J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Mar;32(3):415-420. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.3.415.
Analysis of Fifty Hotspot Mutations of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Never-smokers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. mdyspark@gmail.com
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Macrogen Inc., Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2366636
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.3.415
Abstract
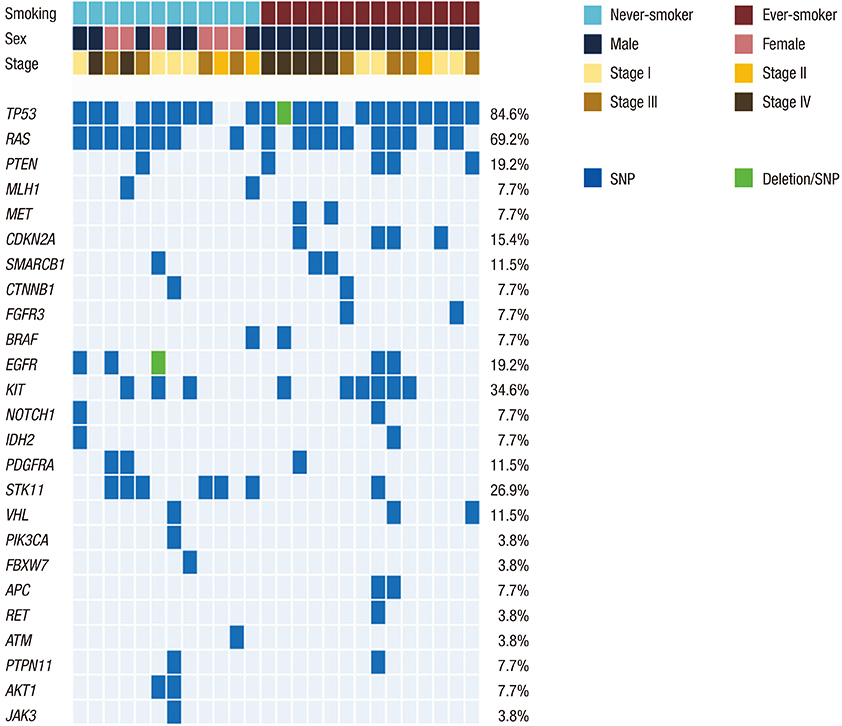
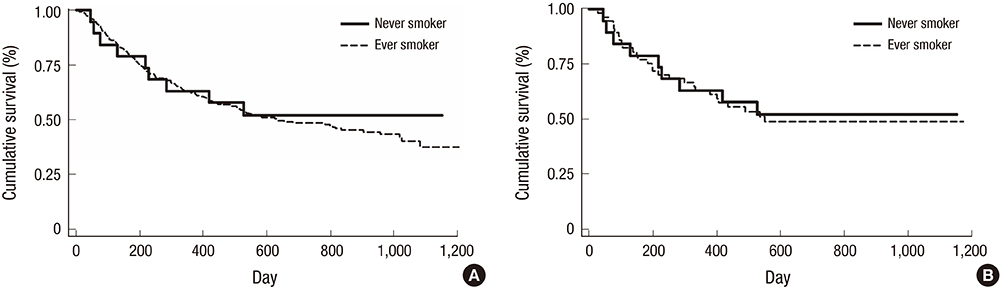
- Smoking is the major risk factor for lung squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), although a small number of lung SCCs occurs in never-smokers. The purpose of this study was to compare 50 hotspot mutations of lung SCCs between never-smokers and smokers. We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of patients newly diagnosed with lung SCC between January 1, 2011 and December 31, 2013 in the Seoul National University Hospital. Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor samples were used for analysis of hotspot mutations. Fifty cancer-related genes in never-smokers were compared to those in ever-smokers. Of 379 lung SCC patients, 19 (5.0%) were never-smokers. The median age of these 19 patients was 67 years (interquartile range 57-73 years), and 10 of these patients were women (52.5%). The incidence rates of stage I, II, III, and IV disease in this group were 26.4%, 5.3%, 31.6%, and 36.8%, respectively, and sequencing was performed successfully in 14 cases. In the 26 lung SCC tumor samples (12 from never-smokers and 14 from ever-smokers) sequenced using personal genome machine, the most common mutations were in TP53 (75.0%), RAS (66.7%), and STK11 (33.3%), but mutations were also found in EGFR, KIT, and PTEN. The distribution of hotspot mutations in never-smokers was similar to that in ever-smokers. There was no significant difference in overall survival between the 2 groups. The 50 hotspot mutations of lung SCC in never-smokers were similar to those of ever-smokers.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:69–90.2. Pfeifer GP, Denissenko MF, Olivier M, Tretyakova N, Hecht SS, Hainaut P. Tobacco smoke carcinogens, DNA damage and p53 mutations in smoking-associated cancers. Oncogene. 2002; 21:7435–7451.3. Gibbons DL, Byers LA, Kurie JM. Smoking, p53 mutation, and lung cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2014; 12:3–13.4. Kenfield SA, Wei EK, Stampfer MJ, Rosner BA, Colditz GA. Comparison of aspects of smoking among the four histological types of lung cancer. Tob Control. 2008; 17:198–204.5. Okazaki I, Ishikawa S, Sohara Y. Genes associated with succeptibility to lung adenocarcinoma among never smokers suggest the mechanism of disease. Anticancer Res. 2014; 34:5229–5240.6. Le Calvez F, Mukeria A, Hunt JD, Kelm O, Hung RJ, Tanière P, Brennan P, Boffetta P, Zaridze DG, Hainaut P. TP53 and KRAS mutation load and types in lung cancers in relation to tobacco smoke: distinct patterns in never, former, and current smokers. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:5076–5083.7. Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature. 2012; 489:519–525.8. Singh RR, Patel KP, Routbort MJ, Reddy NG, Barkoh BA, Handal B, Kanagal-Shamanna R, Greaves WO, Medeiros LJ, Aldape KD, et al. Clinical validation of a next-generation sequencing screen for mutational hotspots in 46 cancer-related genes. J Mol Diagn. 2013; 15:607–622.9. Cooper WA, Lam DC, O’Toole SA, Minna JD. Molecular biology of lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 2013; 5:Suppl 5. S479–90.10. Weiss J, Sos ML, Seidel D, Peifer M, Zander T, Heuckmann JM, Ullrich RT, Menon R, Maier S, Soltermann A, et al. Frequent and focal FGFR1 amplification associates with therapeutically tractable FGFR1 dependency in squamous cell lung cancer. Sci Transl Med. 2010; 2:62ra93.11. Kim Y, Hammerman PS, Kim J, Yoon JA, Lee Y, Sun JM, Wilkerson MD, Pedamallu CS, Cibulskis K, Yoo YK, et al. Integrative and comparative genomic analysis of lung squamous cell carcinomas in East Asian patients. J Clin Oncol. 2014; 32:121–128.12. Govindan R, Ding L, Griffith M, Subramanian J, Dees ND, Kanchi KL, Maher CA, Fulton R, Fulton L, Wallis J, et al. Genomic landscape of non-small cell lung cancer in smokers and never-smokers. Cell. 2012; 150:1121–1134.13. Lee SM, Lee WK, Kim DS, Park JY. Quantitative promoter hypermethylation analysis of RASSF1A in lung cancer: comparison with methylation-specific PCR technique and clinical significance. Mol Med Rep. 2012; 5:239–244.14. Seo AN, Jin Y, Lee HJ, Sun PL, Kim H, Jheon S, Kim K, Lee CT, Chung JH. FGFR1 amplification is associated with poor prognosis and smoking in non-small-cell lung cancer. Virchows Arch. 2014; 465:547–558.15. Scesnaite A, Jarmalaite S, Mutanen P, Anttila S, Nyberg F, Benhamou S, Boffetta P, Husgafvel-Pursiainen K. Similar DNA methylation pattern in lung tumours from smokers and never-smokers with second-hand tobacco smoke exposure. Mutagenesis. 2012; 27:423–429.16. Kawaguchi T, Takada M, Kubo A, Matsumura A, Fukai S, Tamura A, Saito R, Kawahara M, Maruyama Y. Gender, histology, and time of diagnosis are important factors for prognosis: analysis of 1499 never-smokers with advanced non-small cell lung cancer in Japan. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:1011–1017.17. Kawaguchi T, Takada M, Kubo A, Matsumura A, Fukai S, Tamura A, Saito R, Maruyama Y, Kawahara M, Ignatius Ou SH. Performance status and smoking status are independent favorable prognostic factors for survival in non-small cell lung cancer: a comprehensive analysis of 26,957 patients with NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:620–630.18. Yun YH, Lim MK, Jung KW, Bae JM, Park SM, Shin SA, Lee JS, Park JG. Relative and absolute risks of cigarette smoking on major histologic types of lung cancer in Korean men. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005; 14:2125–2130.19. Scarpa A, Sikora K, Fassan M, Rachiglio AM, Cappellesso R, Antonello D, Amato E, Mafficini A, Lambiase M, Esposito C, et al. Molecular typing of lung adenocarcinoma on cytological samples using a multigene next generation sequencing panel. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e80478.20. Kim HS, Sung JS, Yang SJ, Kwon NJ, Jin L, Kim ST, Park KH, Shin SW, Kim HK, Kang JH, et al. Predictive efficacy of low burden EGFR mutation detected by next-generation sequencing on response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e81975.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multiple primary lung cancer: Synchronous small cell lung carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma
- Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations and the Clinical Outcome in Male Smokers with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Lung
- Druggable Targets of Squamous Cell Lung Cancer
- Histopathologic Findings, and p53 and K-ras Mutational Analysis in Biopsy Specimens Using Fluorescence Bronchoscopy
- The National Survey of Lung Cancer in Korea