Ewha Med J.
2016 Oct;39(4):125-128. 10.12771/emj.2016.39.4.125.
Corticosteroid Therapy for Refractory Uremic Pleurisy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. humanmd04@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2356385
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2016.39.4.125
Abstract
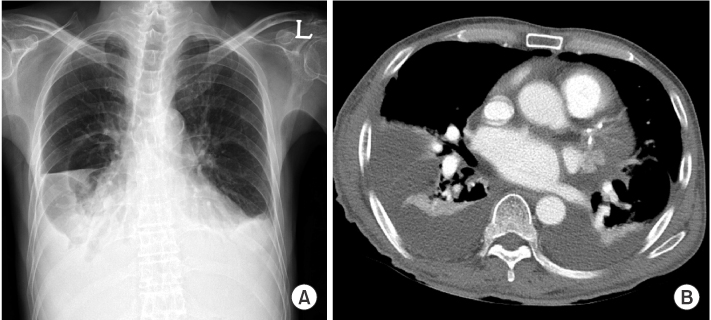
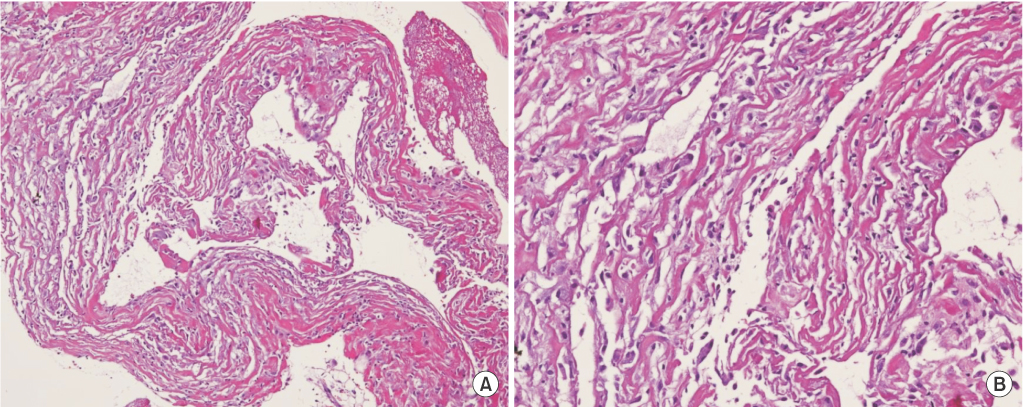
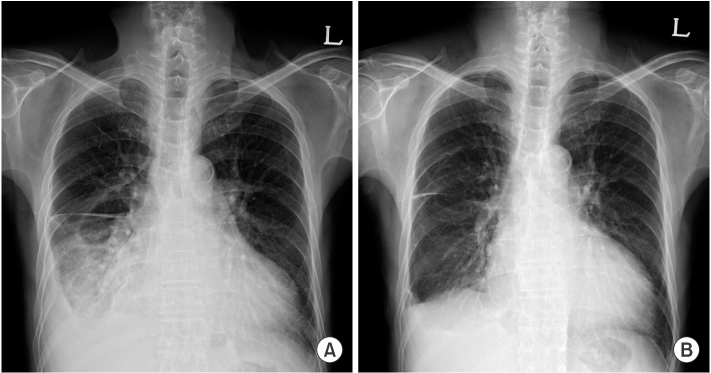
- Uremic pleuritis is a fibrinous pleuritis of unknown pathogenesis in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although it responds to regular dialysis or repeated thoracentesis, cases that are refractory to those therapies have been reported. We report a case of uremic pleuritis which showed marked improvement following corticosteroid therapy. The effusion was exudate, and negative in cytology and microbiology. Pleural biopsy revealed chronic inflammation with fibrosis. The pleural effusion did not respond to chest tube drainage and continuance of hemodialysis. With a diagnosis of refractory uremic pleuritis, we started methylprednisolone. The pleural effusion responded to the treatment and resolved without complication.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rashid-Farokhi F, Pourdowlat G, Nikoonia MR, Behzadnia N, Kahkouee S, Nassiri AA, et al. Uremic pleuritis in chronic hemodialysis patients. Hemodial Int. 2013; 17:94–100.2. Iyoda M, Ajiro Y, Sato K, Kuroki A, Shibata T, Kitazawa K, et al. A case of refractory uremic pleuropericarditis: successful corticosteroid treatment. Clin Nephrol. 2006; 65:290–293.3. Nidus BD, Matalon R, Cantacuzino D, Eisinger RP. Uremic pleuritic: a clinicopathological entity. N Engl J Med. 1969; 281:255–256.4. Ray S, Mukherjee S, Ganguly J, Abhishek K, Mitras S, Kundu S. A cross-sectional prospective study of pleural effusion among cases of chronic kidney disease. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2013; 55:209–213.5. Berger HW, Rammohan G, Neff MS, Buhain WJ. Uremic pleural effusion. A study in 14 patients on chronic dialysis. Ann Intern Med. 1975; 82:362–364.6. Agusti C, Campistol JM, Xaubet A, Picado C, Cases A, Revert L, et al. Characteristics and evolution of uremic pleural effusion. Med Clin (Barc). 1988; 90:693–695.7. Kim KM, Cho JM, Park HJ, Kim HW, Yang WS, Kim SB, et al. A case of refractory uremic pleuritis improved completely with corticosteroid treatment. Clin Nephrol. 2008; 70:451–452.8. Lee SY, Hong GY, Chung JG, Yang DH, Kim HJ. Refractory uraemic pleuropericarditis treated successfully with corticosteroid therapy. NDT Plus. 2009; 2:473–475.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful treatment of refractory hemolytic uremic syndrome with intravenous gamma-immunoglobulin therapy
- Treatment of a refractory allergic reaction to a red tattoo with the combination of picosecond neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser, fractional carbon dioxide laser, and corticosteroid intralesional injections: a case report
- Evaluation of Steroid Therapy in Tuberculous Pleurisy: A Prospective, randomized study
- Concomitant use of corticosteroid and antimicrobials for liver abscesses in patients with chronic granulomatous disease
- The Effect of Corticosteroid Treatment on Myopic Regression after Laser in situ Keratomileusis[LASIK]