Yonsei Med J.
2015 Jan;56(1):227-234. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.1.227.
A Polymorphism of the Renin Gene rs6682082 Is Associated with Essential Hypertension Risk and Blood Pressure Levels in Korean Women
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Life Science, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. sjkyoon@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biostatistics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Cardiovascular Genome Center, Cardiovascular Yonsei University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2352811
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.1.227
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of the present study was to investigate associations between the renin gene (REN) and the risk of essential hypertension and blood pressure (BP) levels in Koreans.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
To outline the functional role of a single nucleotide polymorphism in the transcription of the REN gene, we conducted a case-control study of 1975 individuals: 646 hypertension (HT) patients and 1329 ethnically and age-matched normotensive subjects.
RESULTS
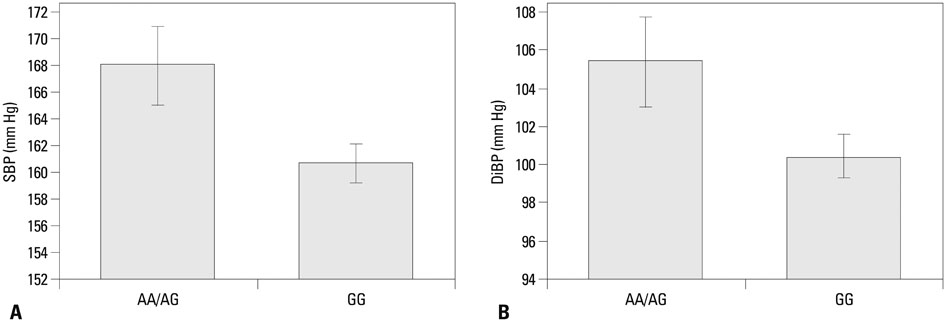
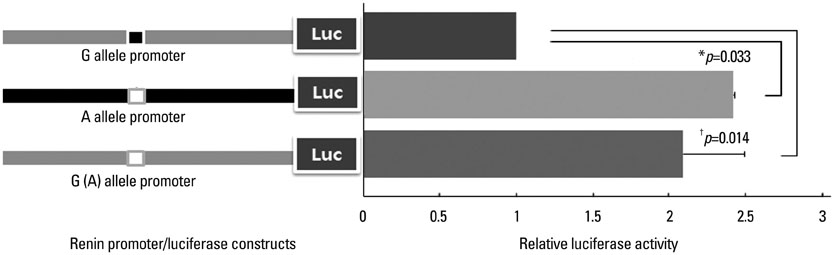
Logistic regression analysis indicated that the genotypes AA/AG were strongly associated with risk of HT (odds ratio, 1.493; 95% confidence interval, 1.069-2.086, p=0.018) in female subjects. The genotypes AA/AG also showed significant association with higher blood pressure levels, both systolic and diastolic, in postmenopausal HT women (p=0.003 and p=0.017, respectively). Analysis of the promoter containing rs6682082 revealed a 2.4+/-0.01-fold higher activity in the A variant promoter than the G variant promoter, suggesting that rs6682082 is itself a functional variant.
CONCLUSION
We suggest that the A allele of rs6682082 is a positive genetic marker for predisposition to essential hypertension and high BP in Korean women and may be mediated through the transcriptional activation of REN.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Alleles
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/*genetics
Blood Pressure/*genetics
Case-Control Studies
Diastole/genetics
Female
Gene Frequency
*Genetic Association Studies
*Genetic Predisposition to Disease
Humans
Hypertension/*genetics/*physiopathology
Luciferases/metabolism
Middle Aged
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide/*genetics
Promoter Regions, Genetic/genetics
Renin/*genetics
Republic of Korea
Risk Factors
Systole/genetics
Transfection
Luciferases
Renin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Williams FM, Cherkas LF, Spector TD, MacGregor AJ. A common genetic factor underlies hypertension and other cardiovascular disorders. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2004; 4:20.
Article2. Staessen JA, Wang J, Bianchi G, Birkenhäger WH. Essential hypertension. Lancet. 2003; 361:1629–1641.
Article3. Song SB, Jin HS, Hong KW, Lim JE, Moon JY, Jeong KH, et al. Association between renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system-related genes and blood pressure in a Korean population. Blood Press. 2011; 20:204–210.
Article4. Morales-Suárez-Varela MM, Mansego ML, Vicedo-Cabrera AM, Pineda-Alonso M, Llopis-González A, Martin-Moreno JM, et al. Inefficient arterial hypertension control in patients with metabolic syndrome and its link to renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system polymorphisms. Hypertens Res. 2011; 34:758–766.
Article5. Ji L, Cai X, Zhang L, Fei L, Wang L, Su J, et al. Association between polymorphisms in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system genes and essential hypertension in the Han Chinese population. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e72701.
Article6. Kelly TN, Takeuchi F, Tabara Y, Edwards TL, Kim YJ, Chen P, et al. Genome-wide association study meta-analysis reveals transethnic replication of mean arterial and pulse pressure loci. Hypertension. 2013; 62:853–859.
Article7. Ichikawa M, Konoshita T, Nakaya T, Yamamoto K, Yamada M, Sato S, et al. Genetic variant of the renin-angiotensin system and prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a modest but significant effect of aldosterone synthase. Acta Diabetol. 2014; 51:595–599.
Article8. Griendling KK, Murphy TJ, Alexander RW. Molecular biology of the renin-angiotensin system. Circulation. 1993; 87:1816–1828.
Article9. Morris BJ, Griffiths LR. Frequency in hypertensives of alleles for a RFLP associated with the renin gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988; 150:219–224.
Article10. Jeunemaitre X, Rigat B, Charru A, Houot AM, Soubrier F, Corvol P. Sib pair linkage analysis of renin gene haplotypes in human essential hypertension. Hum Genet. 1992; 88:301–306.
Article11. Afruza R, Islam LN, Banerjee S, Hassan MM, Suzuki F, Nabi AN. Renin gene polymorphisms in bangladeshi hypertensive population. J Genomics. 2014; 2:45–53.
Article12. Mansego ML, Redon J, Marin R, González-Albert V, Martin-Escudero JC, Fabia MJ, et al. Renin polymorphisms and haplotypes are associated with blood pressure levels and hypertension risk in postmenopausal women. J Hypertens. 2008; 26:230–237.
Article13. Frossard PM, Lestringant GG, Malloy MJ, Kane JP. Human renin gene BglI dimorphism associated with hypertension in two independent populations. Clin Genet. 1999; 56:428–433.
Article14. Qi Y, Niu W, Cen W, Cui C, Zhuoma C, Zhuang L, et al. Strong association of the renin TaqI polymorphism with essential hypertension in Chinese Han and Tibetan populations. J Hum Hypertens. 2007; 21:907–910.
Article15. Ying CQ, Wang YH, Wu ZL, Fang MW, Wang J, Li YS, et al. Association of the renin gene polymorphism, three angiotensinogen gene polymorphisms and the haplotypes with essential hypertension in the Mongolian population. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2010; 32:293–300.
Article16. Mohana Vamsi U, Swapna N, Usha G, Vishnupriya S, Padma T. Contribution of REN gene MBbo I polymorphism in conferring risk for essential hypertension: a case control study from South India. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2013; 14:242–247.
Article17. Niu W, Qi Y, Guo S, Gao P, Zhu D. Association of renin BglI polymphism with essential hypertension: a meta-analysis involving 1811 cases and 1626 controls. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2010; 32:431–438.
Article18. Sun B, Williams JS, Pojoga L, Chamarthi B, Lasky-Su J, Raby BA, et al. Renin gene polymorphism: its relationship to hypertension, renin levels and vascular responses. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2011; 12:564–571.
Article19. Fuchs S, Philippe J, Germain S, Mathieu F, Jeunemaitre X, Corvol P, et al. Functionality of two new polymorphisms in the human renin gene enhancer region. J Hypertens. 2002; 20:2391–2398.
Article20. Borensztein P, Germain S, Fuchs S, Philippe J, Corvol P, Pinet F. cis-regulatory elements and trans-acting factors directing basal and cAMP-stimulated human renin gene expression in chorionic cells. Circ Res. 1994; 74:764–773.
Article21. Konoshita T, Makino Y, Wakahara S, Ido K, Yoshida M, Kawai Y, et al. Candidate cis-elements for human renin gene expression in the promoter region. J Cell Biochem. 2004; 93:327–336.
Article22. Germain S, Konoshita T, Philippe J, Corvol P, Pinet F. Transcriptional induction of the human renin gene by cyclic AMP requires cyclic AMP response element-binding protein (CREB) and a factor binding a pituitary-specific trans-acting factor (Pit-1) motif. Biochem J. 1996; 316(Pt 1):107–113.
Article23. Germain S, Konoshita T, Fuchs S, Philippe J, Corvol P, Pinet F. Regulation of human renin gene transcription by cAMP. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1997; 19:543–550.
Article24. Moore N, Dicker P, O'Brien JK, Stojanovic M, Conroy RM, Treumann A, et al. Renin gene polymorphisms and haplotypes, blood pressure, and responses to renin-angiotensin system inhibition. Hypertension. 2007; 50:340–347.
Article25. Itani HA, Liu X, Pratt JH, Sigmund CD. Functional characterization of polymorphisms in the kidney enhancer of the human renin gene. Endocrinology. 2007; 148:1424–1430.
Article26. Kim BK, Lee HY, Choi JH, Kim JK, Yoon JB, Yoon SK. Hairless plays a role in formation of inner root sheath via regulation of Dlx3 gene. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287:16681–16688.
Article27. Tanimoto K, Sugiura A, Kanafusa S, Saito T, Masui N, Yanai K, et al. A single nucleotide mutation in the mouse renin promoter disrupts blood pressure regulation. J Clin Invest. 2008; 118:1006–1016.
Article28. Niu W, Qi Y, Hou S, Zhai X, Zhou W, Qiu C. Haplotype-based association of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system genes polymorphisms with essential hypertension among Han Chinese: the Fangshan study. J Hypertens. 2009; 27:1384–1391.
Article29. Barley J, Carter ND, Cruickshank JK, Jeffery S, Smith A, Charlett A, et al. Renin and atrial natriuretic peptide restriction fragment length polymorphisms: association with ethnicity and blood pressure. J Hypertens. 1991; 9:993–996.
Article30. Morales-Suárez-Varela MM, Mansego ML, Martín-Escudero JC, Llopis-González A, Chaves FJ, López-Izquierdo R, et al. How ineffective hypertension control in subjects treated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors is related to polymorphisms in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2010; 39:380–386.
Article31. Coylewright M, Reckelhoff JF, Ouyang P. Menopause and hypertension: an age-old debate. Hypertension. 2008; 51:952–959.32. Reckelhoff JF, Fortepiani LA. Novel mechanisms responsible for postmenopausal hypertension. Hypertension. 2004; 43:918–923.
Article33. Yanes LL, Romero DG, Iliescu R, Zhang H, Davis D, Reckelhoff JF. Postmenopausal hypertension: role of the Renin-Angiotensin system. Hypertension. 2010; 56:359–363.34. Bowles J, Schepers G, Koopman P. Phylogeny of the SOX family of developmental transcription factors based on sequence and structural indicators. Dev Biol. 2000; 227:239–255.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fok I and Bsm I gene polymorphism of vitamin D receptor and essential hypertension: a mechanistic link
- Angiotensinogen gene M235T polymorphism as a predictor of cardiovascular risk in hypertensive adolescents
- Relationships among Ambulatory Plasma Renin Activity, Blood Pressure and Urinary Microalbumin Excretion Rate in Essential Hypertension
- Essential Hypertension and renal role: Low renin hypertension
- Percutaneous transluminal angiography of renal arterial stenosis