Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2016 Dec;20(4):231-240. 10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.231.
Clinical Utility of Liver Stiffness Measurements on Magnetic Resonance Elastrography in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Radiofrequency Ablation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. jmlshy2000@gmail.com
- KMID: 2366405
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.231
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To determine whether liver stiffness (LS) measured by magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) can predict the outcome of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 107 patients with Child-Pugh class A liver function who were treated with RFA for single HCC and who had undergone a gradient-echo MRE within 6 months before RFA were included. We evaluated the relationship between the LS values and the ablation volume, local tumor progression (LTP), and intrahepatic distant recurrence (IDR). We also constructed receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves to examine the role of LS in predicting liver function deterioration, which was defined as an increase of Child-Pugh score by one point or more at 1 year after RFA.
RESULTS
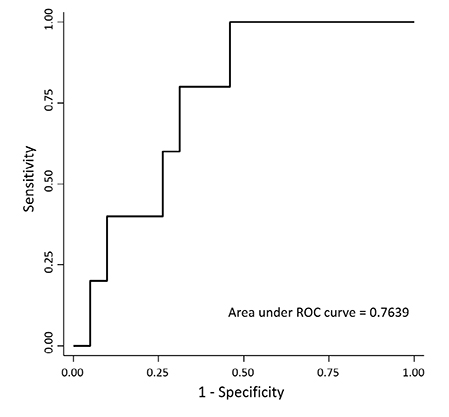
There was no significant correlation between LS and ablation volume, and neither time to LTP nor IDR was associated with LS. Among the 66 patients who did not have recurrence 1 year after RFA, 5 patients (7.6%) developed liver function deterioration. A high LS value was significantly associated with development of liver function deterioration after RFA and the area under the ROC curve was 0.764 (95% CI 0.598-0.929, P = 0.003).
CONCLUSION
LS measured by MRE could not predict ablation volume and tumor recurrence. However, high LS values were significantly associated with development of liver function deterioration.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. El-Serag HB. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2012; 142:1264–1273. e12612. Raza A, Sood GK. Hepatocellular carcinoma review: current treatment, and evidence-based medicine. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:4115–4127.3. European Association For The Study Of The Liver. European Organisation For Research And Treatment Of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012; 56:908–943.4. Bruix J, Sherman M. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011; 53:1020–1022.5. Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012; 379:1245–1255.6. Cho YK, Kim JK, Kim WT, Chung JW. Hepatic resection versus radiofrequency ablation for very early stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a Markov model analysis. Hepatology. 2010; 51:1284–1290.7. Cucchetti A, Piscaglia F, Cescon M, et al. Cost-effectiveness of hepatic resection versus percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2013; 59:300–307.8. Clasen S, Schmidt D, Boss A, et al. Multipolar radiofrequency ablation with internally cooled electrodes: experimental study in ex vivo bovine liver with mathematic modeling. Radiology. 2006; 238:881–890.9. Ahmed M, Liu Z, Humphries S, Goldberg SN. Computer modeling of the combined effects of perfusion, electrical conductivity, and thermal conductivity on tissue heating patterns in radiofrequency tumor ablation. Int J Hyperthermia. 2008; 24:577–588.10. Bosch J, Garcia-Pagan JC. Complications of cirrhosis. I. Portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2000; 32:141–156.11. Liu Z, Ahmed M, Sabir A, Humphries S, Goldberg SN. Computer modeling of the effect of perfusion on heating patterns in radiofrequency tumor ablation. Int J Hyperthermia. 2007; 23:49–58.12. Ahmed M, Brace CL, Lee FT Jr, Goldberg SN. Principles of and advances in percutaneous ablation. Radiology. 2011; 258:351–336.13. Kim JW, Shin SS, Heo SH, et al. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: how we do it safely and completely. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16:1226–1239.14. Tu R, Xia LP, Yu AL, Wu L. Assessment of hepatic functional reserve by cirrhosis grading and liver volume measurement using CT. World J Gastroenterol. 2007; 13:3956–3961.15. Lu LG, Zeng MD, Wan MB, et al. Grading and staging of hepatic fibrosis, and its relationship with noninvasive diagnostic parameters. World J Gastroenterol. 2003; 9:2574–2578.16. Tsochatzis EA, Gurusamy KS, Ntaoula S, Cholongitas E, Davidson BR, Burroughs AK. Elastography for the diagnosis of severity of fibrosis in chronic liver disease: a meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. J Hepatol. 2011; 54:650–659.17. Chang W, Lee JM, Yoon JH, et al. Liver fibrosis staging with MR elastography: comparison of diagnostic performance between patients with chronic hepatitis B and those with other etiologic causes. Radiology. 2016; 280:88–97.18. Maurice JB, Brodkin E, Arnold F, et al. Validation of the Baveno VI criteria to identify low risk cirrhotic patients not requiring endoscopic surveillance for varices. J Hepatol. 2016; 65:899–905.19. Augustin S, Pons M, Genesca J. Ruling in and ruling out with elastography in compensated advanced chronic liver disease. Gut. 2017; 66:197–198.20. Shin SU, Lee JM, Yu MH, et al. Prediction of esophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis: usefulness of three-dimensional MR elastography with echo-planar imaging technique. Radiology. 2014; 272:143–153.21. Yoon JH, Lee JM, Joo I, et al. Hepatic fibrosis: prospective comparison of MR elastography and US shear-wave elastography for evaluation. Radiology. 2014; 273:772–782.22. Huber A, Ebner L, Heverhagen JT, Christe A. State-of-the-art imaging of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis: a comprehensive review of current applications and future perspectives. Eur J Radiol Open. 2015; 2:90–100.23. Venkatesh SK, Ehman RL. Magnetic resonance elastography of liver. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2014; 22:433–446.24. Mitchell DG, Bruix J, Sherman M, Sirlin CB. LI-RADS (Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System): summary, discussion, and consensus of the LI-RADS Management Working Group and future directions. Hepatology. 2015; 61:1056–1065.25. Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Sou H, et al. Effects of gadoxetic acid on liver elasticity measurement by using magnetic resonance elastography. Magn Reson Imaging. 2012; 30:128–132.26. Huwart L, Peeters F, Sinkus R, et al. Liver fibrosis: non-invasive assessment with MR elastography. NMR Biomed. 2006; 19:173–179.27. Manduca A, Oliphant TE, Dresner MA, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography: non-invasive mapping of tissue elasticity. Med Image Anal. 2001; 5:237–254.28. Silva AM, Grimm RC, Glaser KJ, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography: evaluation of new inversion algorithm and quantitative analysis method. Abdom Imaging. 2015; 40:810–817.29. Nedredal GI, Yin M, McKenzie T, et al. Portal hypertension correlates with splenic stiffness as measured with MR elastography. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011; 34:79–87.30. Woo S, Lee JM, Yoon JH, et al. Small- and medium-sized hepatocellular carcinomas: monopolar radiofrequency ablation with a multiple-electrode switching system-mid-term results. Radiology. 2013; 268:589–600.31. Lu DS, Raman SS, Limanond P, et al. Influence of large peritumoral vessels on outcome of radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003; 14:1267–1274.32. Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF, et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. Radiology. 2005; 235:728–739.33. Wright AS, Sampson LA, Warner TF, Mahvi DM, Lee FT Jr. Radiofrequency versus microwave ablation in a hepatic porcine model. Radiology. 2005; 236:132–139.34. Lee HS, Park SY, Kim SK, et al. Thrombocytopenia represents a risk for deterioration of liver function after radiofrequency ablation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2012; 18:302–308.35. Kuroda H, Kasai K, Kakisaka K, et al. Changes in liver function parameters after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 2010; 40:550–554.36. Ishikawa M, Yogita S, Miyake H, et al. Clarification of risk factors for hepatectomy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002; 49:1625–1631.37. Farges O, Malassagne B, Flejou JF, Balzan S, Sauvanet A, Belghiti J. Risk of major liver resection in patients with underlying chronic liver disease: a reappraisal. Ann Surg. 1999; 229:210–215.38. Bensamoun SF, Wang L, Robert L, Charleux F, Latrive JP, Ho Ba. Measurement of liver stiffness with two imaging techniques: magnetic resonance elastography and ultrasound elastometry. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008; 28:1287–1292.39. Sun HY, Lee JM, Han JK, Choi BI. Usefulness of MR elastography for predicting esophageal varices in cirrhotic patients. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014; 39:559–566.40. Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Mueller PR. Thermal ablation therapy for focal malignancy: a unified approach to underlying principles, techniques, and diagnostic imaging guidance. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000; 174:323–331.41. Moreno AH, Burchell AR, Rousselot LM, Panke WF, Slafsky F, Burke JH. Portal blood flow in cirrhosis of the liver. J Clin Invest. 1967; 46:436–445.42. Zurbuchen U, Holmer C, Lehmann KS, et al. Determination of the temperature-dependent electric conductivity of liver tissue ex vivo and in vivo: Importance for therapy planning for the radiofrequency ablation of liver tumours. Int J Hyperthermia. 2010; 26:26–33.43. Tung-Ping Poon R, Fan ST, Wong J. Risk factors, prevention, and management of postoperative recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 2000; 232:10–24.44. Ng IO, Lai EC, Fan ST, Ng MM, So MK. Prognostic significance of pathologic features of hepatocellular carcinoma. A multivariate analysis of 278 patients. Cancer. 1995; 76:2443–2448.45. Wu JC, Huang YH, Chau GY, et al. Risk factors for early and late recurrence in hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2009; 51:890–897.46. Poon RT, Fan ST, Ng IO, Lo CM, Liu CL, Wong J. Different risk factors and prognosis for early and late intrahepatic recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2000; 89:500–507.47. Fernandez M, Trepo E, Degre D, et al. Transient elastography using Fibroscan is the most reliable non-invasive method for the diagnosis of advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis in alcoholic liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 27:1074–1079.48. Kim SU, Han KH, Ahn SH. Transient elastography in chronic hepatitis B: an Asian perspective. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:5173–5180.49. Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Amemiya F, et al. Cross-validation of MR elastography and ultrasound transient elastography in liver stiffness measurement: discrepancy in the results of cirrhotic liver. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012; 35:607–610.50. Oudry J, Chen J, Glaser KJ, Miette V, Sandrin L, Ehman RL. Cross-validation of magnetic resonance elastography and ultrasound-based transient elastography: a preliminary phantom study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009; 30:1145–1150.51. Sturm N, Marlu A, Arvers P, Zarski JP, Leroy V. Comparative assessment of liver fibrosis by computerized morphometry in naive patients with chronic hepatitis B and C. Liver Int. 2013; 33:428–438.52. Pinzani M, Rombouts K, Colagrande S. Fibrosis in chronic liver diseases: diagnosis and management. J Hepatol. 2005; 42:Suppl. S22–S36.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Completely Ablated Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Percutaneous Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation
- Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinomas
- Microwave thermosphere versus radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Are we approaching the time to end the debate?
- The Role of Combination of Transarterial Chemoebolization and Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment
- Chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation is the best option for the local treatment of early hepatocellular carcinoma?