J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2016 Dec;42(6):379-382. 10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.6.379.
Lymphocytoma cutis: diagnostic enigma for the maxillofacial surgeon
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, KLE Viswanath Katti Institute of Dental Sciences, KLE University, Belagavi, India. arjun193@gmail.com
- 2Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, KLE Viswanath Katti Institute of Dental Sciences, KLE University, Belagavi, India.
- KMID: 2364007
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.6.379
Abstract
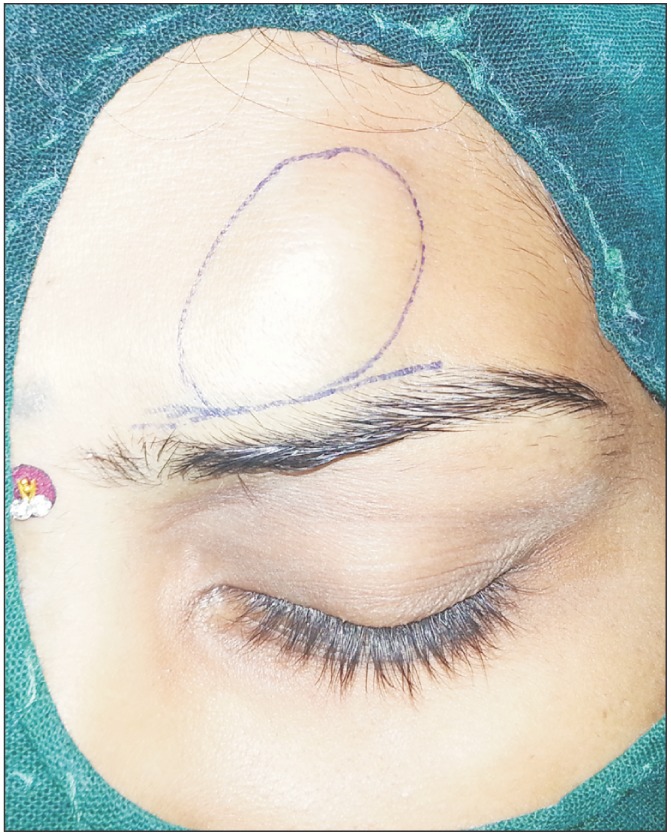
- Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia (CLH) is a cutaneous pseudolymphoma with a worldwide distribution, equally affecting all races and ethnic groups. Due to its vast array of characteristics, it is most often missed in the differential diagnosis of firm to soft lumps on the head and neck. A systematic approach to the workup and diagnosis along with treatment of such lesions is discussed in this article. A 20-year-old Asian Indian female presented to our Oral and Maxillofacial unit with a lump on the left side of her forehead for 1 month. Local examination revealed a 2.5×3.0 cm², well circumscribed swelling over the left para median region that was firm to doughy and non-tender. There was no other significant finding on general examination. Excisional biopsy of the lesion was performed, followed by histopathologic processing. The general etiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, differential diagnosis, clinical course, prognosis, treatment, and prevention have been discussed in line with the recent modalities of diagnosis and treatment of CLH. Due to the overlapping clinical and histological characteristics of CLH with many other lesions, it is important to consider this lesion in the differential diagnosis of cutaneous lesions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. McElroy MK, Kulidjian AA, Sumit R, Weidner N. Benign lymphoid hyperplasia (pseudolymphoma) of soft tissue. Hum Pathol. 2011; 42:1813–1818. PMID: 21663938.
Article2. Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;2008. p. 1407–1408.3. Salama S. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma and lymphoproliferative disorders of skin: current status of pathology and classification. Am J Clin Pathol. 2000; 114(Suppl 1):S104–S128. PMID: 11996165.4. Takeda H, Kaneko T, Harada K, Matsuzaki Y, Nakano H, Hanada K. Successful treatment of lymphadenosis benigna cutis with topical photodynamic therapy with delta-aminolevulinic acid. Dermatology. 2005; 211:264–266. PMID: 16205072.
Article5. Schartz NE, De La Blanchardiére A, Alaoui S, Morel P, Sigaux F, Vignon-Pennamen MD, et al. Regression of CD8+ pseudolymphoma after HIV antiviral triple therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003; 49:139–141. PMID: 12833028.
Article6. El-Dars LD, Statham BN, Blackford S, Williams N. Lymphocytoma cutis treated with topical tacrolimus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005; 30:305–307. PMID: 15807704.
Article7. Mikasa K, Watanabe D, Kondo C, Tamada Y, Matsumoto Y. Topical 5-aminolevulinic acid-based photodynamic therapy for the treatment of a patient with cutaneous pseudolymphoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005; 53:911–912. PMID: 16243162.
Article8. Arai E, Shimizu M, Tsuchida T, Izaki S, Ogawa F, Hirose T. Lymphomatoid keratosis: an epidermotropic type of cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia: clinicopathological, immunohistochemical, and molecular biological study of 6 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2007; 143:53–59. PMID: 17224542.