Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2016 Nov;4(6):436-441. 10.4168/aard.2016.4.6.436.
Analysis of clinical characteristics of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis at a single tertiary hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. helenmed@snu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2361259
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2016.4.6.436
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis (FDEIA) is a rare subtype of food allergy in which both sensitization to food allergen and exercise as a trigger contribute to its development. However, its pathogenesis is still under investigation. This study compared clinical features, the causative foods, and the degree of sensitization to food between FDEIA and food anaphylaxis to characterize FDEIA more clearly.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of patients who were diagnosed with FDEIA (n=89) or food anaphylaxis (n=115) between 2003 and 2015 at Seoul National University Hospital.
RESULTS
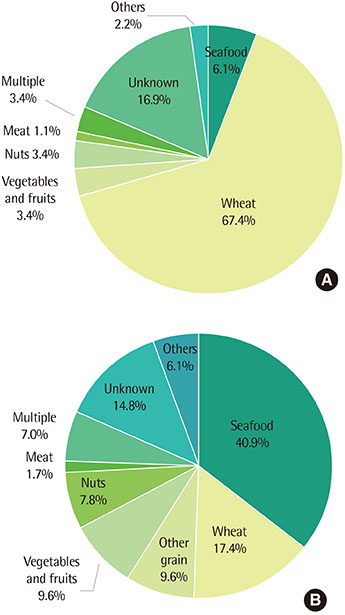
Subjects with FDEIA more frequently had urticaria than those with food anaphylaxis (88.8% vs. 76.5%, P=0.024). Whereas patients with FDEIA had less laryngeal edema than those with food anaphylaxis (12.4% vs. 30.4%, P=0.02). Wheat (67.4%) was the most common causative food allergen in FDEIA, whereas seafood (40.9%) was the most common culprit food allergen in food anaphylaxis. Also, subjects with FDEIA showed a lower atopic index score than those with food anaphylaxis (0.55±1.07 vs. 1.21±1.82, P=0.006).
CONCLUSION
There were significant differences in clinical manifestation, causative food allergens and the degree of sensitization to food between FDEIA and food anaphylaxis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aihara Y, Takahashi Y, Kotoyori T, Mitsuda T, Ito R, Aihara M, et al. Frequency of food-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Japanese junior-high-school students. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:1035–1039.
Article2. Yang MS, Lee SH, Kim TW, Kwon JW, Lee SM, Kim SH, et al. Epidemiologic and clinical features of anaphylaxis in Korea. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 100:31–36.
Article3. Lee BJ, Ban JW, Kim YK, Cho SH, Min KU, Kim YY. Three cases of fooddependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Korean J Med. 1998; 54:718–722.4. Maulitz RM, Pratt DS, Schocket AL. Exercise-induced anaphylactic reaction to shellfish. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979; 63:433–434.
Article5. Lee SE, Lee SY, Jo EJ, Kim MY, Kim SH, Chang YS. Wheat-Induced Anaphylaxis in Korean Adults: A Report of 6 Cases. Clin Nutr Res. 2013; 2:76–79.
Article6. Yoon TY, Choi KH, Lee KM, Ahn JY, Kim MK. Crown daisy-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in a patient with mugwort-sensitized pollinosis. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:63–66.7. Lee HH, Lee KE, Kim KE. Food allergy and anaphylaxis–2065. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in a patient with sensitization to pork. World Allergy Organ J. 2013; 6:Suppl 1. P148.8. Simons FE, Ardusso LR, Bilò MB, El-Gamal YM, Ledford DK, Ring J, et al. World allergy organization guidelines for the assessment and management of anaphylaxis. World Allergy Organ J. 2011; 4:13–37.
Article9. Laprise C, Boulet LP. Asymptomatic airway hyperresponsiveness: a threeyear follow-up. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997; 156(2 Pt 1):403–409.
Article10. Sampson HA, Muñoz-Furlong A, Campbell RL, Adkinson NF Jr, Bock SA, Branum A, et al. Second symposium on the definition and management of anaphylaxis: summary report: second National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease/Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network symposium. Ann Emerg Med. 2006; 47:373–380.
Article11. Morita E, Kunie K, Matsuo H. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Dermatol Sci. 2007; 47:109–117.
Article12. Romano A, Di Fonso M, Giuffreda F, Papa G, Artesani MC, Viola M, et al. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: clinical and laboratory findings in 54 subjects. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001; 125:264–272.
Article13. Morita E, Matsuo H, Chinuki Y, Takahashi H, Dahlström J, Tanaka A. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis -importance of omega-5 gliadin and HMW-glutenin as causative antigens for wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis-. Allergol Int. 2009; 58:493–498.
Article14. Im JH, Kwon HY, Ye YM, Park HS, Kim TB, Choi GS, et al. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Korea: a multicenter retrospective case study. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:203–210.
Article15. Kim MJ, Choi GS, Um SJ, Sung JM, Shin YS, Park HJ, et al. Anaphylaxis; 10 years' experience at a university hospital in Suwon. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 28:298–304.16. Seo MH, Kim SH, Hong JS, Kim WY, Choe SW. Clinical features of foodinduced anaphylaxis in the southeastern coasted area of Korea. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 30:110–115.17. Koh YI, Choi IS, Chung SU, Cho S. Clinical features of adult patients with anaphylaxis associated with food in Gwangju and Chonnam area. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 24:217–223.18. Shadick NA, Liang MH, Partridge AJ, Bingham CO III, Wright E, Fossel AH, et al. The natural history of exercise-induced anaphylaxis: survey results from a 10-year follow-up study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 104:123–127.
Article19. Barg W, Medrala W, Wolanczyk-Medrala A. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis: an update on diagnosis and treatment. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011; 11:45–51.
Article20. Tanaka S. An epidemiological survey on food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in kindergartners, schoolchildren and junior high school students. Asia Pac J Public Health. 1994; 7:26–30.
Article21. Morisset M, Richard C, Astier C, Jacquenet S, Croizier A, Beaudouin E, et al. Anaphylaxis to pork kidney is related to IgE antibodies specific for galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose. Allergy. 2012; 67:699–704.
Article22. Robson-Ansley P, Toit GD. Pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 10:312–317.
Article23. Palosuo K, Varjonen E, Kekki OM, Klemola T, Kalkkinen N, Alenius H, et al. Wheat omega-5 gliadin is a major allergen in children with immediate allergy to ingested wheat. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:634–638.
Article24. Battais F, Courcoux P, Popineau Y, Kanny G, Moneret-Vautrin DA, Denery-Papini S. Food allergy to wheat: differences in immunoglobulin Ebinding proteins as a function of age or symptoms. J Cereal Sci. 2005; 42:109–117.
Article25. Adachi A, Horikawa T, Shimizu H, Sarayama Y, Ogawa T, Sjolander S, et al. Soybean beta-conglycinin as the main allergen in a patient with fooddependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis by tofu: food processing alters pepsin resistance. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009; 39:167–173.
Article26. Miceli Sopo S, Monaco S, Giorgio V, Calvani M, Mistrello G, Onesimo R. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis (FDEIA) by nectarine in a paediatric patient with weakly positive nectarine prick-by-prick and negative specific IgE to Pru p 3. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2013; 41:201–203.
Article27. Matsuo H, Morimoto K, Akaki T, Kaneko S, Kusatake K, Kuroda T, et al. Exercise and aspirin increase levels of circulating gliadin peptides in patients with wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:461–466.
Article28. Gonzalez-Quintela A, Vidal C, Gude F. Alcohol, IgE and allergy. Addict Biol. 2004; 9:195–204.
Article29. Shin YS, Youn SH, Kim MC, Choi JH, Suh YJ, Suh CH, et al. A case of wheat-induced anaphylaxis in an adult. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 23:539–543.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Food allergies and food-induced anaphylaxis: role of cofactors
- A Case of Wheat-Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis
- Wheat-dependent, Exercise-induced Anaphylaxis: A Successful Case of Prevention with Ketotifen
- Three Cases of Food-dependent Exercise-induced Anaphylaxis
- A case of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis developed only in winter