents. In the non-adhesive luting groups, only zinc phosphate cement was used for luting the specimen to the bovine tooth. In the adhesive luting groups, specimens were pretreated, and the adhesive luting procedure was performed using a self-adhesive resin cement. For all the groups, a flexural test was performed using universal testing machine, in which the fracture resistance was measured by recording the force at which the specimen was fractured.
RESULTS
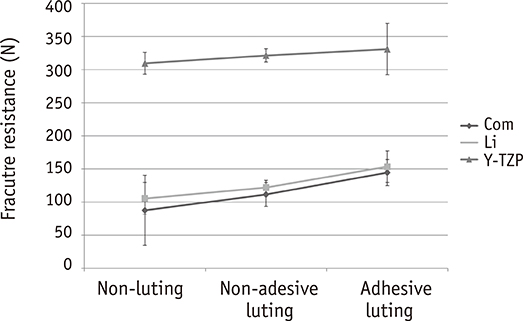
The fracture resistance after adhesive luting increased by approximately 29% in the case of the composite resin, 26% in the case of the lithium disilicate glass ceramic, and only 2% in the case of Y-TZP as compared to non-adhesive luting.
CONCLUSIONS
The fracture resistance of Y-TZP did not increased significantly after adhesive luting as compared to that of the composite resin and the lithium disilicate glass ceramic.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Piconi C, Maccauro G. Zirconia as a ceramic biomaterial. Biomaterials. 1999; 20:1–25.
Article2. Swain MV. Limitation of maximum strength of zirconia-toughened ceramics by transformation toughening increment. J Am Ceram Soc. 1985; 68:C97–C99.
Article3. Chevalier J, Olagnon C, Fantozzi G, Galès B. Crack propagation behavior of Y‐TZP ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc. 1995; 78:1889–1894.
Article4. Guazzato M, Albakry M, Ringer SP, Swain MV. Strength, fracture toughness and microstructure of a selection of all-ceramic materials. Part II. Zirconia-based dental ceramics. Dent Mater. 2004; 20:449–456.
Article5. Memarpour M, Mesbahi M, Rezvani G, Rahimi M. Microleakage of adhesive and nonadhesive luting cements for stainless steel crowns. Pediatr Dent. 2011; 33:501–504.6. Hill EE. Dental cements for definitive luting: a review and practical clinical considerations. Dent Clin North Am. 2007; 51:643–658.
Article7. de la Macorra JC, Pradíes G. Conventional and adhesive luting cements. Clin Oral Investig. 2002; 6:198–204.
Article8. Manhart J, Scheibenbogen-Fuchsbrunner A, Chen HY, Hickel R. A 2-year clinical study of composite and ceramic inlays. Clin Oral Investig. 2000; 4:192–198.
Article9. Peumans M, Van Meerbeek B, Lambrechts P, Vanherle G. Porcelain veneers: a review of the literature. J Dent. 2000; 28:163–177.
Article10. Platt JA. Resin cements: into the 21st century. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 1999; 20:1173–1182.11. Mak YF, Lai SC, Cheung GS, Chan AW, Tay FR, Pashley DH. Micro-tensile bond testing of resin cements to dentin and an indirect resin composite. Dent Mater. 2002; 18:609–621.
Article12. Scherrer SS, de Rijk WG, Belser UC, Meyer JM. Effect of cement film thickness on the fracture resistance of a machinable glass-ceramic. Dent Mater. 1994; 10:172–177.
Article13. Burke FJ, Wilson NH, Watts DC. Fracture resistance of teeth restored with indirect composite resins: the effect of alternative luting procedures. Quintessence Int. 1994; 25:269–275.14. Burke FJ. The effect of variations in bonding procedure on fracture resistance of dentin-bonded all-ceramic crowns. Quintessence Int. 1995; 26:293–300.15. Dérand P, Dérand T. Bond strength of luting cements to zirconium oxide ceramics. Int J Prosthodont. 2000; 13:131–135.16. Wegner SM, Kern M. Long-term resin bond strength to zirconia ceramic. J Adhes Dent. 2000; 2:139–147.17. Valandro LF, Ozcan M, Amaral R, Leite FP, Bottino MA. Microtensile bond strength of a resin cement to silica-coated and silanized In-Ceram Zirconia before and after aging. Int J Prosthodont. 2007; 20:70–72.18. Chen L, Suh BI, Kim J, Tay FR. Evaluation of silica-coating techniques for zirconia bonding. Am J Dent. 2011; 24:79–84.19. Atsu SS, Kilicarslan MA, Kucukesmen HC, Aka PS. Effect of zirconium-oxide ceramic surface treatments on the bond strength to adhesive resin. J Prosthet Dent. 2006; 95:430–436.
Article20. Ozcan M, Alkumru HN, Gemalmaz D. The effect of surface treatment on the shear bond strength of luting cement to a glass-infiltrated alumina ceramic. Int J Prosthodont. 2001; 14:335–339.21. Ozcan M, Vallittu PK. Effect of surface conditioning methods on the bond strength of luting cement to ceramics. Dent Mater. 2003; 19:725–731.
Article22. Tanaka R, Fujishima A, Shibata Y, Manabe A, Miyazaki T. Cooperation of phosphate monomer and silica modification on zirconia. J Dent Res. 2008; 87:666–670.
Article23. Rüttermann S, Fries L, Raab WH, Janda R. The effect of different bonding techniques on ceramic/resin shear bond strength. J Adhes Dent. 2008; 10:197–203.24. Piwowarczyk A, Lauer HC, Sorensen JA. The shear bond strength between luting cements and zirconia ceramics after two pre-treatments. Oper Dent. 2005; 30:382–388.25. Furukawa K, Inai N, Tagami J. The effects of luting resin bond to dentin on the strength of dentin supported by indirect resin composite. Dent Mater. 2002; 18:136–142.
Article26. Swain MV, Garvie RC, Hannink RHJ. Influence of thermal decomposition on the mechanical properties of magnesia‐stabilized cubic zirconia. J Am Ceram Soc. 1983; 66:358–362.
Article27. Masaki T. Mechanical properties of toughened ZrO2‐Y2O3 ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc. 1986; 69:638–640.28. Lehmann F, Kern M. Durability of resin bonding to zirconia ceramic using different primers. J Adhes Dent. 2009; 11:479–483.29. Kitayama S, Nikaido T, Takahashi R, Zhu L, Ikeda M, Foxton RM, Sadr A, Tagami J. Effect of primer treatment on bonding of resin cements to zirconia ceramic. Dent Mater. 2010; 26:426–432.
Article30. Ozcan M, Nijhuis H, Valandro LF. Effect of various surface conditioning methods on the adhesion of dualcure resin cement with MDP functional monomer to zirconia after thermal aging. Dent Mater J. 2008; 27:99–104.
Article31. Kern M, Barloi A, Yang B. Surface conditioning influences zirconia ceramic bonding. J Dent Res. 2009; 88:817–822.
Article32. Kern M, Wegner SM. Bonding to zirconia ceramic: adhesion methods and their durability. Dent Mater. 1998; 14:64–71.
Article33. Yoshida K, Tsuo Y, Atsuta M. Bonding of dual‐cured resin cement to zirconia ceramic using phosphate acid ester monomer and zirconate coupler. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2006; 77:28–33.
Article34. Ernst CP, Cohnen U, Stender E, Willershausen B. In vitro retentive strength of zirconium oxide ceramic crowns using different luting agents. J Prosthet Dent. 2005; 93:551–558.
Article35. Kumbuloglu O, Lassila LV, User A, Vallittu PK. Bonding of resin composite luting cements to zirconium oxide by two air-particle abrasion methods. Oper Dent. 2006; 31:248–255.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of marginal fit of 2 CAD-CAM anatomic contour zirconia crown systems and lithium disilicate glass-ceramic crown
- The effect of silane applied to glass ceramics on surface structure and bonding strength at different temperatures
- Comparison of the translucency of shaded zirconia all-ceramic systems
- Physical properties of different self-adhesive resin cements and their shear bond strength on lithium disilicate ceramic and dentin
- Effect of core design on fracture resistance of zirconia-lithium disilicate anterior bilayered crowns