J Bone Metab.
2016 Nov;23(4):223-231. 10.11005/jbm.2016.23.4.223.
Relationship between Heavy Metal Exposure and Bone Mineral Density in Korean Adult
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Nutrition, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea. heeobgy@naver.com
- 4Department of Biostatistics, Clinical Trial Center, Soonchunhyang Unversity Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2361584
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2016.23.4.223
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Exposure to heavy metals from environmental and industrial sources remains a concern of serious public health risk. This study was conducted to analysis the relationship between heavy metal concentrations and bone density.
METHODS
This study used data from a nation-based sample of Koreans (n=2,429) from 2008 to 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. We were obtained heavy metals (lead, mercury and cadmium), socioeconomic and demographic factors and bone mineral density (BMD) measured by T-score.
RESULTS
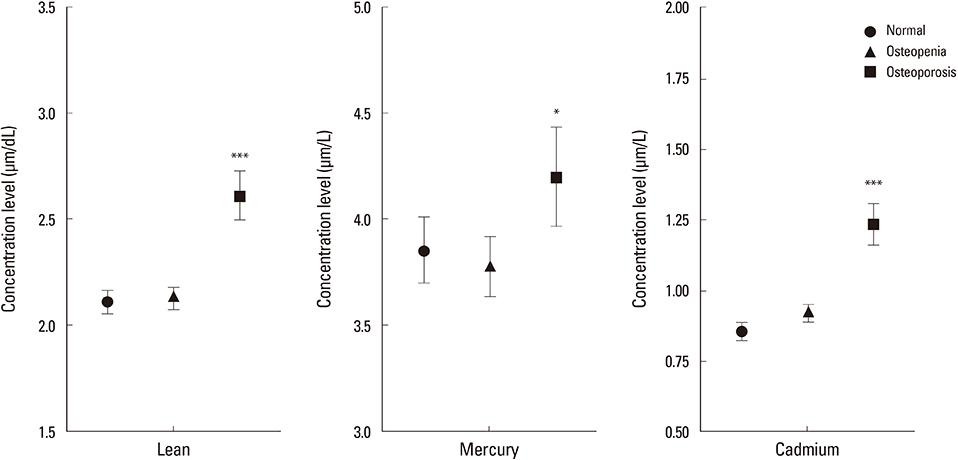
Menopausal women, current smoker or the frequent alcohol drinking, low educational level and low family income were greater in the osteopenia or osteoporosis groups than normal group, and were associated with an increased blood heavy metal concentration levels. The highest quartile group in blood lead had a 1.47 times (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.16-1.87) risk of osteopenia or osteoporosis. In case of blood cadmium, the risk for osteopenia or osteoporosis increased 2.1 times (95% CI 1.64-2.68).
CONCLUSIONS
We observed a significant association between blood heavy metals (lead and cadmium) levels and low BMD. Our findings suggest that heavy metal exposure may be a risk factor for osteoporosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chowdhury BA, Chandra RK. Biological and health implications of toxic heavy metal and essential trace element interactions. Prog Food Nutr Sci. 1987; 11:55–113.2. Maes GE, Raeymaekers JA, Hellemans B, et al. Gene transcription reflects poor health status of resident European eel chronically exposed to environmental pollutants. Aquat Toxicol. 2013; 126:242–255.
Article3. Chowdhury S, Mazumder MA, Al-Attas O, et al. Heavy metals in drinking water: Occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci Total Environ. 2016; 569-570:476–488.
Article4. Landsberger S, Wu D. The impact of heavy metals from environmental tobacco smoke on indoor air quality as determined by Compton suppression neutron activation analysis. Sci Total Environ. 1995; 173-174:323–337.
Article5. Bosch AC, O'Neill B, Sigge GO, et al. Heavy metals in marine fish meat and consumer health: a review. J Sci Food Agric. 2016; 96:32–48.
Article6. Rebolledo J, Fierens S, Versporten A, et al. Human biomonitoring on heavy metals in Ath: methodological aspects. Arch Public Health. 2011; 69:10.
Article7. Cebi A, Kaya Y, Gungor H, et al. Trace elements, heavy metals and vitamin levels in patients with coronary artery disease. Int J Med Sci. 2011; 8:456–460.
Article8. Kido S. Secondary osteoporosis or secondary contributors to bone loss in fracture. Bone metabolism and heavy metals (cadmium and iron). Clin Calcium. 2013; 23:1299–1306.9. Chisolm JJ Jr. Poisoning from heavy metals (mercury, lead, and cadmium). Pediatr Ann. 1980; 9:458–468.
Article10. Fukushima M, Ishizaki A, Sakamoto M, et al. On distribution of heavy metals in rice field soil in the "Itai-itai" disease epidemic district. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 1970; 24:526–535.
Article11. Lucchini RG, Hashim D. Tremor secondary to neurotoxic exposure: mercury, lead, solvents, pesticides. Handb Clin Neurol. 2015; 131:241–249.12. Kim YD, Eom SY, Yim DH, et al. Environmental exposure to arsenic, lead, and cadmium in people living near Janghang copper smelter in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:489–496.
Article13. Korean Society for Bone and Mineral Research. Physician's guide for diagnosis & treatment of osteoporosis. 2015. cited by 2016 April 8. Available from: http://www.ksbmr.org/image/journal/골다공증%20지침서2015_final_1002.pdf.14. Lim HS, Kim SK, Lee HH, et al. Comparison in adherence to osteoporosis guidelines according to bone health status in Korean adult. J Bone Metab. 2016; 23:143–148.
Article15. Brennan SL, Henry MJ, Wluka AE, et al. BMD in population-based adult women is associated with socioeconomic status. J Bone Miner Res. 2009; 24:809–815.
Article16. Myong JP, Kim HR, Choi SE, et al. Dose-related effect of urinary cotinine levels on bone mineral density among Korean females. Osteoporos Int. 2013; 24:1339–1346.
Article17. Akesson A, Bjellerup P, Lundh T, et al. Cadmium-induced effects on bone in a population-based study of women. Environ Health Perspect. 2006; 114:830–834.
Article18. Staessen JA, Roels HA, Emelianov D, et al. Environmental exposure to cadmium, forearm bone density, and risk of fractures: prospective population study. Public Health and Environmental Exposure to Cadmium (PheeCad) Study Group. Lancet. 1999; 353:1140–1144.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The relationship of maturation value of vaginal epithelium and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women
- Differences in Maternal Hair Heavy Metal and Mineral Levels between Preterm Delivery and Full-term Delivery
- Dietary Nutrient and Food Intake and Their Relations with Serum Heavy Metals in Osteopenic and Osteoporotic Patients
- Early immune response of neuronal cells (U87) to heavy metal Cd or Pb exposure
- The relationship between grip strength and femoral and vertebral bone mineral density in peri-and postmenopausal women