Korean J Pain.
2016 Oct;29(4):270-273. 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.4.270.
Neurogenic muscle hypertrophy: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. saeyoung@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2354221
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2016.29.4.270
Abstract
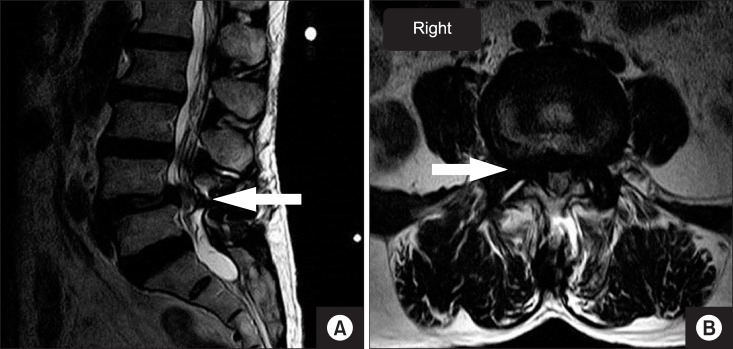
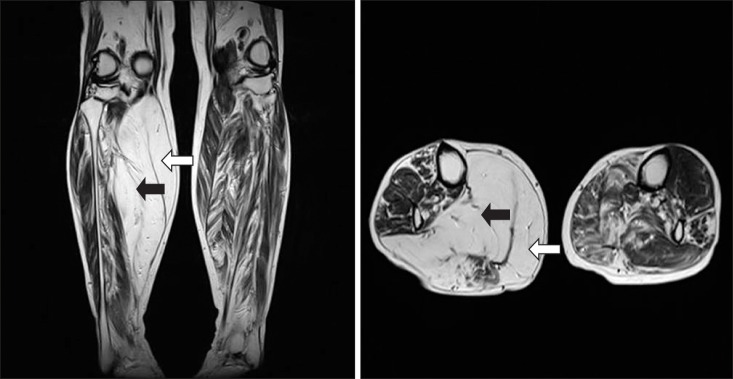
- Muscular hypertrophy is caused mainly due to myopathic disorder. But, it is also rarely produced by neurogenic disorder. A 74-year-old woman complained of right calf pain with hypertrophy for several years. Recent lumbar spine magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed central and lateral canal narrowing at the L4-L5 intervertebral space. Lower extremity MRI revealed fatty change of right medial head of the gastrocnemius and soleus, causing right calf hypertrophy. Electrodiagnostic examinations including electromyography and nerve conduction velocity testing demonstrated 5(th) lumbar and 1(st) sacral polyradiculopathy. Integrating all the results, the diagnosis was neurogenic muscle hypertrophy. Neurogenic muscle hypertrophy is very rare, but we recommend that clinicians consider this problem when a patient complains of lower limb hypertrophy and pain.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gutmann L. AAEM minimonograph #46: neurogenic muscle hypertrophy. Muscle Nerve. 1996; 19:811–818. PMID: 8965832.
Article2. Pareyson D, Morandi L, Scaioli V, Marazzi R, Boiardi A, Sghirlanzoni A. Neurogenic muscle hypertrophy. Report of two cases. J Neurol. 1989; 236:292–295. PMID: 2760647.3. Deffond D, Clavelou P, Colamarino R, Roche C, Dordain G, Tournilhac M. Neurogenic muscle hypertrophy: 3 cases. Rev Neurol (Paris). 1996; 152:272–278. PMID: 8763656.4. Krendel DA, Hedaya EV, Gottleib AJ. Calf enlargement, S1 radiculopathy, and focal myositis. Muscle Nerve. 1992; 15:517–518. PMID: 1565123.5. Heuss D, Schober S, Eberhardt K, Probst-Cousin S, Kayser C, Hecht M, et al. Muscle hypertrophy due to scarring of the S1 nerve root. Neurol Res. 2000; 22:469–472. PMID: 10935218.6. Walcott BP, Nahed BV, Redjal N, Stein TD, Kahle KT, Coumans JV. Pathological mechanism of lumbar disc herniation resulting in neurogenic muscle hypertrophy. J Clin Neurosci. 2011; 18:1682–1684. PMID: 21985744.
Article7. Beydoun SR, Shapiro C, Engel WK. Calf muscle hypertrophy, complex repetitive discharges and spinal stenosis. Muscle Nerve. 1993; 16:322–323. PMID: 8446132.8. Mattle HP, Hess CW, Ludin HP, Mumenthaler M. Isolated muscle hypertrophy as a sign of radicular or peripheral nerve injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991; 54:325–329. PMID: 2056318.
Article9. Liguori R, Fuglsang-Frederiksen A, Nix W, Fawcett PR, Andersen K. Electromyography in myopathy. Neurophysiol Clin. 1997; 27:200–203. PMID: 9260160.
Article10. Garmirian LP, Chin AB, Rutkove SB. Discriminating neurogenic from myopathic disease via measurement of muscle anisotropy. Muscle Nerve. 2009; 39:16–24. PMID: 19058193.
Article11. Swartz KR, Fee DB, Trost GR, Waclawik AJ. Unilateral calf hypertrophy seen in lumbosacral stenosis: case report and review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:E406–E409. PMID: 12634577.12. Lattanzi S, Cagnetti C, Di Bella P, Scarpelli M, Provinciali L, Silvestrini M. Neurogenic muscle hypertrophy. Neurology. 2014; 83:2191. PMID: 25452457.
Article13. Costa J, Graça P, Evangelista T, de Carvalho M. Pain and calf hypertrophy associated with spontaneous repetitive discharges treated with botulinum toxin. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005; 116:2847–2852. PMID: 16256429.
Article14. Hemmi S, Shirakawa S, Kurokawa K, Sunada Y. Unilateral calf hypertrophy and focal myositis induced by S1 radiculopathy: dramatic response to steroid treatment. BMJ Case Rep. 2013; 2013:bcr2013200870.
Article15. Gibson JN, Waddell G. Surgical interventions for lumbar disc prolapse. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007; CD001350.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Induced by Subclavius Muscle Hypertrophy: A Case Report
- Focal Ligamentum Flavum Hypertrophy with Ochronotic Deposits: An Unusual Cause for Neurogenic Claudication in Alkaptonuria
- Pseudohypertrophy of the Calf Muscles in a Patient with Diabetic Neuropathy: A Case Report
- Congenital Bladder Diverticulum Misdiagnosed as Non-neurogenic Neurogenic Bladder
- Restoration of calf deformities in a 35-year-old man following 2 calf reduction surgical procedures