J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Nov;31(Suppl 2):S178-S183. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.S2.S178.
Disability-Adjusted Life Years for Communicable Disease in the Korean Burden of Disease Study 2012
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. parenchyme@gmail.com
- 2Cancer Policy Branch, National Cancer Control Institute, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Medical Education and Humanities, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Cancer Registration and Statistic Branch, National Cancer Control Institute, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 5Department of Pediatrics, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2360668
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.S2.S178
Abstract
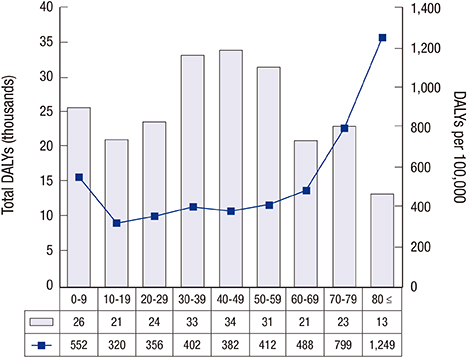
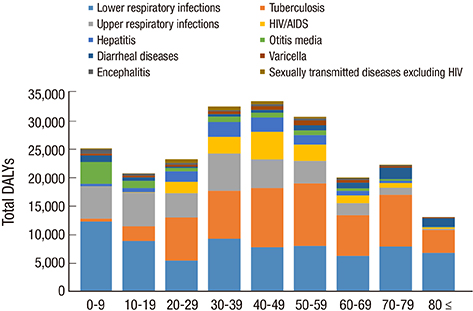
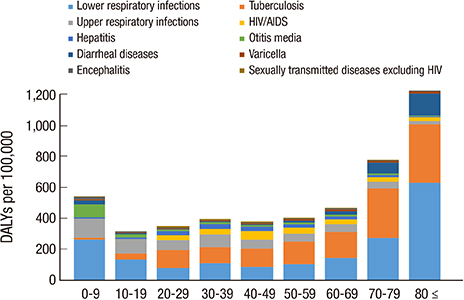
- Globally, the incidence of communicable diseases has decreased compared to non-communicable diseases. However, chronic communicable diseases such as HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis persist worldwide. Furthermore, emerging new infections such as H1N1 influenza pose a new threat to public health. However, most studies have focused on non-communicable diseases because of their increasing incidence, with fewer studies investigating communicable diseases. Therefore, we estimated the burden of communicable diseases in Korea using national representative 2012 data. To estimate the disability-adjusted life years (DALY), we used cause of death data from the Statistics Korea to estimate the years of life lost (YLL), applied the Korean garbage code algorithm, and used national claims data from the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) to estimate years lived with disability (YLD). In 2012, the total DALYs of communicable disease were 445 per 100,000, with 129 YLLs per 100,000 and 316 YLDs per 100,000. The total DALYs in men were 468 per 100,000, greater than the 422 per 100,000 DALYs seen in women. The DALYs of lower respiratory infections were the highest value among communicable diseases at 143/100,000 DALYs followed by tuberculosis and upper respiratory infections. The 40-49 years old age group had the largest number of total DALYs. In contrast, the over 80 years old age group had the largest number of total DALYs per 100,000 followed by the 70-79 and 0-9 years old age groups. These results enable the prioritization of interventions related to communicable diseases and can be used for evidence-based public health policies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Burden of Disease due to COVID-19 in Korea Using Disability-Adjusted Life Years
Min-Woo Jo, Dun-Sol Go, Rhieun Kim, Seung Won Lee, Minsu Ock, Young-Eun Kim, In-Hwan Oh, Seok-Jun Yoon, Hyesook Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(21):e199. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e199.
Reference
-
1. Oh IH, Yoon SJ, Kim EJ. The burden of disease in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2011; 54:646–652.2. Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, Ezzati M, Shibuya K, Salomon JA, Abdalla S, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 2012; 380:2197–2223.3. Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) [Internet]. accessed on 10 November 2015. Available at http://www.healthdata.org/.4. Mathers C, Fat DM, Boerma JT. The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update. Geneva: World Health Organization;2008.5. Baker MG, Barnard LT, Kvalsvig A, Verrall A, Zhang J, Keall M, Wilson N, Wall T, Howden-Chapman P. Increasing incidence of serious infectious diseases and inequalities in New Zealand: a national epidemiological study. Lancet. 2012; 379:1112–1119.6. Lim SS, Mokdad AH. Socioeconomic inequalities and infectious disease burden. Lancet. 2012; 379:1080–1081.7. National Health Insurance Service, Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service (KR). 2012 National Health Insurance Statistical Yearbook. Seoul: National Health Insurance Service;2013.8. Statistics Korea [Internet]. accessed on 1 September 2015. Available at http://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/index.action.9. Yang JH. Development and evaluation of a program to promote self management in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2012; 42:258–268.10. World Health Organization. WHO TB burden estimates [Internet]. accessed on 11 November 2015. Available at http://www.who.int/tb/country/data/download/en/.11. Yoon SJ, Bae SC. Current scope and perspective of burden of disease study based on health related quality of life. J Korean Med Assoc. 2004; 47:600–602.12. Yoon SJ. A Study on Research Methodology and Long-term Planning regarding Estimating of Economic Burden of Major Diseases in Korea. Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2009.13. Yoon J, Oh IH, Seo H, Kim EJ, Gong YH, Ock M, Lim D, Lee WK, Lee YR, Kim D, et al. Disability-adjusted Life Years for 313 Diseases and Injuries: the 2012 Korean Burden of Disease Study. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:Suppl 2. S146–S157.14. Lee YR, Kim YA, Park SY, Oh CM, Kim YE, Oh IH. Application of a Modified Garbage Code Algorithm to Estimate Cause-Specific Mortality and Years of Life Lost in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:Suppl 2. S121–S128.15. Ock M, Lee JY, Oh IH, Park H, Yoon SJ, Jo MW. Disability Weights Measurement for 228 Causes of Disease in the Korean Burden of Disease Study 2012. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:Suppl 2. S129–S138.16. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2014 Case definitions for national notifiable infectious diseases [Internet]. accessed on 11 October 2015. Available at http://www.cdc.go.kr.17. Yoon SJ, Jo MW, Park HS, Oh IH. A Study on Measuring and Forecasting the Burden of Disease in Korea. Seoul: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center;2015.18. Jung YH. Avoidable mortality in Korea. Health Welf Policy Forum. 2014; 8:42–53.19. World Health Organization (CH). Global Tuberculosis Report 2013. Geneva: World Health Organization;2013.20. World Health Organization (CH). Global Tuberculosis Report 2014. Geneva: World Health Organization;2014.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Disability-adjusted Life Years (DALYs) for Mental and Substance Use Disorders in the Korean Burden of Disease Study 2012
- Years of Life Lost due to Premature Death in People with Disabilities in Korea: the Korean National Burden of Disease Study Framework
- Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) for Injuries Using Death Certificates and Hospital Discharge Survey by the Korean Burden of Disease Study 2012
- The burden of disease in Korea
- The Non-Communicable Disease Burden in Korea: Findings from the 2012 Korean Burden of Disease Study