J Breast Cancer.
2014 Mar;17(1):76-82.
Diagnostic Value of Elastography Using Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging and Strain Ratio for Breast Tumors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Busan, Korea. mammomaster@naver.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Busan, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to determine whether the combination of B-mode ultrasonography (BUS), acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography, and strain ratio (SR) provides better diagnostic performance of breast lesion differentiation than BUS alone.
METHODS
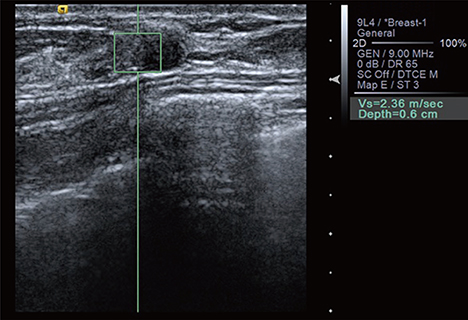
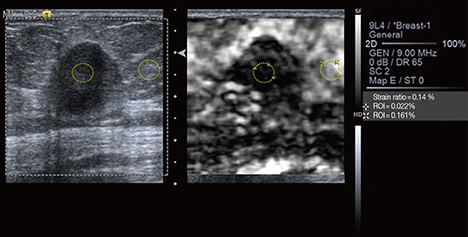
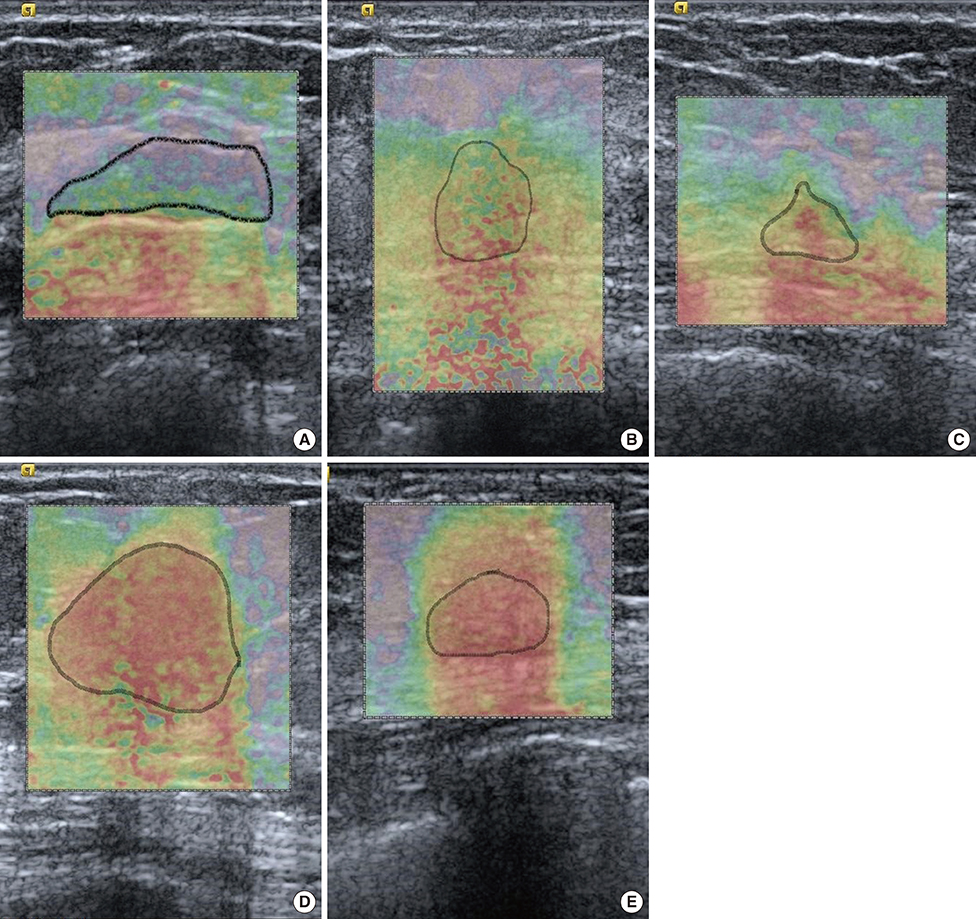
ARFI elastography and SR evaluations were performed on patients with 157 breast lesions diagnosed by BUS from June to September 2013. BUS images were classified according to the Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System. ARFI elastography was performed using Virtual Touch(TM) tissue imaging (VTI) and Virtual Touch(TM) tissue quantification (VTQ). In VTI mode, we evaluated the color-mapped patterns of the breast lesion and surrounding tissue. The lesions were classified into five categories by elasticity score. In VTQ mode, each lesion was assessed using shear wave velocity (SWV) measurements. SR was calculated from the lesion and comparable lateral fatty tissue. We compared the diagnostic performance of BUS alone and the combination of BUS, ARFI elastography, and SR evaluations.
RESULTS
Among the 157 lesions, 40 were malignant and 117 were benign. The mean elasticity score (3.7+/-1.0 vs. 1.6+/-0.8, p<0.01), SWV (4.23+/-1.09 m/sec vs. 2.22+/-0.88 m/sec, p<0.01), and SR (5.69+/-1.63 vs. 2.69+/-1.40, p<0.01) were significantly higher for malignant lesions than benign lesions. The results for BUS combined with ARFI elastography and SR values were 97.5% sensitivity, 92.3% specificity, 93.6% accuracy, a 79.6% positive predictive value (PPV), and a 99.1% negative predictive value. The combination of the 3 radiologic examinations yielded superior specificity, accuracy, and PPV compared to BUS alone (p<0.01 for each).
CONCLUSION
ARFI elastography and SR evaluations showed significantly different mean values for benign and malignant lesions. Moreover, these two modalities complemented BUS and improved the diagnostic performance of breast lesion detection. Therefore, ARFI elastography and SR evaluations can be used as complementary modalities to make more accurate breast lesion diagnoses.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:2137–2150.
Article2. Lee JH, Shim JW, Choi YJ, Heo K, Yang K. The combination of sorafenib and radiation preferentially inhibits breast cancer stem cells by suppressing HIF-1α expression. Oncol Rep. 2013; 29:917–924.
Article3. Bai M, Du L, Gu J, Li F, Jia X. Virtual touch tissue quantification using acoustic radiation force impulse technology: initial clinical experience with solid breast masses. J Ultrasound Med. 2012; 31:289–294.
Article4. Stavros AT, Thickman D, Rapp CL, Dennis MA, Parker SH, Sisney GA. Solid breast nodules: use of sonography to distinguish between benign and malignant lesions. Radiology. 1995; 196:123–134.
Article5. Reinikainen H, Rissanen T, Päivänsalo M, Pääkkö E, Jauhiainen J, Suramo I. B-mode, power Doppler and contrast-enhanced power Doppler ultrasonography in the diagnosis of breast tumors. Acta Radiol. 2001; 42:106–113.
Article6. Athanasiou A, Tardivon A, Tanter M, Sigal-Zafrani B, Bercoff J, Deffieux T, et al. Breast lesions: quantitative elastography with supersonic shear imaging--preliminary results. Radiology. 2010; 256:297–303.
Article7. Berg WA. Supplemental screening sonography in dense breasts. Radiol Clin North Am. 2004; 42:845–851.
Article8. Corsetti V, Ferrari A, Ghirardi M, Bergonzini R, Bellarosa S, Angelini O, et al. Role of ultrasonography in detecting mammographically occult breast carcinoma in women with dense breasts. Radiol Med. 2006; 111:440–448.
Article9. Goddi A, Bonardi M, Alessi S. Breast elastography: a literature review. J Ultrasound. 2012; 15:192–198.
Article10. Zhi H, Ou B, Xiao XY, Peng YL, Wang Y, Liu LS, et al. Ultrasound elastography of breast lesions in chinese women: a multicenter study in China. Clin Breast Cancer. 2013; 13:392–400.
Article11. Meng W, Zhang G, Wu C, Wu G, Song Y, Lu Z. Preliminary results of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) ultrasound imaging of breast lesions. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2011; 37:1436–1443.
Article12. Chang JM, Won JK, Lee KB, Park IA, Yi A, Moon WK. Comparison of shear-wave and strain ultrasound elastography in the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 201:W347–W356.
Article13. Tozaki M, Isobe S, Sakamoto M. Combination of elastography and tissue quantification using the acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) technology for differential diagnosis of breast masses. Jpn J Radiol. 2012; 30:659–670.
Article14. Balleyguier C, Canale S, Ben Hassen W, Vielh P, Bayou EH, Mathieu MC, et al. Breast elasticity: principles, technique, results: an update and overview of commercially available software. Eur J Radiol. 2013; 82:427–434.
Article15. Chang JM, Moon WK, Cho N, Yi A, Koo HR, Han W, et al. Clinical application of shear wave elastography (SWE) in the diagnosis of benign and malignant breast diseases. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 129:89–97.
Article16. Jin ZQ, Li XR, Zhou HL, Chen JX, Huang X, Dai HX, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography of breast imaging reporting and data system category 4 breast lesions. Clin Breast Cancer. 2012; 12:420–427.
Article17. Gong X, Xu Q, Xu Z, Xiong P, Yan W, Chen Y. Real-time elastography for the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions: a metaanalysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 130:11–18.
Article18. Zhao QL, Ruan LT, Zhang H, Yin YM, Duan SX. Diagnosis of solid breast lesions by elastography 5-point score and strain ratio method. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:3245–3249.
Article19. Zhi H, Xiao XY, Yang HY, Ou B, Wen YL, Luo BM. Ultrasonic elastography in breast cancer diagnosis: strain ratio vs 5-point scale. Acad Radiol. 2010; 17:1227–1233.20. Sohn YM, Kim MJ, Kim EK, Kwak JY, Moon HJ, Kim SJ. Sonographic elastography combined with conventional sonography: how much is it helpful for diagnostic performance? J Ultrasound Med. 2009; 28:413–420.21. Cho N, Moon WK, Kim HY, Chang JM, Park SH, Lyou CY. Sonoelastographic strain index for differentiation of benign and malignant nonpalpable breast masses. J Ultrasound Med. 2010; 29:1–7.
Article22. Thomas A, Degenhardt F, Farrokh A, Wojcinski S, Slowinski T, Fischer T. Significant differentiation of focal breast lesions: calculation of strain ratio in breast sonoelastography. Acad Radiol. 2010; 17:558–563.23. Itoh A, Ueno E, Tohno E, Kamma H, Takahashi H, Shiina T, et al. Breast disease: clinical application of US elastography for diagnosis. Radiology. 2006; 239:341–350.
Article24. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977; 33:159–174.
Article25. Gheonea IA, Stoica Z, Bondari S. Differential diagnosis of breast lesions using ultrasound elastography. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2011; 21:301–305.
Article26. Tozaki M, Isobe S, Fukuma E. Preliminary study of ultrasonographic tissue quantification of the breast using the acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) technology. Eur J Radiol. 2011; 80:e182–e187.
Article27. Youk JH, Kim EK, Kim MJ, Kwak JY, Son EJ. Analysis of false-negative results after US-guided 14-gauge core needle breast biopsy. Eur Radiol. 2010; 20:782–789.
Article28. Youk JH, Kim EK, Kim MJ, Oh KK. Sonographically guided 14-gauge core needle biopsy of breast masses: a review of 2,420 cases with longterm follow-up. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:202–207.
Article29. Evans A, Whelehan P, Thomson K, McLean D, Brauer K, Purdie C, et al. Invasive breast cancer: relationship between shear-wave elastographic findings and histologic prognostic factors. Radiology. 2012; 263:673–677.
Article30. Yoon JH, Kim MJ, Kim EK, Moon HJ, Choi JS. Discordant elastography images of breast lesions: how various factors lead to discordant findings. Ultraschall Med. 2013; 34:266–271.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum: Diagnostic Value of Elastography Using Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging and Strain Ratio for Breast Tumors
- Future of breast elastography
- Ultrasound elastography for thyroid nodules: recent advances
- Advances in ultrasound elasticity imaging
- Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography for Focal Hepatic Tumors: Usefulness for Differentiating Hemangiomas from Malignant Tumors