J Vet Sci.
2016 Mar;17(1):45-51. 10.4142/jvs.2016.17.1.45.
Time-course changes in the expression levels of miR-122, -155, and -21 as markers of liver cell damage, inflammation, and regeneration in acetaminophen-induced liver injury in rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul 05505, Korea. wcson@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Institute for Innovative Cancer Research, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul 05505, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul 05505, Korea.
- KMID: 2363334
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2016.17.1.45
Abstract
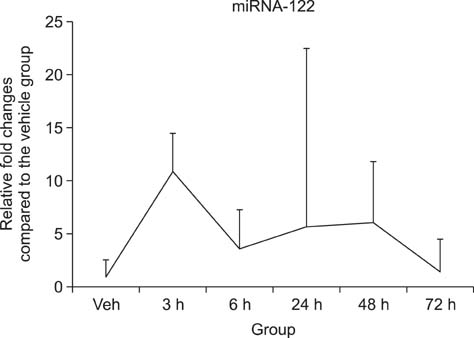
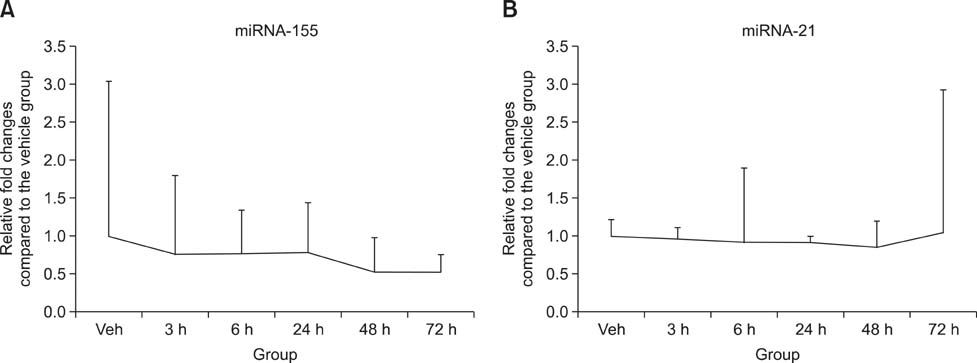
- Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant threat to patient health and a major concern during drug development. Recently, multiple circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) have been reported to be potential biomarkers for DILI. To adapt and validate miRNAs for clinical use, we investigated the time-course changes in miR-122 expression levels in an acetaminophen-induced liver injury model in rats. In addition, miR-155 and miR-21 were evaluated as makers of inflammation and regeneration, respectively, to characterize liver status. Our results revealed that miR-122 is an early and sensitive biomarker of hepatocellular injury at a stage when alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, and total bilirubin were not detectable. However, no significant differences in the expression levels of other miRNAs (miR-155 and -21) were observed between treatment and vehicle groups. Collectively, these time-course changes in the expression levels of miRNAs may be useful as markers for clinical decision-making, in the diagnosis and treatment of DILI.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acetaminophen/*toxicity
Animals
Biomarkers/*blood
Chemical and Drug Induced Liver Injury/*blood/*diagnosis/pathology
Gene Expression Profiling
Gene Expression Regulation/*drug effects
Hepatocytes/*drug effects
Inflammation/blood/diagnosis
Liver Regeneration
MicroRNAs/*blood/genetics
Predictive Value of Tests
Rats
Time
Acetaminophen
Biomarkers
MicroRNAs
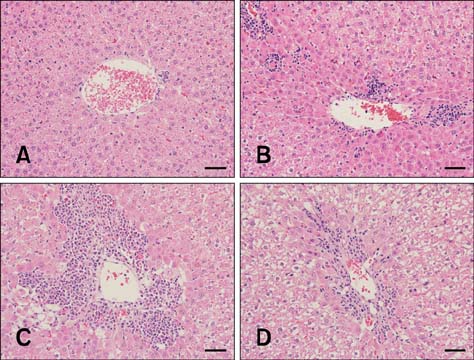
Figure
Reference
-
1. Amar PJ, Schiff ER. Acetaminophen safety and hepatotoxicity–where do we go from here? Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2007; 6:341–355.2. Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004; 431:350–355.
Article3. Antoine DJ, Dear JW, Lewis PS, Platt V, Coyle J, Masson M, Thanacoody RH, Gray AJ, Webb DJ, Moggs JG, Bateman DN, Goldring CE, Park BK. Mechanistic biomarkers provide early and sensitive detection of acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury at first presentation to hospital. Hepatology. 2013; 58:777–787.
Article4. Assis DN, Navarro VJ. Human drug hepatotoxicity: a contemporary clinical perspective. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2009; 5:463–473.
Article5. Atkuri KR, Mantovani JJ, Herzenberg LA, Herzenberg LA. N-acetylcysteine–a safe antidote for cysteine/glutathione deficiency. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2007; 7:355–359.6. Bala S, Marcos M, Kodys K, Csak T, Catalano D, Mandrekar P, Szabo G. Up-regulation of microRNA-155 in macrophages contributes to increased tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) production via increased mRNA half-life in alcoholic liver disease. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286:1436–1444.
Article7. Bala S, Petrasek J, Mundkur S, Catalano D, Levin I, Ward J, Alao H, Kodys K, Szabo G. Circulating microRNAs in exosomes indicate hepatocyte injury and inflammation in alcoholic, drug-induced, and inflammatory liver diseases. Hepatology. 2012; 56:1946–1957.
Article8. Bernal W, Auzinger G, Dhawan A, Wendon J. Acute liver failure. Lancet. 2010; 376:190–201.
Article9. Castro RE, Ferreira DM, Zhang X, Borralho PM, Sarver AL, Zeng Y, Steer CJ, Kren BT, Rodrigues CMP. Identification of microRNAs during rat liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy and modulation by ursodeoxycholic acid. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010; 299:G887–G897.
Article10. Chalasani N, Fontana RJ, Bonkovsky HL, Watkins PB, Davern T, Serrano J, Yang H, Rochon J. Drug Induced Liver Injury Network (DILIN). Causes, clinical features, and outcomes from a prospective study of drug-induced liver injury in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2008; 135:1924–1934. 1934.e1–1934.e4.
Article11. Chong VH. Acetaminophen overdose and N-acetylcysteine therapy. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2007; 36:704.12. Craig DG, Bates CM, Davidson JS, Martin KG, Hayes PC, Simpson KJ. Staggered overdose pattern and delay to hospital presentation are associated with adverse outcomes following paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012; 73:285–294.
Article13. Finch ML, Marquardt JU, Yeoh GC, Callus BA. Regulation of microRNAs and their role in liver development, regeneration and disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014; 54:288–303.
Article14. Imaeda AB, Watanabe A, Sohail MA, Mahmood S, Mohamadnejad M, Sutterwala FS, Flavell RA, Mehal WZ. Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice is dependent on Tlr9 and the Nalp3 inflammasome. J Clin Invest. 2009; 119:305–314.
Article15. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT Method. Methods. 2001; 25:402–408.
Article16. Marquez RT, Wendlandt E, Galle CS, Keck K, McCaffrey AP. MicroRNA-21 is upregulated during the proliferative phase of liver regeneration, targets Pellino-1, and inhibits NF-κB signaling. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010; 298:G535–G541.17. O'Connell RM, Kahn D, Gibson WSJ, Round JL, Scholz RL, Chaudhuri AA, Kahn ME, Rao DS, Baltimore D. MicroRNA-155 promotes autoimmune inflammation by enhancing inflammatory T cell development. Immunity. 2010; 33:607–619.18. Raschzok N, Sallmon H, Dame C, Sauer IM. Liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy: inconsistent results of expression screenings for human, mouse, and rat microRNAs. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012; 302:G470–G471.
Article19. Schug J, McKenna LB, Walton G, Hand N, Mukherjee S, Essuman K, Shi Z, Gao Y, Markley K, Nakagawa M, Kameswaran V, Vourekas A, Friedman JR, Kaestner KH, Greenbaum LE. Dynamic recruitment of microRNAs to their mRNA targets in the regenerating liver. BMC Genomics. 2013; 14:264.
Article20. Sgro C, Clinard F, Ouazir K, Chanay H, Allard C, Guilleminet C, Lenoir C, Lemoine A, Hillon P. Incidence of drug-induced hepatic injuries: a French population-based study. Hepatology. 2002; 36:451–455.
Article21. Starckx S, Batheja A, Verheyen GR, Jonghe SD, Steemans K, Van Dijck B, Singer M, Bogdan N, Snoeys J, Vinken P, Sasaki JC, Van Gompel J, Guzzie-Peck P, Lampo A, Lammens L. Evaluation of miR-122 and other biomarkers in distinct acute liver injury in rats. Toxicol Pathol. 2013; 41:795–804.
Article22. Starkey Lewis PJ, Dear J, Platt V, Simpson KJ, Craig DGN, Antoine DJ, French NS, Dhaun N, Webb DJ, Costello EM, Neoptolemos JP, Moggs J, Goldring CE, Park BK. Circulating microRNAs as potential markers of human drug-induced liver injury. Hepatology. 2011; 54:1767–1776.
Article23. Tili E, Michaille JJ, Wernicke D, Alder H, Costinean S, Volinia S, Croce CM. Mutator activity induced by microRNA-155 (miR-155) links inflammation and cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108:4908–4913.
Article24. Wang K, Zhang S, Marzolf B, Troisch P, Brightman A, Hu Z, Hood LE, Galas DJ. Circulating microRNAs, potential biomarkers for drug-induced liver injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106:4402–4407.
Article25. Yamaura Y, Nakajima M, Takagi S, Fukami T, Tsuneyama K, Yokoi T. Plasma microRNA profiles in rat models of hepatocellular injury, cholestasis, and steatosis. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e30250.
Article26. Zhang Y, Jia Y, Zheng R, Guo Y, Wang Y, Guo H, Fei M, Sun S. Plasma microRNA-122 as a biomarker for viral-, alcohol-, and chemical-related hepatic diseases. Clin Chem. 2010; 56:1830–1838.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Circulating Plasma and Exosomal microRNAs as Indicators of Drug-Induced Organ Injury in Rodent Models
- Gene Expression in Rat Hearts Following Oral Administration of a Single Hepatotoxic Dose of Acetaminophen
- miRNA-125b Signaling Ameliorates Liver Injury Against Obstructive Jaundice-Induced Excessive Fibrosis in Experimental Rats
- Lysophosphatidic acid protects against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury
- Hepatoprotective Effects of Resveratrol on Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury and Its Implications for Tofacitinib Disposition in Rats