J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Feb;31(2):231-239. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.2.231.
In-Silico Trials for Glucose Control in Hospitalized Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Interdisciplinary Program for Bioengineering, Graduate School, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Institute of Medical and Biological Engineering, Medical Research Center, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. sungwan@snu.ac.kr
- 5Department of Biomedical Engineering, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Biomedical Engineering, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2360047
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.2.231
Abstract
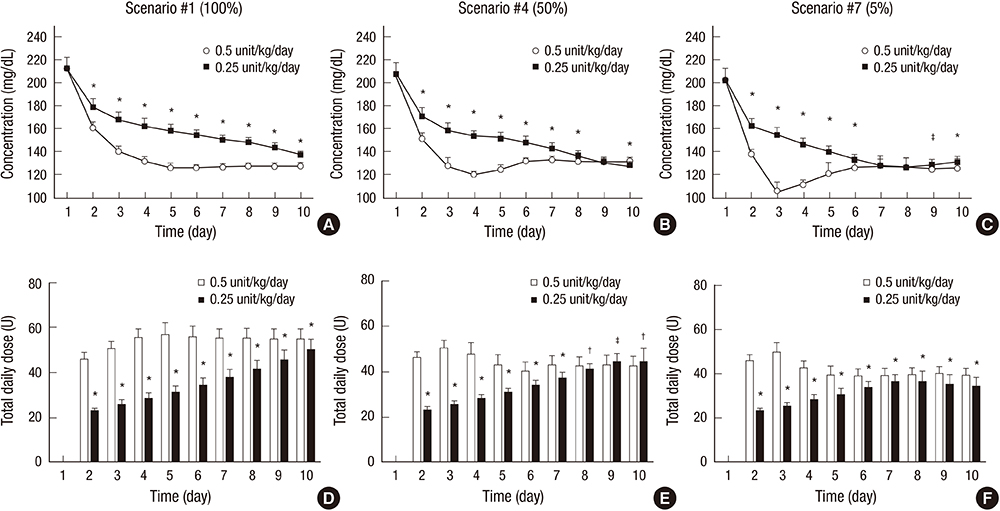
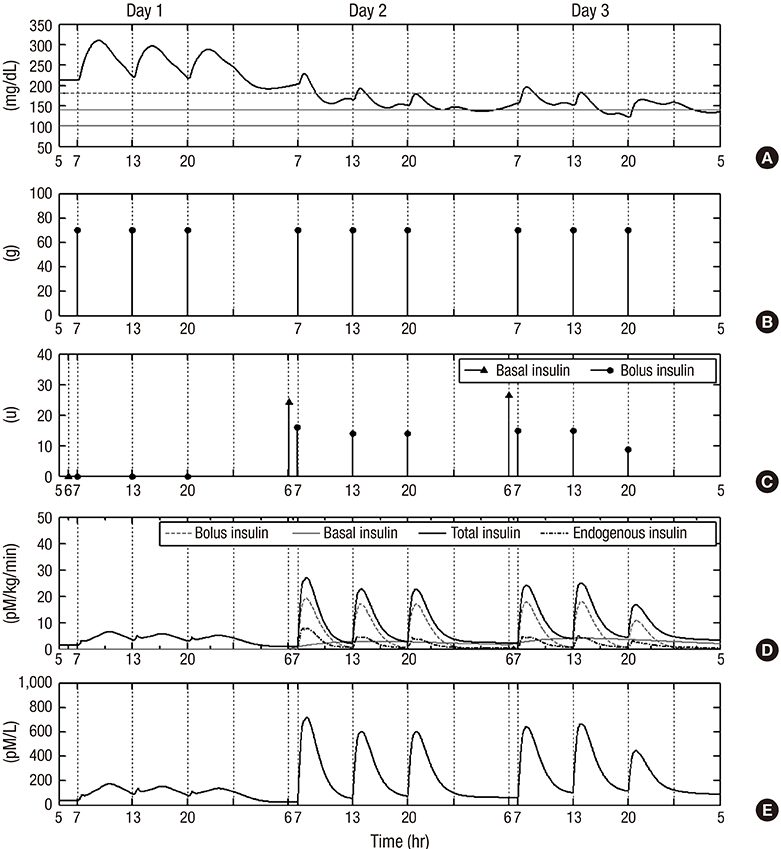
- Although various basal-bolus insulin therapy (BBIT) protocols have been used in the clinical environment, safer and more effective BBIT protocols are required for glucose control in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). Modeling approaches could provide an evaluation environment for developing the optimal BBIT protocol prior to clinical trials at low cost and without risk of danger. In this study, an in-silico model was proposed to evaluate subcutaneous BBIT protocols in hospitalized patients with T2D. The proposed model was validated by comparing the BBIT protocol and sliding-scale insulin therapy (SSIT) protocol. The model was utilized for in-silico trials to compare the protocols of adjusting basal-insulin dose (BBIT1) versus adjusting total-daily-insulin dose (BBIT2). The model was also used to evaluate two different initial total-daily-insulin doses for various levels of renal function. The BBIT outcomes were superior to those of SSIT, which is consistent with earlier studies. BBIT2 also outperformed BBIT1, producing a decreased daily mean glucose level and longer time-in-target-range. Moreover, with a standard dose, the overall daily mean glucose levels reached the target range faster than with a reduced-dose for all degrees of renal function. The in-silico studies demonstrated several significant findings, including that the adjustment of total-daily-insulin dose is more effective than changes to basal-insulin dose alone. This research represents a first step toward the eventual development of an advanced model for evaluating various BBIT protocols.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Umpierrez GE, Isaacs SD, Bazargan N, You X, Thaler LM, Kitabchi AE. Hyperglycemia: an independent marker of in-hospital mortality in patients with undiagnosed diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87:978–982.2. Moghissi ES, Korytkowski MT, DiNardo M, Einhorn D, Hellman R, Hirsch IB, Inzucchi SE, Ismail-Beigi F, Kirkman MS, Umpierrez GE, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American Diabetes Association consensus statement on inpatient glycemic control. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:1119–1131.3. Varghese P, Gleason V, Sorokin R, Senholzi C, Jabbour S, Gottlieb JE. Hypoglycemia in hospitalized patients treated with antihyperglycemic agents. J Hosp Med. 2007; 2:234–240.4. Wexler DJ, Meigs JB, Cagliero E, Nathan DM, Grant RW. Prevalence of hyper- and hypoglycemia among inpatients with diabetes: a national survey of 44 U.S. hospitals. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:367–369.5. Turchin A, Matheny ME, Shubina M, Scanlon JV, Greenwood B, Pendergrass ML. Hypoglycemia and clinical outcomes in patients with diabetes hospitalized in the general ward. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:1153–1157.6. Carey M, Boucai L, Zonszein J. Impact of hypoglycemia in hospitalized patients. Curr Diab Rep. 2013; 13:107–113.7. Umpierrez GE, Smiley D, Zisman A, Prieto LM, Palacio A, Ceron M, Puig A, Mejia R. Randomized study of basal-bolus insulin therapy in the inpatient management of patients with type 2 diabetes (RABBIT 2 trial). Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:2181–2186.8. Umpierrez GE, Smiley D, Jacobs S, Peng L, Temponi A, Mulligan P, Umpierrez D, Newton C, Olson D, Rizzo M. Randomized study of basal-bolus insulin therapy in the inpatient management of patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing general surgery (RABBIT 2 surgery). Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:256–261.9. Baldwin D, Zander J, Munoz C, Raghu P, DeLange-Hudec S, Lee H, Emanuele MA, Glossop V, Smallwood K, Molitch M. A randomized trial of two weight-based doses of insulin glargine and glulisine in hospitalized subjects with type 2 diabetes and renal insufficiency. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:1970–1974.10. Chase JG, Le Compte AJ, Preiser JC, Shaw GM, Penning S, Desaive T. Physiological modeling, tight glycemic control, and the ICU clinician: what are models and how can they affect practice. Ann Intensive Care. 2011; 1:11.11. Lee JC, Kim M, Choi KR, Oh TJ, Kim MY, Cho YM, Kim K, Kim HC, Kim S. In silico evaluation of glucose control protocols for critically ill patients. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2012; 59:54–57.12. Kim M, Oh TJ, Lee JC, Choi K, Kim MY, Kim HC, Cho YM, Kim S. Simulation of oral glucose tolerance tests and the corresponding isoglycemic intravenous glucose infusion studies for calculation of the incretin effect. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29:378–385.13. Dalla Man C, Camilleri M, Cobelli C. A system model of oral glucose absorption: validation on gold standard data. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2006; 53:2472–2478.14. Dalla Man C, Rizza RA, Cobelli C. Meal simulation model of the glucose-insulin system. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2007; 54:1740–1749.15. Kovatchev BP, Breton M, Man CD, Cobelli C. In silico preclinical trials: a proof of concept in closed-loop control of type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2009; 3:44–55.16. Hovorka R, Canonico V, Chassin LJ, Haueter U, Massi-Benedetti M, Orsini Federici M, Pieber TR, Schaller HC, Schaupp L, Vering T, et al. Nonlinear model predictive control of glucose concentration in subjects with type 1 diabetes. Physiol Meas. 2004; 25:905–920.17. Oh TJ, Kim MY, Shin JY, Lee JC, Kim S, Park KS, Cho YM. The incretin effect in Korean subjects with normal glucose tolerance or type 2 diabetes. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014; 80:221–227.18. Hirsch IB. Insulin analogues. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:174–183.19. Snyder RW, Berns JS. Use of insulin and oral hypoglycemic medications in patients with diabetes mellitus and advanced kidney disease. Semin Dial. 2004; 17:365–370.20. Service FJ, Molnar GD, Rosevear JW, Ackerman E, Gatewood LC, Taylor WF. Mean amplitude of glycemic excursions, a measure of diabetic instability. Diabetes. 1970; 19:644–655.21. Kovatchev BP, Otto E, Cox D, Gonder-Frederick L, Clarke W. Evaluation of a new measure of blood glucose variability in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:2433–2438.22. Moen MF, Zhan M, Hsu VD, Walker LD, Einhorn LM, Seliger SL, Fink JC. Frequency of hypoglycemia and its significance in chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009; 4:1121–1127.23. Mak RH, DeFronzo RA. Glucose and insulin metabolism in uremia. Nephron. 1992; 61:377–382.24. Saxena A. Nutritional problems in adult patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin Queries Nephrol. 2012; 1:222–235.25. Chassin LJ, Wilinska ME, Hovorka R. Evaluation of glucose controllers in virtual environment: methodology and sample application. Artif Intell Med. 2004; 32:171–181.26. Biermann E, Barkhausen K, Standl E. How would patients behave if they were continually informed of their blood glucose levels? A simulation study using a "virtual" patient. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2008; 10:178–187.27. Faulenbach M, Uthoff H, Schwegler K, Spinas GA, Schmid C, Wiesli P. Effect of psychological stress on glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2012; 29:128–131.28. Kruyt ND, van Westerloo DJ, DeVries JH. Stress-induced hyperglycemia in healthy bungee jumpers without diabetes due to decreased pancreatic β-cell function and increased insulin resistance. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2012; 14:311–314.29. Carroll MF, Schade DS. The dawn phenomenon revisited: implications for diabetes therapy. Endocr Pract. 2005; 11:55–64.30. Hovorka R, Chassin LJ, Ellmerer M, Plank J, Wilinska ME. A simulation model of glucose regulation in the critically ill. Physiol Meas. 2008; 29:959–978.31. DeFronzo RA, Hompesch M, Kasichayanula S, Liu X, Hong Y, Pfister M, Morrow LA, Leslie BR, Boulton DW, Ching A, et al. Characterization of renal glucose reabsorption in response to dapagliflozin in healthy subjects and subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:3169–3176.