Anesth Pain Med.
2016 Apr;11(2):149-154. 10.17085/apm.2016.11.2.149.
The effect of nerve preservation methods on rat sciatic nerve structures studied with Synchrotron small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. bikim@cu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anatomy, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2358476
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.2.149
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Synchrotron small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) is a very useful technique for experimental study of the nano-structure of the nervous system of animals. The study was designed to evaluate nerve preservation methods for the measurement of SAXS patterns.
METHODS
Normal sciatic nerves extracted from male Sprague- Dawley rats were preserved in saline (N = 2), formalin (N = 2) or liquid nitrogen (N = 2) for 1 day, followed by measurement of SAXS patterns. SAXS patterns of normal sciatic nerves (N = 3) extracted just before the initiation of the experiment were used as controls. The study was carried out using the 4C1 beamline at Pohang Accelerator Laboratory in Korea. Incoming X-rays were monochromatized at 11 keV using a double multilayer (WB4C) monochromator with beam size of approximately 0.5 (V) × 0.8 (H) mm2. The exposure time was set at 60 sec, and 8 to 12 images per sample were acquired at a 0.5 mm interval.
RESULTS
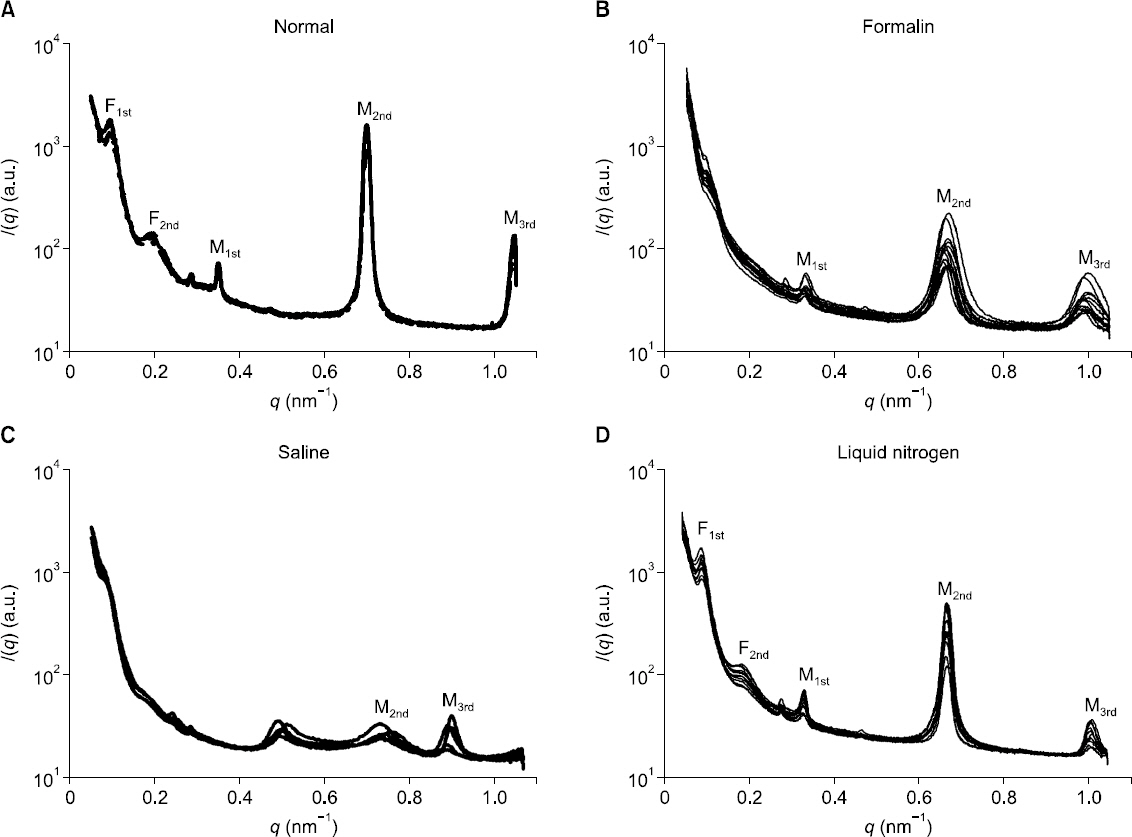
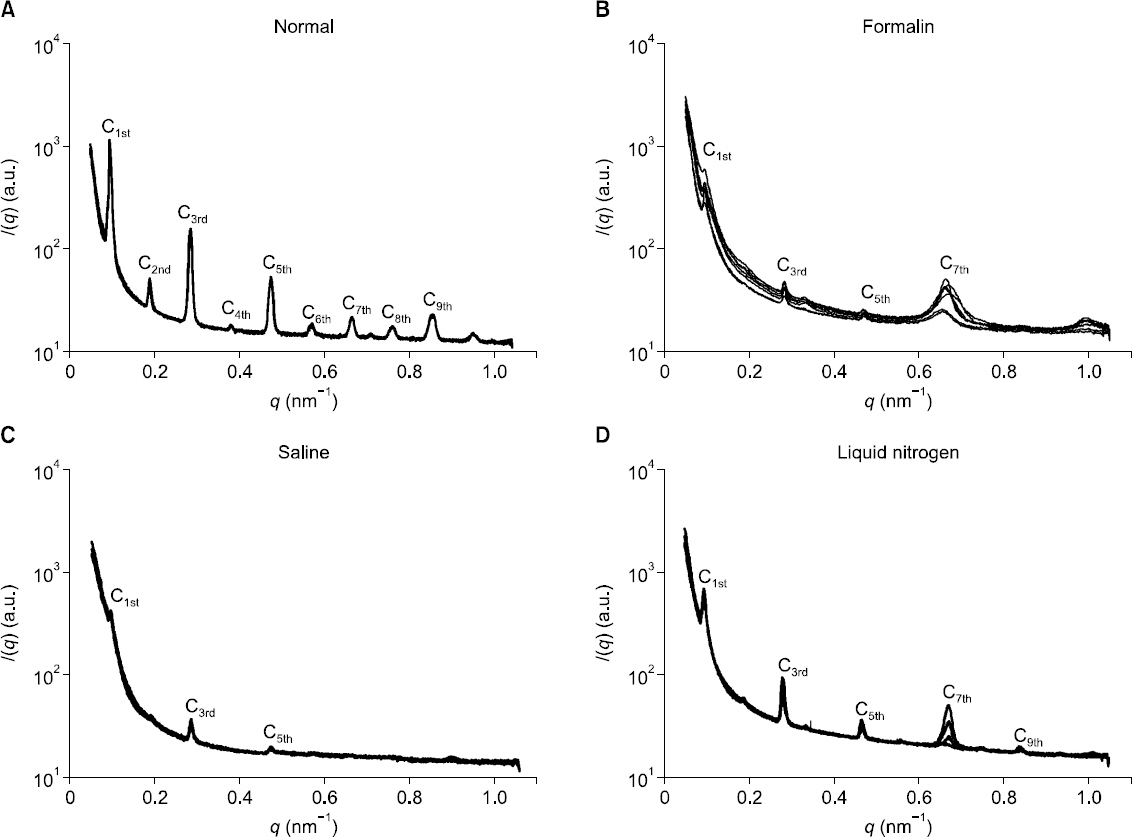
The periodic peaks of interfibrillar space between collagen fibrils were undetectable. The periodic peaks of the myelin sheath and collagen fibers were weakly detected or undetected in the nerves preserved in normal saline or formalin. The periodic peaks and intensity of the myelin sheath, collagen fibers, and interfibrillar space between collagens in the nerves preserved in liquid nitrogen were comparable to those of nerves in the ex vivo state.
CONCLUSIONS
The study results indicated that preservation of nerves in liquid nitrogen is adequate for measurements with SAXS. However, saline and formalin preservation techniques were inadequate for SAXS measurement.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim BI, Kim KH, Youn HS, Jheon S, Kim JK, Kim H. High resolution X-ray phase contrast synchrotron imaging of normal and ligation damaged rat sciatic nerves. Microsc Res Tech. 2008; 71:443–7. DOI: 10.1002/jemt.20571. PMID: 18398835.
Article2. Kim BI, Song SY, Ryu T, Choi YH, Jung JY, Shin TJ. Peripheral nerve injury caused by needle impalement: Synchrotron small-angle X-ray scattering study in ex-vivo rat sciatic nerve. Anesth Pain Med. 2014; 9:268–73.3. Lee TH, Lee S, Kim JH, Jung JY, Kim BI, Shin TJ. Analysis of ultrastructural changes in the rat sciatic nerve after exposure to pulsed radiofrequency using small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). Anesth Pain Med. 2014; 9:209–16.4. Erdine S, Bilir A, Cosman ER, Cosman ER Jr. Ultrastructural changes in axons following exposure to pulsed radiofrequency fields. Pain Pract. 2009; 9:407–17. DOI: 10.1111/j.1533-2500.2009.00317.x. PMID: 19761513.
Article5. McInnes E. Artifacts in histopathology. Comp Clin Path. 2005; 13:100–8. DOI: 10.1007/s00580-004-0532-4.6. Schmit FO, Bear RS. The ultrastructure of the nerve axon sheath. Biological Rev. 1939; 14:27–50. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.1939.tb00922.x.7. Inouye H, Worthington CR. X-ray observations on a collagen fibril lattice structure in peripheral nerve. Int J Biol Macromol. 1983; 5:199–203. DOI: 10.1016/0141-8130(83)90002-8.
Article8. Avila RL, Inouye H, Baek RC, Yin X, Trapp BD, Feltri ML, et al. Structure and stability of internodal myelin in mouse models of hereditary neuropathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2005; 64:976–90. DOI: 10.1097/01.jnen.0000186925.95957.dc. PMID: 16254492.
Article9. Suhonen H, Fernández M, Serimaa R, Suortti P. Simulation of small-angle x-ray scattering from collagen fibrils and comparison with experimental patterns. Phys Med Biol. 2005; 50:5401–16. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/50/22/012. PMID: 16264260.
Article10. Chen J, Burger C, Kirshnan CV, Chu B, Hsiao BS, Glimcher MJ. In vitro mineralization of collagen in demineralized fish bone. Macromol Chem Phys. 2005; 206:43–51. DOI: 10.1002/macp.200400066.
Article11. Kwon KY, Kim YH, Chung ES. Methodology of electron microscopy. 2004. Seoul: Jungmunkag;p. 23–7.12. Changizi V, Wilkinson S, Hall CJ, Grossmann G. A study of the effect of formalin preservation on normal and cancerous breast tissues using small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). Radiat Phys Chem. 2006; 75:932–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2006.02.005.
Article13. Jeon JP, Han BK. Towards the era of biobank. 2009. Seoul: World science publishing;p. 125–42.14. Changizi V, Oghabian MA, Speller R, Sarkar S, Kheradmand AA. Application of small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) for differentiation between normal and cancerous breast tissue. Int J Med Sci. 2005; 2:118–21. DOI: 10.7150/ijms.2.118. PMID: 16007264. PMCID: PMC1168877.
Article15. McIntosh TJ, Worthington CR. The lamellar structure of nerve myelin after rehydration. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974; 162:523–9. DOI: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90212-4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis of ultrastructural changes in the rat sciatic nerve after exposure to pulsed radiofrequency using small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS)
- Peripheral nerve injury caused by needle impalement: Synchrotron small-angle X-ray scattering study in ex-vivo rat sciatic nerve
- Structural analysis of a ligatured rat sciatic nerve in the ex vivo state using synchrotron small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS)
- Histological and electrophysiological study on nerve regenerationfollowing nerve repair in rat sciatic nerve
- The effect of degenerated muscle graft on nerve regeneration of the rat sciatic nerve defect