Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2015 Mar;7(2):195-198. 10.4168/aair.2015.7.2.195.
An IgE-Mediated Allergic Reaction Caused by Mulberry Fruit
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. gyhur@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2365549
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.2.195
Abstract
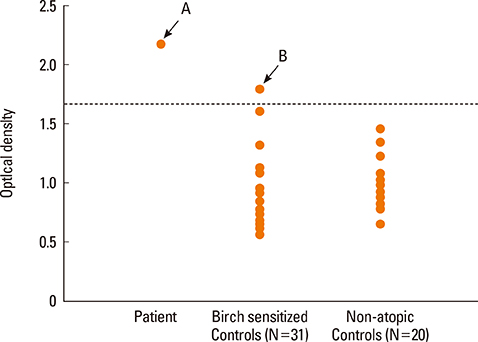
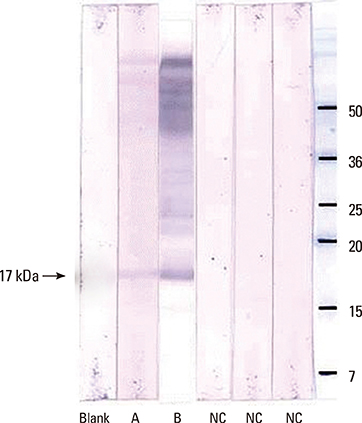
- Mulberry (Morus spp.) is a widespread deciduous tree and its fruit is commonly eaten in Korea and eastern Asia. Some reports demonstrate that mulberry fruit is a food allergen in the Mediterranean area. However, there has been no report of systemic allergic reactions after ingesting mulberry fruit in Korea. An 18-year-old boy with a mulberry fruit allergy visited our allergy clinic. He had experienced generalized urticaria, chest tightness, breathing difficulty, and abdominal cramping after ingesting mulberry fruit. The patient had a positive skin reaction to mulberry fruit extract (mean wheal size, 5 mm). We performed an ELISA to detect specific IgE antibody (Ab) to mulberry fruit extract in the patient's serum compared to those of non-atopic healthy controls and birch-sensitized individuals. Specific IgE Ab to mulberry fruit extract was detected in the patient's serum, as compared to non-atopic healthy controls. Another subject, who was strongly sensitized to birch pollen, also had a positive serum-specific IgE Ab to mulberry fruit. We performed IgE immunoblot analysis using the patient's and the other subject's sera, who had serum-specific IgE to mulberry fruit, to identify the IgE-binding component. An identical IgE-binding component to mulberry extract was detected in the two subjects at around 17 kDa, and which might be PR 10 of Bet v 1. In conclusion, mulberry fruit could induce a systemic allergic reaction through an IgE-mediated mechanism, and cross-reactivity might occur between mulberry fruit and birch pollen.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sneller MR, Hayes HD, Pinnas JL. Pollen changes during five decades of urbanization in Tucson, Arizona. Ann Allergy. 1993; 71:519–524.2. Subiza J, Jerez M, Jiménez JA, Narganes MJ, Cabrera M, Varela S, Subiza E. Allergenic pollen pollinosis in Madrid. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995; 96:15–23.3. Kosisky SE, Marks MS, Nelson MR. Pollen aeroallergens in the Washington, DC, metropolitan area: a 10-year volumetric survey (1998-2007). Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010; 104:223–235.4. Muñoz FJ, Delgado J, Palma JL, Giménez MJ, Monteseirín FJ, Conde J. Airborne contact urticaria due to mulberry (Morus alba) pollen. Contact Dermatitis. 1995; 32:61.5. Wüthrich B, Borga A, Yman L. Oral allergy syndrome to a jackfruit (Artocarpus integrifolia). Allergy. 1997; 52:428–431.6. Johansson SG, Bieber T, Dahl R, Friedmann PS, Lanier BQ, Lockey RF, Motala C, Ortega Martell JA, Platts-Mills TA, Ring J, Thien F, Van Cauwenberge P, Williams HC. Revised nomenclature for allergy for global use: report of the Nomenclature Review Committee of the World Allergy Organization, October 2003. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:832–836.7. Robison RG, Pongracic JA. Chapter 23: food allergy. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012; 33:Suppl 1. S77–S79.8. Ahn K, Kim J, Hahm MI, Lee SY, Kim WK, Chae Y, Park YM, Han MY, Lee KJ, Kim JK, Yang ES, Kwon HJ. Prevalence of immediate-type food allergy in Korean schoolchildren: a population-based study. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012; 33:481–487.9. Zuidmeer L, Goldhahn K, Rona RJ, Gislason D, Madsen C, Summers C, Sodergren E, Dahlstrom J, Lindner T, Sigurdardottir ST, McBride D, Keil T. The prevalence of plant food allergies: a systematic review. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:1210–1218.e4.10. Hauser M, Roulias A, Ferreira F, Egger M. Panallergens and their impact on the allergic patient. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2010; 6:1.11. van Loon LC, van Strien EA. The families of pathogenesis-related proteins, their activities, and comparative analysis of PR-1 type proteins. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol. 1999; 55:85–97.12. Midoro-Horiuti T, Brooks EG, Goldblum RM. Pathogenesis-related proteins of plants as allergens. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001; 87:261–271.13. Hemmer W, Focke M, Marzban G, Swoboda I, Jarisch R, Laimer M. Identification of Bet v 1-related allergens in fig and other Moraceae fruits. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010; 40:679–687.14. Valenta R, Duchene M, Ebner C, Valent P, Sillaber C, Deviller P, Ferreira F, Tejkl M, Edelmann H, Kraft D, Scheiner O. Profilins constitute a novel family of functional plant pan-allergens. J Exp Med. 1992; 175:377–385.15. Asero R, Mistrello G, Roncarolo D, Amato S, Zanoni D, Barocci F, Caldironi G. Detection of clinical markers of sensitization to profilin in patients allergic to plant-derived foods. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 112:427–432.16. Zuidmeer L, van Ree R. Lipid transfer protein allergy: primary food allergy or pollen/food syndrome in some cases. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 7:269–273.17. Ciardiello MA, Palazzo P, Bernardi ML, Carratore V, Giangrieco I, Longo V, Melis M, Tamburrini M, Zennaro D, Mari A, Colombo P. Biochemical, immunological and clinical characterization of a cross-reactive nonspecific lipid transfer protein 1 from mulberry. Allergy. 2010; 65:597–605.18. Micheal S, Wangorsch A, Wolfheimer S, Foetisch K, Minhas K, Scheurer S, Ahmed A. Immunoglobulin E reactivity and allergenic potency of Morus papyrifera (paper mulberry) pollen. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2013; 23:168–175.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Food Allergy in Children
- The Diagnosis of Food Allergy in a Pediatric Gastroenterology: Focusing on Non-IgE-mediated Allergic Diseases
- A Case of Allergic Contact Dermatitis Caused by a Duoderm Extrathin? Dressing
- Antioxidant Effects and Improvement of Lipid Metabolism of Mulberry fruit, Mulberry Leaves and Silkworm Powder with Different Mixing Ratios in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- The Effects of Nonspecific IgE and IgG Antibodies on Basophil Histamine Release mediated by Specific IgE Antibodies