Patient Radiation Exposure During Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures for Intracranial Aneurysms: A Multicenter Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, St.Vincent's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. bumrad@catholic.ac.kr
- 3Department of Radiology, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Radiology, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
- 6Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Radiology, Severance Hospital Stroke Center, Yonsei Unviersity College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Neurosurgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea.
- 9Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 10Department of Radiology, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea.
- 11Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 12Department of Radiology, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 13Department of Radiology, Wonkwang University Hospital, Iksan, Korea.
- 14Department of Radiology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
- 15Department of Radiology, Keimyung University College of Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu, Korea.
- 16Department of Radiology, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
- 17Department of Radiology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
- 18Department of Radiology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 19Department of Radiology, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea.
- 20Department of Radiology, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 21Department of Radiology, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 22Department of Radiology, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
- 23Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2350684
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2016.11.2.78
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To assess patient radiation doses during cerebral angiography and embolization of intracranial aneurysms across multi-centers and propose a diagnostic reference level (DRL).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We studied a sample of 490 diagnostic and 371 therapeutic procedures for intracranial aneurysms, which were performed at 23 hospitals in Korea in 2015. Parameters including dose-area product (DAP), cumulative air kerma (CAK), fluoroscopic time and total angiographic image frames were obtained and analyzed.
RESULTS
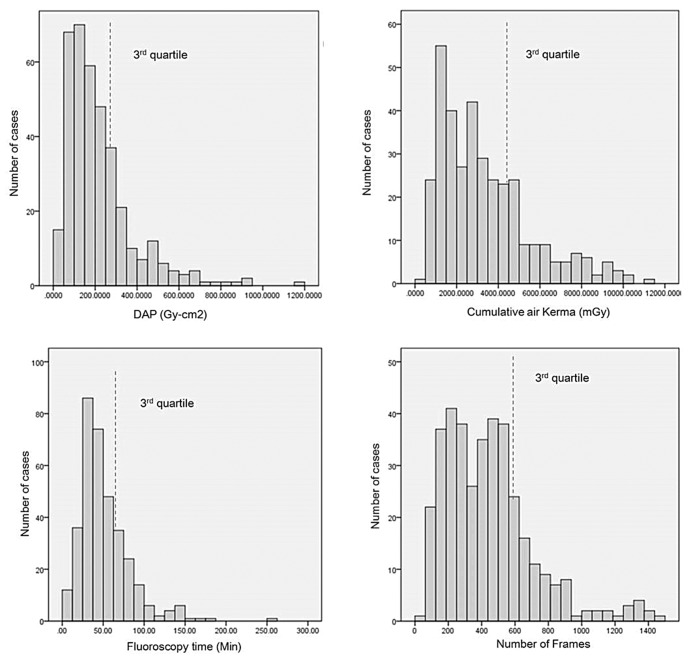
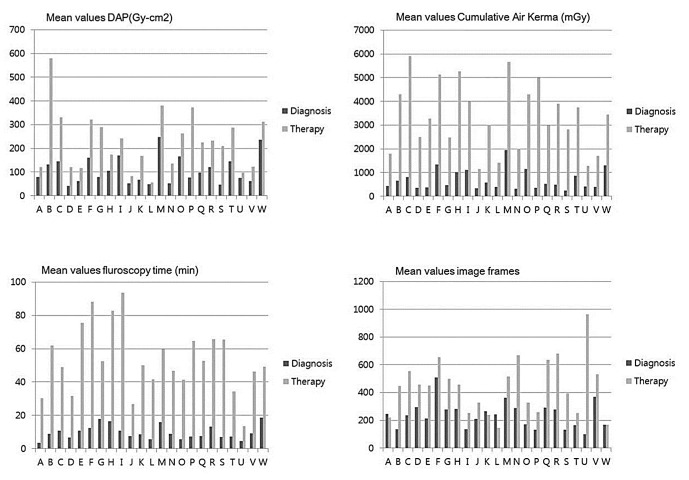
Total mean DAP, CAK, fluoroscopy time, and total angiographic image frames were 106.2 ± 66.4 Gy-cm2, 697.1 ± 473.7 mGy, 9.7 ± 6.5 minutes, 241.5 ± 116.6 frames for diagnostic procedures, 218.8 ± 164.3 Gy-cm², 3365.7 ± 2205.8 mGy, 51.5 ± 31.1 minutes, 443.5 ± 270.7 frames for therapeutic procedures, respectively. For diagnostic procedure, the third quartiles for DRLs were 144.2 Gy-cm² for DAP, 921.1 mGy for CAK, 12.2 minutes for fluoroscopy times and 286.5 for number of image frames, respectively. For therapeutic procedures, the third quartiles for DRLs were 271.0 Gy-cm² for DAP, 4471.3 mGy for CAK, 64.7 minutes for fluoroscopy times and 567.3 for number of image frames, respectively. On average, rotational angiography was used 1.5 ± 0.7 times/session (range, 0-4; n=490) for diagnostic procedures and 1.6 ± 1.2 times/session (range, 0-4; n=368) for therapeutic procedures, respectively.
CONCLUSION
Radiation dose as measured by DAP, fluoroscopy time and image frames were lower in our patients compared to another study regarding cerebral angiography, and DAP was lower with fewer angiographic image frames for therapeutic procedures. Proposed DRLs can be used for quality assurance and patient safety in diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Low-Dose Fluoroscopy Protocol for Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography
Yunsun Song, Seongsik Han, Byung Jun Kim, Seong Heum Oh, Jin Su Kim, Tae Il Kim, Deok Hee Lee
Neurointervention. 2020;15(2):67-73. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2020.00129.Monitoring Radiation Doses during Diagnostic and Therapeutic Neurointerventional Procedures: Multicenter Study for Establishment of Reference Levels
Yon-Kwon Ihn, Bum-soo Kim, Hae Woong Jeong, Sang Hyun Suh, Yoo Dong Won, Young-Jun Lee, Dong Joon Kim, Pyong Jeon, Chang-Woo Ryu, Sang-il Suh, Dae Seob Choi, See Sung Choi, Sang Heum Kim, Jun Soo Byun, Jieun Rho, Yunsun Song, Woo Sang Jeong, Noah Hong, Sung Hyun Baik, Jeong Jin Park, Soo Mee Lim, Jung-Jae Kim, Woong Yoon
Neurointervention. 2021;16(3):240-251. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2021.00437.
Reference
-
1. Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Yu LM, Clarke M, Sneade M, Yarnold JA, et al. International subarachnoid aneurysm trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised comparison of effects on survival, dependency, seizures, rebleeding, subgroups, and aneurysm occlusion. Lancet. 2005; 366:809–817. PMID: 16139655.
Article2. Norbash AM, Busick D, Marks MP. Techniques for reducing interventional neuroradiologic skin dose: tube position rotation and supplemental beam filtration. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996; 17:41–49. PMID: 8770248.3. Suzuki S, Furui S, Matsumaru Y, Nobuyuki S, Ebara M, Abe T, et al. Patient skin dose during neuroembolization by multiple-point measurement using a radiosensitive indicator. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:1076–1081. PMID: 18388215.
Article4. ICRP 103: the 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. Ann ICRP. 2007; 37(2-4):1–332.5. Chung JW. Korea Food & Drug Administration. Evaluation of patient dose in interventional radiology. Seoul: Korea Food & Drug Administration;2007.6. Chun CW, Kim BS, Lee CH, Ihn YK, Shin YS. Patient radiation dose in diagnostic and interventional procedures for intracranial aneurysms: experience at a single center. Korean J Radiol. 2014; 15:844–849. PMID: 25469098.
Article7. Aroua A, Rickli H, Stauffer JC, Schnyder P, Trueb PR, Valley JF, et al. How to set up and apply reference levels in fluoroscopy at a national level. Eur Radiol. 2007; 17:1621–1633. PMID: 17072616.
Article8. Bogaert E, Bacher K, Lemmens K, Carlier M, Desmet W, De Wagter X, et al. A large-scale multicentre study of patient skin doses in interventional cardiology; dose-area product action levels and dose reference levels. Br J Radiol. 2009; 82:303–312. PMID: 19124567.
Article9. D'Ercole L, Thyrion FZ, Bocchiola M, Mantovani L, Klersy C. Proposed local diagnostic reference levels in angiography and interventional neuroradiology and a preliminary analysis according to the complexity of procedures. Phys Med. 2012; 28:61–70. PMID: 21074469.10. Brambilla M, Marano G, Dominietto M, Cotroneo AR, Carriero A. Patient radiation doses and references levels in interventional radiology. Radiol Med. 2004; 107:408–418. PMID: 15103292.11. Miller DL, Balter S, Cole PE, Lu HT, Schueler BA, Geisinger M, et al. Radiation doses in interventional radiology procedures: the RAD-IR study: part I: overall measurement of dose. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003; 14:711–727. PMID: 12817038.12. Theodorakou C, Horrocks JA. A study on radiation doses and irradiated areas in cerebral embolisation. Br J Radiol. 2003; 76:546–552. PMID: 12893697.
Article13. D'Ercole L, Mantovani L, Thyrion FZ, Bocchiola M, Azzaretti A, Di Maria F, et al. A study on maximum skin dose in cerebral embolization procedures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007; 28:503–507. PMID: 17353323.14. Vano E, Fernandez JM, Sanchez RM, Martinez D, Ibor LL, Gil A, et al. Patient radiation dose management in the follow-up of potential skin injuries in neuroradiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013; 34:277–282. PMID: 22859286.
Article15. Valentin J. Avoidance of radiation injuries from medical interventional procedures. Ann ICRP. 2000; 30:7–67. PMID: 11459599.16. Struelens L, Vanhavere F, Bosmans H, Van Loon R, Mol H. Skin dose measurements on patients for diagnostic and interventional neuroradiology: a multicentre study. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2005; 114:143–146. PMID: 15933096.
Article17. Neofotistou V, Vano E, Padovani R, Kotre J, Dowling A, Toivonen M, et al. Preliminary reference levels in interventional cardiology. Eur Radiol. 2003; 13:2259–2263. PMID: 14534803.
Article18. van Rooij WJ, Sprengers ME, de Gast AN, Peluso JP, Sluzewski M. 3D rotational angiography: the new gold standard in the detection of additional intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:976–979. PMID: 18258703.
Article19. Richter G, Engelhorn T, Stuffert T, Doelken M, Ganslandt O, Hornegger J, et al. Flat panel detector angiographic CT for stent-assisted coil embolization of broad-based cerebral aneurysms. ANJR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007; 28:1902–1908. PMID: 17893214.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Patient Radiation Dose in Diagnostic and Interventional Procedures for Intracranial Aneurysms: Experience at a Single Center
- Current Update on the Randomized Controlled Trials of Intracranial Aneurysms
- Two consecutive ruptured intracranial aneurysm in patient with multiple intracranial aneurysms
- Current status of medical radiation exposure and regulation efforts
- Guideline for Management of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms: Preliminary Report