Korean J Crit Care Med.
2016 Aug;31(3):251-255. 10.4266/kjccm.2016.00143.
Brain Oxygen Monitoring via Jugular Venous Oxygen Saturation in a Patient with Fulminant Hepatic Failure
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. sangbai1378@gmail.com
- KMID: 2350910
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/kjccm.2016.00143
Abstract
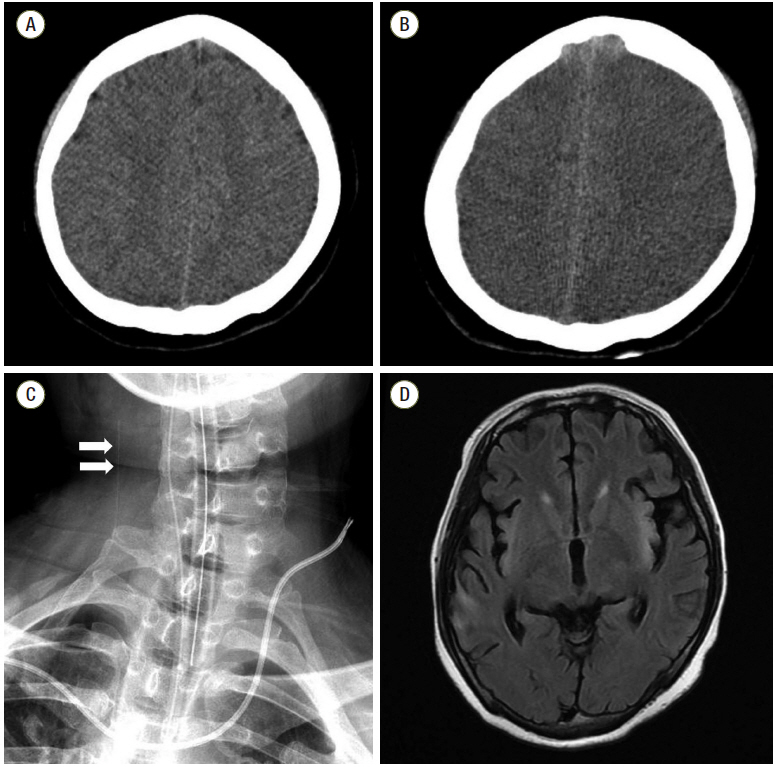
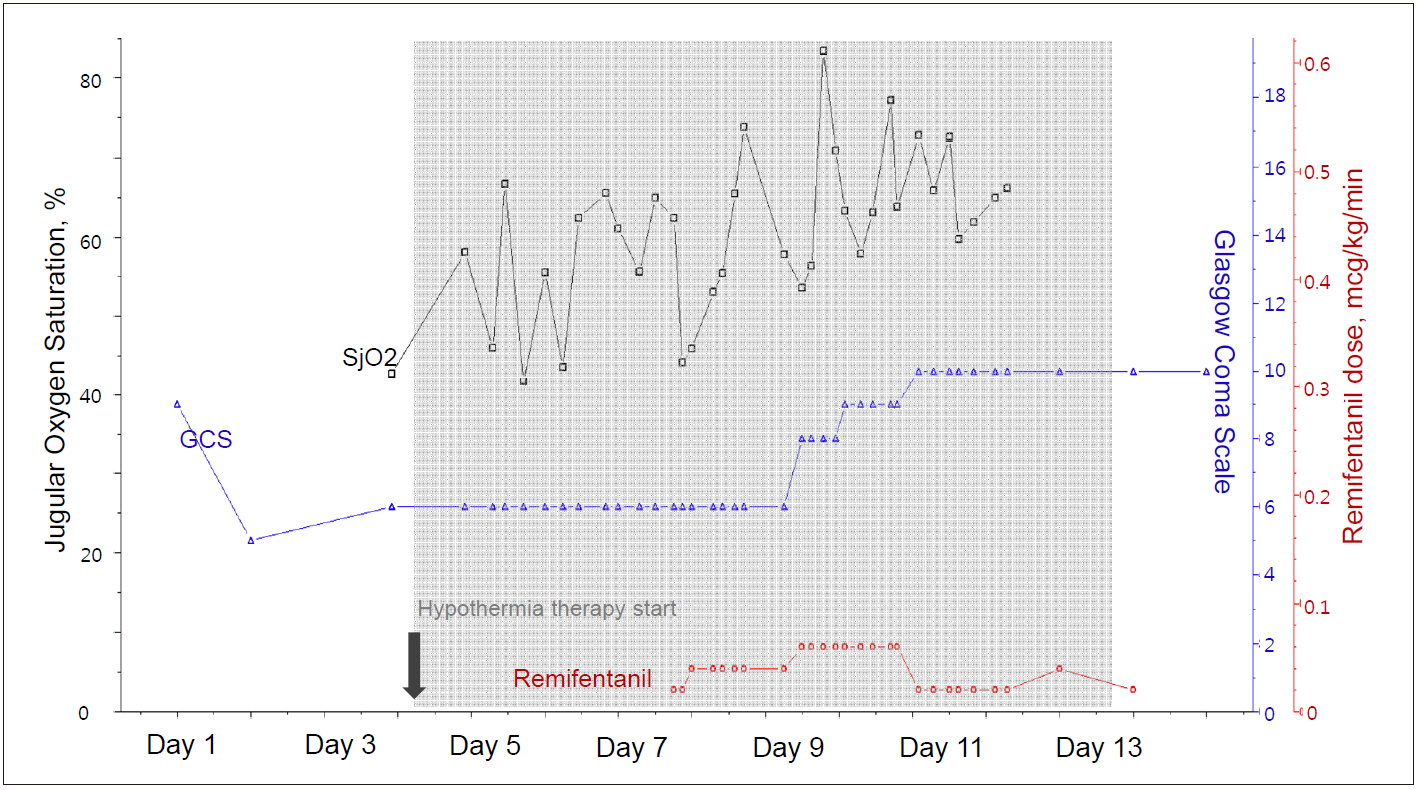
- Fulminant hepatic failure (FHF) is often accompanied by a myriad of neurologic complications, which are associated with high morbidity and mortality. Although appropriate neuromonitoring is recommended for early diagnosis and to minimize secondary brain injury, individuals with FHF usually have a high chance of coagulopathy, which limits the ability to use invasive neuromonitoring. Jugular bulb venous oxygen saturation (JvOâ‚‚) monitoring is well known as a surrogate direct measures of global brain oxygen use. We report the case of a patient with increased intracranial pressure due to FHF, in which JvOâ‚‚ was used for appropriate brain oxygen monitoring.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Bleeding complications associated with the molecular adsorbent recirculating system: a retrospective study
Seon Woo Yoo, Min-Jong Ki, Dal Kim, Seul Ki Kim, SeungYong Park, Hyo Jin Han, Heung Bum Lee
Acute Crit Care. 2021;36(4):322-331. doi: 10.4266/acc.2021.00276.
Reference
-
References
1. Detry O, De Roover A, Honore P, Meurisse M. Brain edema and intracranial hypertension in fulminant hepatic failure: pathophysiology and management. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:7405–12.
Article2. Wendon JA, Larsen FS. Intracranial pressure monitoring in acute liver failure. A procedure with clear indications. Hepatology. 2006; 44:504–6.
Article3. Schell RM, Cole DJ. Cerebral monitoring: jugular venous oximetry. Anesth Analg. 2000; 90:559–66.
Article4. Macmillan CS, Andrews PJ. Cerebrovenous oxygen saturation monitoring: practical considerations and clinical relevance. Intensive Care Med. 2000; 26:1028–36.
Article5. Ellis A, Wendon J. Circulatory, respiratory, cerebral, and renal derangements in acute liver failure: pathophysiology and management. Semin Liver Dis. 1996; 16:379–88.
Article6. Jalan R, Olde Damink SW, Deutz NE, Hayes PC, Lee A. Restoration of cerebral blood flow autoregulation and reactivity to carbon dioxide in acute liver failure by moderate hypothermia. Hepatology. 2001; 34:50–4.
Article7. Roberts DJ, Zygun DA. Comparative efficacy and safety of sedative agents in severe traumatic brain injury. Annual Update in Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine. 1st ed. In : Vincent JL, editor. Berlin: Springer;2012. p. 771–82.8. van Bommel J, Trouwborst A, Schwarte L, Siegemund M, Ince C, Henny ChP. Intestinal and cerebral oxygenation during severe isovolemic hemodilution and subsequent hyperoxic ventilation in a pig model. Anesthesiology. 2002; 97:660–70.
Article9. Yoshitani K, Kawaguchi M, Iwata M, Sasaoka N, Inoue S, Kurumatani N, et al. Comparison of changes in jugular venous bulb oxygen saturation and cerebral oxygen saturation during variations of haemoglobin concentration under propofol and sevoflurane anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 2005; 94:341–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anesthesia for Liver Transplantation in Patients with Fulminant Hepatic Failure under Intracranial Pressure and Jugular Venous Oxygen Saturation Monitoring
- Jugular Bulb Venous Oxygen Saturation Monitoring in Brain Surgery
- Continuous Monitoring of Jugular Venous Oxygen Saturation in Severe Head-injured Patients
- Comparison of Gas Analysis in Arterial and Venous Blood during Inspiration of High Oxygen Concentration
- The Effects of CO2 Insufflation on Jugular Bulb Venous Blood Oxygen Saturation during Thoracoscopy