Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Oct;48(4):1338-1350. 10.4143/crt.2015.430.
Association between Mutation and Expression of TP53 as a Potential Prognostic Marker of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. imyh00@skku.edu yhparkhmo@skku.edu
- 2Samsung Genome Institute, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Biomedical Research Institute, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Cancer of Companion Diagnostics, Innovative Cancer Medicine Institute, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Life Science Solutions Group, Thermo Fisher Scientific Corporation, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2356236
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2015.430
Abstract
- PURPOSE
TP53, the most frequently mutated gene in breast cancer, is more frequently altered in HER2-enriched and basal-like breast cancer. However, no studies have clarified the role of TP53 status as a prognostic and predictive marker of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We performed p53 immunohistochemistry (IHC), nCounter mRNA expression assay, and DNA sequencing to determine the relationship between TP53 alteration and clinical outcomes of TNBC patients.
RESULTS
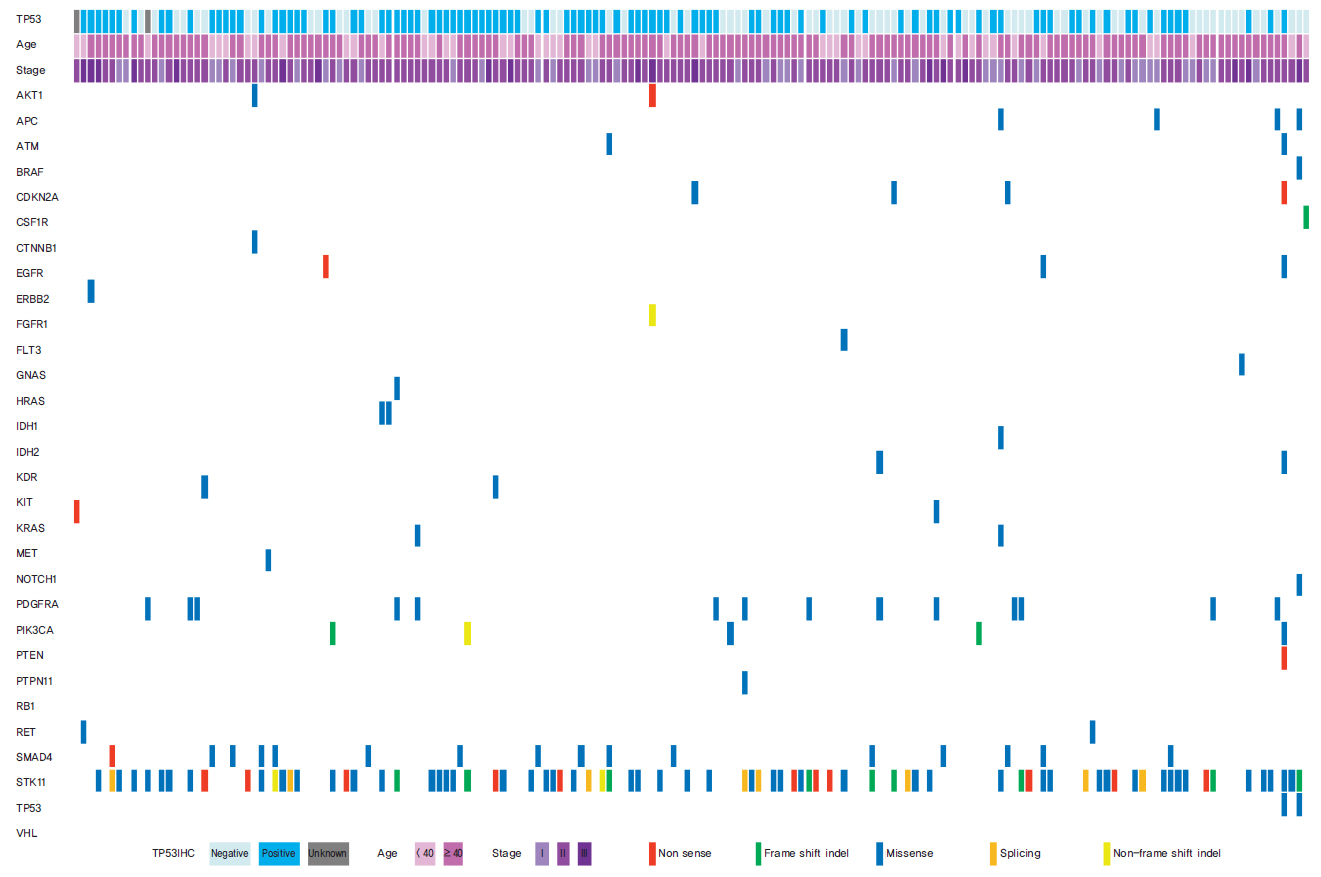
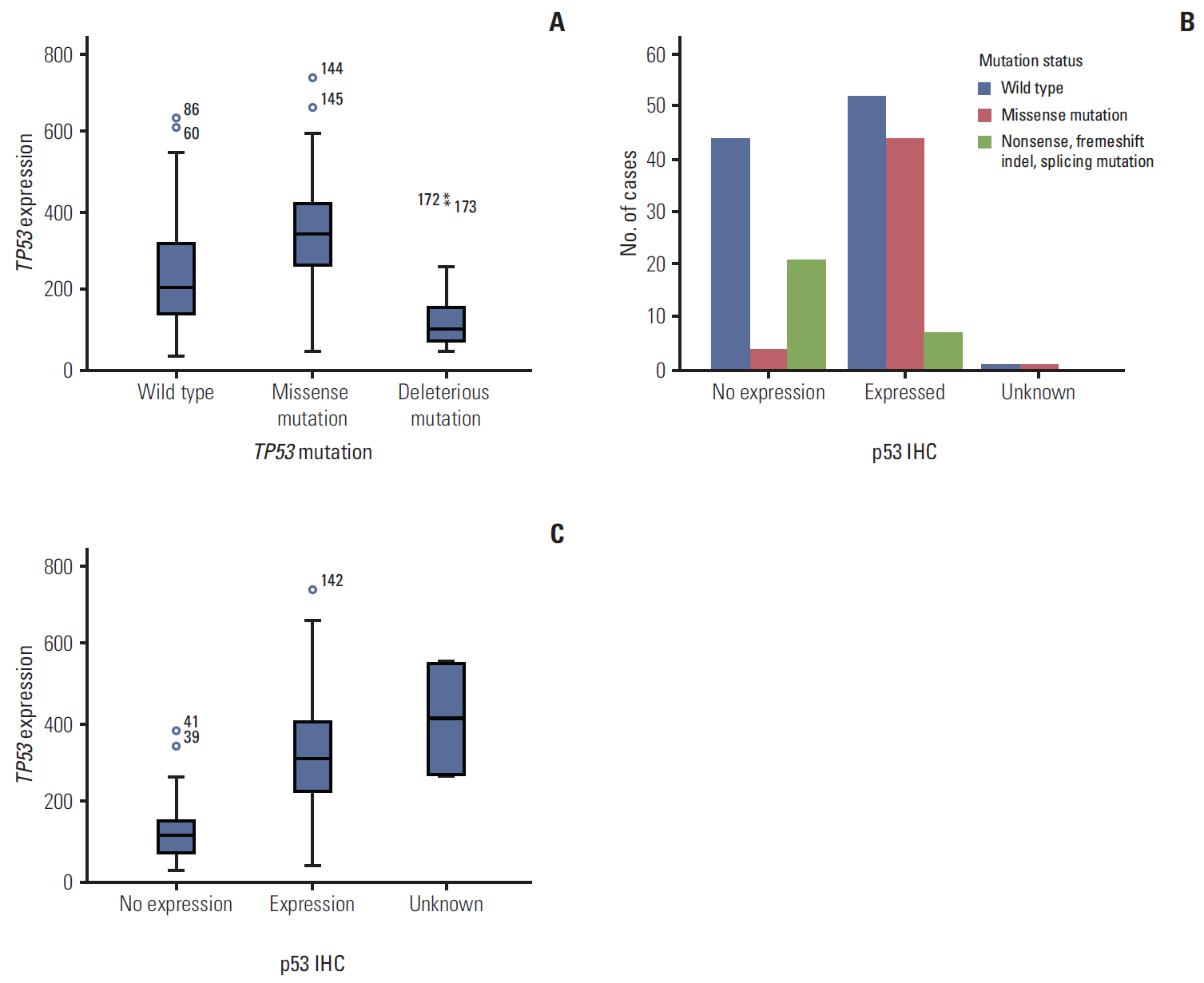
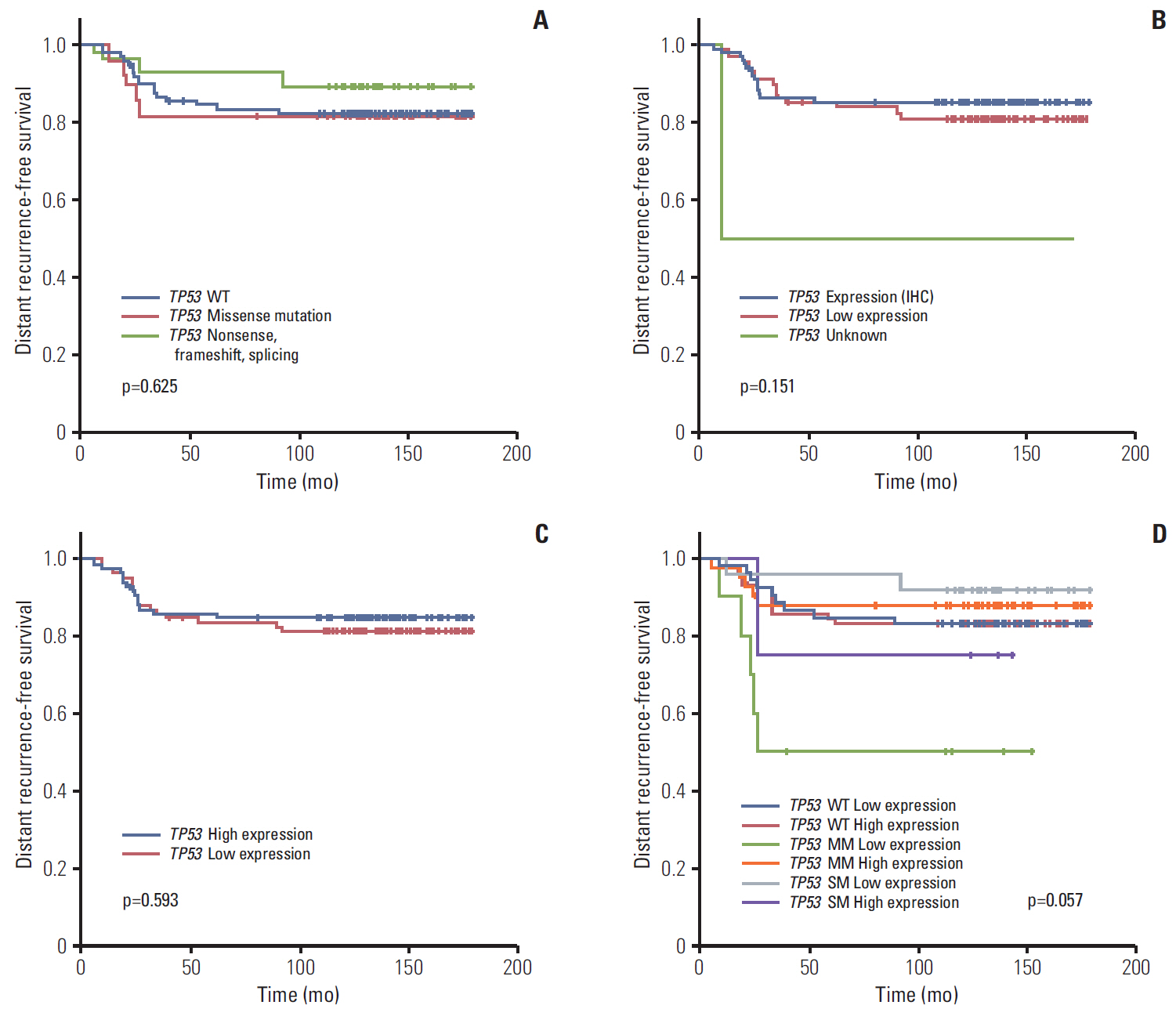
Seventy-seven of 174 TNBC patients were found to harbor a TP53 mutation. Patients with missense mutations showed high protein expression in contrast to patients with deletion mutations (positivity of IHC: wild type vs. missense vs. deletion mutation, 53.6% vs. 89.8% vs. 25.0%, respectively; p < 0.001). TP53 mRNA expression was influenced by mutation status (mRNA expression [median]: wild type vs. missense vs. deletion mutation, 207.36± 132.73 vs. 339.61±143.21 vs. 99.53±99.57, respectively; p < 0.001). According to survival analysis, neither class of mutation nor protein or mRNA expression status had any impact on patient prognosis. In subgroup analysis, low mRNA expression was associated with poor prognosis in patients with a TP53 missense mutation (5-year distant recurrence-free survival [5Y DRFS]: low vs. high, 50.0% vs. 87.8%; p=0.009), while high mRNA expression with a TP53 deletion mutation indicated poor prognosis (5Y DRFS: low vs. high, 91.7% vs. 75.0%; p=0.316).
CONCLUSION
Association between TP53 mutation and expression indicates a potential prognostic marker of TNBC; hence both DNA sequencing and mRNA expression analysis may be required to predict the prognosis of TNBC patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Hainaut P, Hollstein M. p53 and human cancer: the first ten thousand mutations. Adv Cancer Res. 2000; 77:81–137.
Article2. Levine AJ. p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell. 1997; 88:323–31.
Article3. Sigal A, Rotter V. Oncogenic mutations of the p53 tumor suppressor: the demons of the guardian of the genome. Cancer Res. 2000; 60:6788–93.4. Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ. Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 2000; 408:307–10.
Article5. Xu X, Wagner KU, Larson D, Weaver Z, Li C, Ried T, et al. Conditional mutation of Brca1 in mammary epithelial cells results in blunted ductal morphogenesis and tumour formation. Nat Genet. 1999; 22:37–43.
Article6. Jonkers J, Meuwissen R, van der Gulden H, Peterse H, van der Valk M, Berns A. Synergistic tumor suppressor activity of BRCA2 and p53 in a conditional mouse model for breast cancer. Nat Genet. 2001; 29:418–25.
Article7. Malkin D, Li FP, Strong LC, Fraumeni JF Jr, Nelson CE, Kim DH, et al. Germ line p53 mutations in a familial syndrome of breast cancer, sarcomas, and other neoplasms. Science. 1990; 250:1233–8.
Article8. Baker L, Quinlan PR, Patten N, Ashfield A, Birse-Stewart-Bell LJ, McCowan C, et al. p53 mutation, deprivation and poor prognosis in primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2010; 102:719–26.
Article9. Petitjean A, Mathe E, Kato S, Ishioka C, Tavtigian SV, Hainaut P, et al. Impact of mutant p53 functional properties on TP53 mutation patterns and tumor phenotype: lessons from recent developments in the IARC TP53 database. Hum Mutat. 2007; 28:622–9.10. Kato S, Han SY, Liu W, Otsuka K, Shibata H, Kanamaru R, et al. Understanding the function-structure and function-mutation relationships of p53 tumor suppressor protein by high-resolution missense mutation analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003; 100:8424–9.
Article11. Lang GA, Iwakuma T, Suh YA, Liu G, Rao VA, Parant JM, et al. Gain of function of a p53 hot spot mutation in a mouse model of Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Cell. 2004; 119:861–72.
Article12. Zhu J, Sammons MA, Donahue G, Dou Z, Vedadi M, Getlik M, et al. Gain-of-function p53 mutants co-opt chromatin pathways to drive cancer growth. Nature. 2015; 525:206–11.
Article13. Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2012; 490:61–70.14. Eikesdal HP, Knappskog S, Aas T, Lonning PE. TP53 status predicts long-term survival in locally advanced breast cancer after primary chemotherapy. Acta Oncol. 2014; 53:1347–55.15. Miller LD, Smeds J, George J, Vega VB, Vergara L, Ploner A, et al. An expression signature for p53 status in human breast cancer predicts mutation status, transcriptional effects, and patient survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:13550–5.16. Vegran F, Rebucci M, Chevrier S, Cadouot M, Boidot R, Lizard-Nacol S. Only missense mutations affecting the DNA binding domain of p53 influence outcomes in patients with breast carcinoma. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e55103.
Article17. Geiss GK, Bumgarner RE, Birditt B, Dahl T, Dowidar N, Dunaway DL, et al. Direct multiplexed measurement of gene expression with color-coded probe pairs. Nat Biotechnol. 2008; 26:317–25.
Article18. Hong D, Lee J, Bleazard T, Jung H, Ju YS, Yu SB, et al. TIARA genome database: update 2013. Database (Oxford). 2013; 2013:bat003.
Article19. Sidransky D, Tokino T, Helzlsouer K, Zehnbauer B, Rausch G, Shelton B, et al. Inherited p53 gene mutations in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1992; 52:2984–6.20. Coles C, Condie A, Chetty U, Steel CM, Evans HJ, Prosser J. p53 mutations in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1992; 52:5291–8.21. Mazars R, Spinardi L, BenCheikh M, Simony-Lafontaine J, Jeanteur P, Theillet C. p53 mutations occur in aggressive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1992; 52:3918–23.22. Stephens PJ, Tarpey PS, Davies H, Van Loo P, Greenman C, Wedge DC, et al. The landscape of cancer genes and mutational processes in breast cancer. Nature. 2012; 486:400–4.
Article23. Shah SP, Roth A, Goya R, Oloumi A, Ha G, Zhao Y, et al. The clonal and mutational evolution spectrum of primary triple-negative breast cancers. Nature. 2012; 486:395–9.24. Thompson AM, Anderson TJ, Condie A, Prosser J, Chetty U, Carter DC, et al. p53 allele losses, mutations and expression in breast cancer and their relationship to clinico-pathological parameters. Int J Cancer. 1992; 50:528–32.
Article25. Soto-Reyes E, Recillas-Targa F. Epigenetic regulation of the human p53 gene promoter by the CTCF transcription factor in transformed cell lines. Oncogene. 2010; 29:2217–27.
Article26. Saldana-Meyer R, Recillas-Targa F. Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of the p53 tumor suppressor gene. Epigenetics. 2011; 6:1068–77.
Article27. Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME, Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y, et al. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 2011; 121:2750–67.
Article28. Park YH, Jung HH, Do IG, Cho EY, Sohn I, Jung SH, et al. A seven-gene signature can predict distant recurrence in patients with triple-negative breast cancers who receive adjuvant chemotherapy following surgery. Int J Cancer. 2015; 136:1976–84.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Concomitant PIK3CA and TP53 Mutations in Breast Cancer: An Analysis of Clinicopathologic and Mutational Features, Neoadjuvant Therapeutic Response, and Prognosis
- Overexpression of Cell Cycle Progression Inhibitor Geminin is Associated with Tumor Stem-Like Phenotype of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Association between p53 Expression and Amount of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Bilateral Triple-Negative Invasive Breast Cancer with a BRCA2 Mutation, and Glioblastoma: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Somatic Mutations of TP53 Identified by Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Are Poor Prognostic Factors for Primary Operable Breast Cancer: A Single-Center Study