Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Oct;48(4):1443-1447. 10.4143/crt.2016.096.
Severe Hepatic Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome in a Child Receiving Vincristine, Actinomycin-D, and Cyclophosphamide for Rhabdomyosarcoma: Successful Treatment with Defibrotide
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea. junahlee@kcch.re.kr
- KMID: 2356247
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2016.096
Abstract
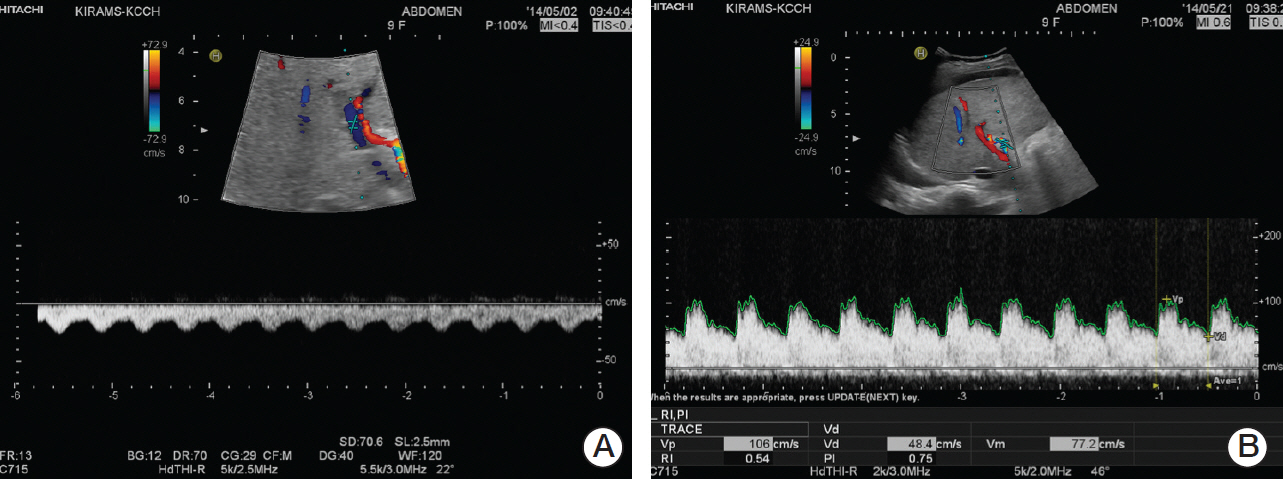
- Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS) is a life-threatening syndrome that generally occurs as a complication after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation or, less commonly, after conventional chemotherapy. Regarding SOS in rhabdomyosarcoma patients who received conventional chemotherapy, the doses of chemotherapeutic agents are associated with the development of SOS. Several cases of SOS in rhabdomyosarcoma patients after receiving chemotherapy with escalated doses of cyclophosphamide have been reported. Here, we report on a 9-year-old female with rhabdomyosarcoma who developed severe SOS after receiving chemotherapy consisting of vincristine, actinomycin-D, and a moderate dose of cyclophosphamide. She was treated successfully with defibrotide without sequelae to the liver.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Carreras E, Diaz-Beya M, Rosinol L, Martinez C, Fernandez-Aviles F, Rovira M, et al. The incidence of veno-occlusive disease following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation has diminished and the outcome improved over the last decade. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011; 17:1713–20.
Article2. Coppell JA, Richardson PG, Soiffer R, Martin PL, Kernan NA, Chen A, et al. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease following stem cell transplantation: incidence, clinical course, and outcome. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010; 16:157–68.
Article3. Richardson PG, Ho VT, Cutler C, Glotzbecker B, Antin JH, Soiffer R. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: novel insights to pathogenesis, current status of treatment, and future directions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013; 19(1 Suppl):S88–90.
Article4. Kotecha RS, Buckland A, Phillips MB, Cole CH, Gottardo NG. Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome during chemotherapy for childhood medulloblastoma: report of a case and review of the literature. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2014; 36:76–80.5. Cesaro S, Pillon M, Talenti E, Toffolutti T, Calore E, Tridello G, et al. A prospective survey on incidence, risk factors and therapy of hepatic veno-occlusive disease in children after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica. 2005; 90:1396–404.6. Gentet JC, Bernard JL, Aimard L, Alfonsi SM, Raybaud C. Veno-occlusive disease in children after intensive chemoand radiotherapy and repeated halothane anesthesias: a report of 2 cases. Acta Oncol. 1988; 27:579–81.
Article7. Wray L, Vujkovic M, McWilliams T, Cannon S, Devidas M, Stork L, et al. TPMT and MTHFR genotype is not associated with altered risk of thioguanine-related sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the Children's Oncology Group. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2014; 61:2086–8.
Article8. Ortega JA, Donaldson SS, Ivy SP, Pappo A, Maurer HM. Venoocclusive disease of the liver after chemotherapy with vincristine, actinomycin D, and cyclophosphamide for the treatment of rhabdomyosarcoma. A report of the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group. Childrens Cancer Group, the Pediatric Oncology Group, and the Pediatric Intergroup Statistical Center. Cancer. 1997; 79:2435–9.9. Arndt C, Hawkins D, Anderson JR, Breitfeld P, Womer R, Meyer W. Age is a risk factor for chemotherapy-induced hepatopathy with vincristine, dactinomycin, and cyclophosphamide. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:1894–901.
Article10. Cecen E, Uysal KM, Ozguven A, Gunes D, Irken G, Olgun N. Veno-occlusive disease in a child with rhabdomyosarcoma after conventional chemotherapy: report of a case and review of the literature. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2007; 24:615–21.
Article11. Senzolo M, Germani G, Cholongitas E, Burra P, Burroughs AK. Veno occlusive disease: update on clinical management. World J Gastroenterol. 2007; 13:3918–24.
Article12. Helmy A. Review article: updates in the pathogenesis and therapy of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 23:11–25.
Article13. Bairey O, Kirgner I, Yakobi M, Hamdan A, Ben-Ari Z, Shaklai M. Clinical severe hepatic venoocclusive disease during induction treatment of acute monoblastic leukemia managed with defibrotide. Am J Hematol. 2002; 69:281–4.
Article14. Bulley SR, Strahm B, Doyle J, Dupuis LL. Defibrotide for the treatment of hepatic veno-occlusive disease in children. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007; 48:700–4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hepatic Veno-occlusive Disease after Combination Chemotherapy with Vincristine, Actinomycin-D, Cyclophosphamide: Successful Treatment with Glutathione and Vitamin E
- A Case of Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma of the External Female Genitalia
- 6-Thioguanine-Induced Hepatic Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome in a Leukemic Child with TPMT Heterozygote
- Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome/veno-occlusive disease after hematopoietic cell transplantation: historical and current considerations in Korea
- A case of bladder rhabdomyosarcoma in an adult