J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Nov;31(Suppl 2):S191-S199. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.S2.S191.
Disability-adjusted Life Years (DALYs) for Mental and Substance Use Disorders in the Korean Burden of Disease Study 2012
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. hpark@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Social and Preventive Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2360670
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.S2.S191
Abstract
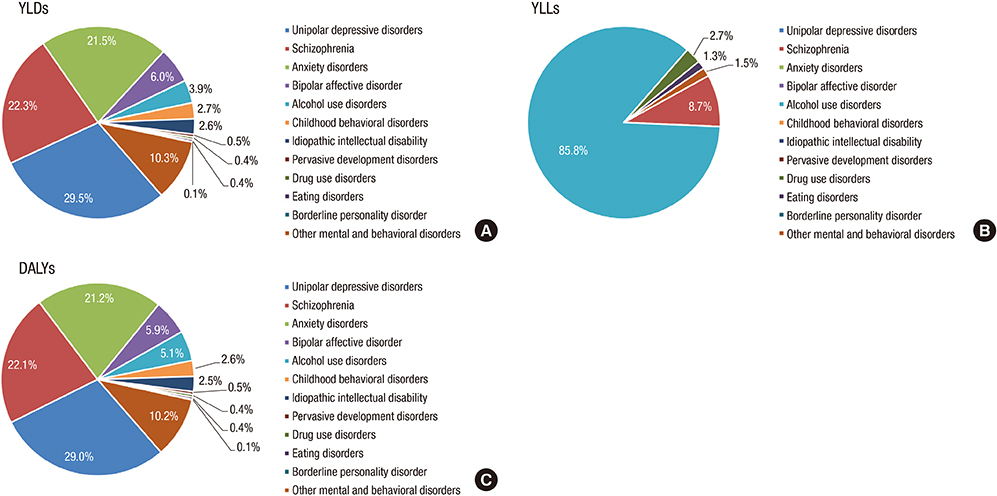
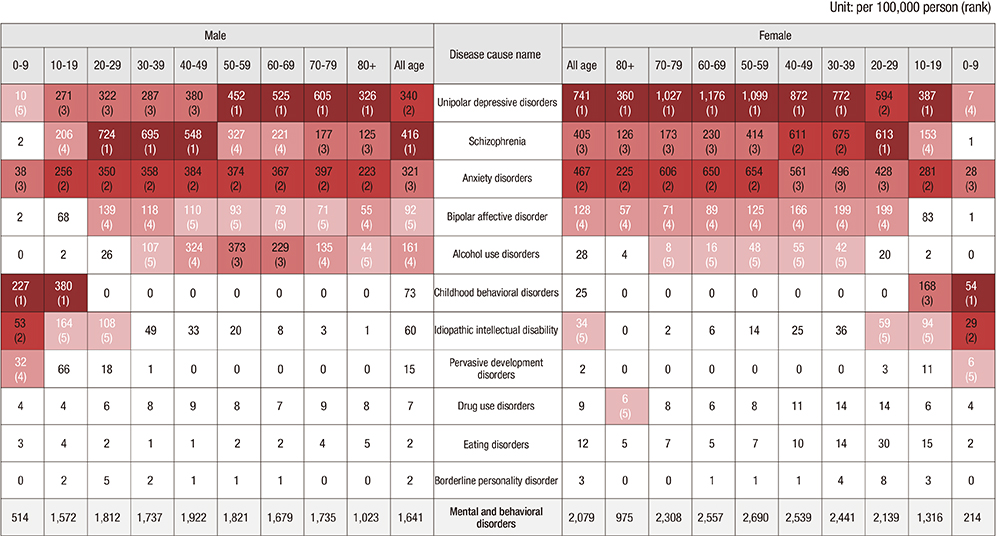
- The purpose of this study was to estimate the national burden of mental substance disorders on medical care utilization in Korea using National Health Insurance System (NHIS) data and updated disability weight, in terms of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). For each of the 24 disorders, the incident years lived with disability (YLDs) was calculated, using NHIS data to estimate prevalence and incidence rates. The DisMod-II software program was used to model duration and remission. The years of life lost (YLLs) due to premature death were calculated from causes of death statistics. DALYs were computed as the sum of YLDs and YLLs, and time discounting and age weighting were applied. The year examined was 2012, and the subjects were divided into 9 groups according to age. In 2012, the Korean burden of mental and substance use disorders was 945,391 DALYs. More than 98% of DALYs were from YLDs, and the burden in females was greater than that in males, though the burden in males aged less than 19 years old was greater than that in females. Unipolar depressive disorders, schizophrenia, and anxiety disorders were found to be major diseases that accounted for more than 70% of the burden, and most DALYs occurred in their 30-59. Mental and substance use disorders accounted for 6.2% of the total burden of disease and were found to be the 7th greatest burden of disease. Therefore, mental and substance use disorders need to be embraced by mainstream health care with resources commensurate with the burden.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Comparison of Services for Autism Spectrum Disorder in Massachusetts with Those in Seoul
Jung Won Kim, Hyo-Won Kim, Duk-Soo Moon, Yun Shin Lim, Christopher J. McDougle, Yamini Jagannath Howe
J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(43):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e288.The association between dependent self-employment and self-reported depression/anxiety and sleep disorder in South Korea
Guyeon Won, Jae Bum Park, Kyung-Jong Lee, Ryun Ha, Seungho Lee, Inchul Jeong
Ann Occup Environ Med. 2019;31(1):. doi: 10.35371/aoem.2019.31.e13.Korean National Burden of Disease: The Importance of Diabetes Management
Chung-Nyun Kim, Yoon-Sun Jung, Young-Eun Kim, Minsu Ock, Seok-Jun Yoon
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(4):518-530. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0087.
Reference
-
1. Seoul National University College of Medicine (KR). The Epidemiological Survey of Mental Disorders in Korea 2011. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2011.2. Murray CJ, Lopez AD, Jamison DT. The global burden of disease in 1990: summary results, sensitivity analysis and future directions. Bull World Health Organ. 1994; 72:495–509.3. Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Quantifying disability: data, methods and results. Bull World Health Organ. 1994; 72:481–494.4. Whiteford HA, Degenhardt L, Rehm J, Baxter AJ, Ferrari AJ, Erskine HE, Charlson FJ, Norman RE, Flaxman AD, Johns N, et al. Global burden of disease attributable to mental and substance use disorders: findings from the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 2013; 382:1575–1586.5. Ministry of Health (NZ). The Burden of Disease and Injury in New Zealand. Wellington: Ministry of Health;2001.6. Yoon SJ, Bae SC, Lee SI, Chang H, Jo HS, Sung JH, Park JH, Lee JY, Shin Y. Measuring the burden of disease in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2007; 22:518–523.7. Lee KS, Park JH. Burden of disease in Korea during 2000-10. J Public Health (Oxf). 2014; 36:225–234.8. Park JH, Yoon SJ, Lee HY, Cho HS, Lee JY, Eun SJ, Park JH, Kim Y, Kim YI, Shin YS. Estimating the burden of psychiatric disorder in Korea. J Prev Med Public Health. 2006; 39:39–45.9. Do YK, Yoon SJ, Lee JK, Kwon YH, Lee SI, Kim C, Park K, Kim YI, Shin Y. Disability weights for the Korean burden of disease study: focused on comparison with disability weights in the Australian burden of disease study. J Prev Med Public Health. 2004; 37:59–71.10. National Health Insurance Service (KR). Major statistics on National Health Insurance Service 2012 [Internet]. accessed on 11 November 2015. Available at http://www.nhis.or.kr.11. Yoon J, Oh IH, Seo H, Kim EJ, Gong YH, Ock M, Lim D, Lee WK, Lee YR, Kim D, et al. Disability-adjusted Life Years for 313 Diseases and Injuries: the 2012 Korean Burden of Disease Study. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:Suppl 2. S146–S157.12. Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, Ezzati M, Shibuya K, Salomon JA, Abdalla S, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 2012; 380:2197–2223.13. Korean Statistical Information Service. Resident population (mid-year) [Internet]. accessed on 11 November 2015. Available at http://kosis.kr/ups/ups_01List01.jsp?grp_no=&pubcode=AW&type=.14. Korean Statistical Information Service [Internet]. accessed on 11 November 2015. Available at http://kosis.kr/.15. Barendregt JJ, Van Oortmarssen GJ, Vos T, Murray CJ. A generic model for the assessment of disease epidemiology: the computational basis of DisMod II. Popul Health Metr. 2003; 1:4.16. Ock M, Lee JY, Oh IH, Park H, Yoon SJ, Jo MW. Disability Weights Measurement for 228 Causes of Disease in the Korean Burden of Disease Study 2012. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:Suppl 2. S129–S138.17. Mandelblatt JS, Fryback DG, Weinstein MC, Russell LB, Gold MR. Assessing the effectiveness of health interventions for cost-effectiveness analysis. Panel on Cost-Effectiveness in Health and Medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 1997; 12:551–558.18. Kim TN, Yang SJ, Yoo HJ, Lim KI, Kang HJ, Song W, Seo JA, Kim SG, Kim NH, Baik SH, et al. Prevalence of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in Korean adults: the Korean sarcopenic obesity study. Int J Obes. 2009; 33:885–892.19. World Health Organization. Prevention of Mental Disorders: Effective Interventions and Policy Options (Summary Report). Geneva: World Health Organization;2004.20. Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Comorbidity of Mental Disorders and Physical Conditions, 2007. Canberra: Australian Institute of Health and Welfare;2012.21. Sartorious N. Comorbidity of mental and physical diseases: a main challenge for medicine of the 21st century. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2013; 25:68–69.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Trends and Patterns of Burden of Disease and Injuries in Korea Using Disability-Adjusted Life Years
- Measuring the Burden of Disease in Korea Using Disability-Adjusted Life Years (2008–2020)
- Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) for Injuries Using Death Certificates and Hospital Discharge Survey by the Korean Burden of Disease Study 2012
- Disability-Adjusted Life Years for Maternal, Neonatal, and Nutritional Disorders in Korea
- Estimation of the National Burden of Disease and Vulnerable Population Associated with Natural Disasters in Korea: Heavy Precipitation and Typhoon