J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2016 Aug;42(4):174-181. 10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.4.174.
Prevalence, pattern, etiology, and management of maxillofacial trauma in a developing country: a retrospective study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dentistry, ESIC Medical College and Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Chennai, India. mona13omfs@gmail.com
- KMID: 2350068
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.4.174
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
This retrospective study aims to evaluate the prevalence of maxillofacial trauma in a developing country, along with its pattern, etiology and management. Data for the present study were collected from the Department of Dentistry, ESIC Medical College and Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Chennai in India.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The medical records of patients treated for maxillofacial injuries between May 2014 and November 2015 were retrospectively retrieved and analyzed for prevalence, pattern, etiology, and management of maxillofacial trauma. SPSS software version 16.0 was used for the data analysis.
RESULTS
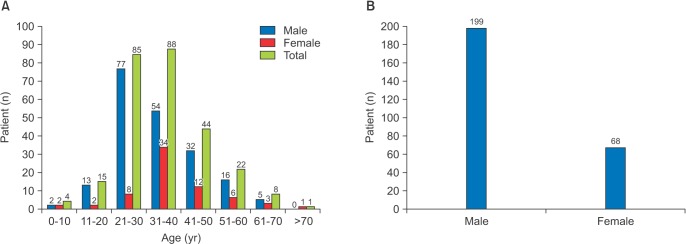
Maxillofacial fractures accounts for 93.3% of total injuries. The mean and standard deviation for the age of the patients were 35.0±11.8 years and with a minimum age of 5 years and maximum age of 75 years. Adults from 20 to 40 years age groups were more commonly involved, with a male to female ratio of 3:1. There was a statistically significantly higher proportion of males more commonly involved in accident and injuries (P <0.001).
CONCLUSION
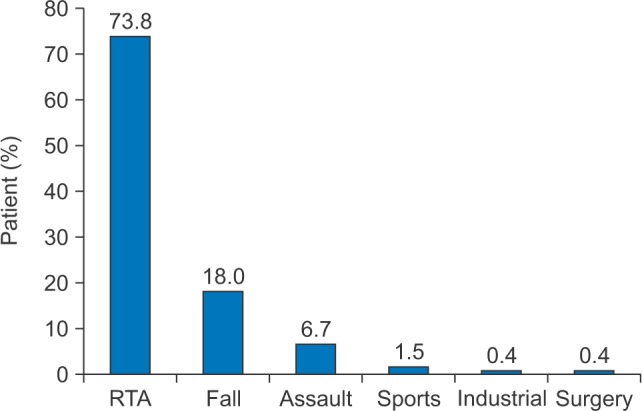
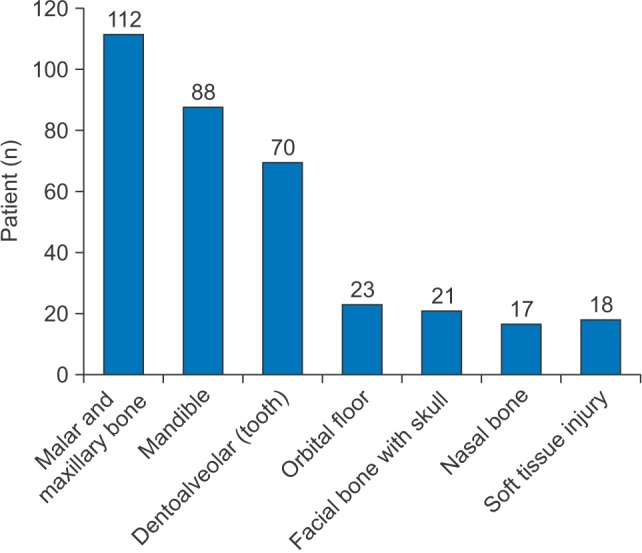
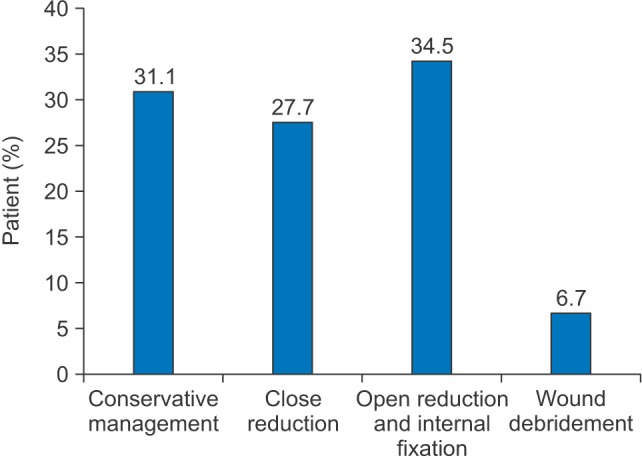
The most common etiology of maxillofacial injury was road traffic accidents (RTA) followed by falls and assaults, the sports injuries seem to be very less. In RTA, motorized two-wheelers (MTW) were the most common cause of incidents. The majority of victims of RTA were young adult males between the ages of 20 to 40 years. The malar bone and maxilla were the most common sites of fracture, followed by the mandible. The right side of the zygomatic complex was the predominant side of MTW injury. The majority of the zygomatic complex fractures were treated by conservative management. Open reduction and internal fixation were performed for indicated fracture patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
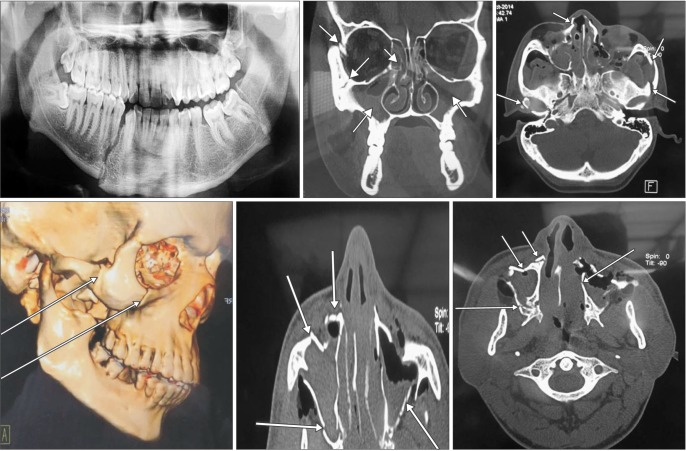
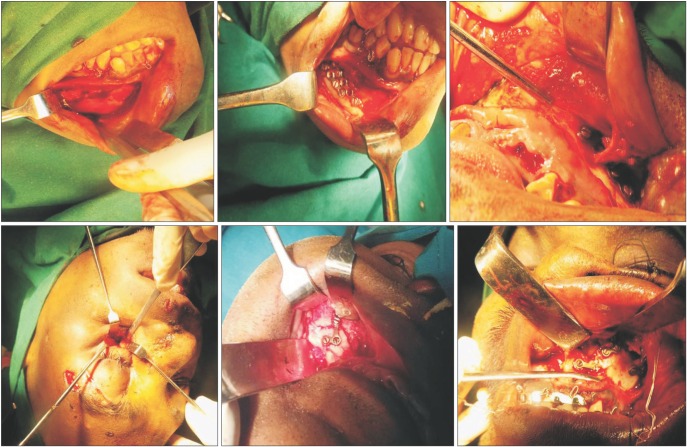
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Oral and maxillofacial injuries in children: a retrospective study
Santanu Mukhopadhyay, Sauvik Galui, Raju Biswas, Subrata Saha, Subir Sarkar
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020;46(3):183-190. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2020.46.3.183.
Reference
-
1. Gassner R, Tuli T, Hächl O, Rudisch A, Ulmer H. Cranio-maxillofacial trauma: a 10 year review of 9,543 cases with 21,067 injuries. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2003; 31:51–61. PMID: 12553928.
Article2. Akama MK, Chindia ML, Macigo FG, Guthua SW. Pattern of maxillofacial and associated injuries in road traffic accidents. East Afr Med J. 2007; 84:287–295. PMID: 18254472.
Article3. Qudah MA, Bataineh AB. A retrospective study of selected oral and maxillofacial fractures in a group of Jordanian children. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002; 94:310–314. PMID: 12324784.
Article4. Subhashraj K, Nandakumar N, Ravindran C. Review of maxillofacial injuries in Chennai, India: a study of 2748 cases. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 45:637–639. PMID: 17524534.
Article5. Mohan D. The road ahead: traffic injuries and fatalities in India. New Delhi: Transportation Research and Injury Prevention Programme, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi;2004. p. 1–30.6. Jagnoor J. Road traffic injury prevention: a public health challenge. Indian J Community Med. 2006; 31:129–131.7. Septa D, Newaskar VP, Agrawal D, Tibra S. Etiology, incidence and patterns of mid-face fractures and associated ocular injuries. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2014; 13:115–119. PMID: 24822001.
Article8. Subhashraj K, Ramkumar S, Ravindran C. Pattern of mandibular fractures in Chennai, India. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 46:126–127. PMID: 17098339.
Article9. Bataineh AB. Etiology and incidence of maxillofacial fractures in the north of Jordan. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998; 86:31–35. PMID: 9690242.
Article10. Ferreira P, Marques M, Pinho C, Rodrigues J, Reis J, Amarante J. Midfacial fractures in children and adolescents: a review of 492 cases. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004; 42:501–505. PMID: 15544878.
Article11. Imahara SD, Hopper RA, Wang J, Rivara FP, Klein MB. Patterns and outcomes of pediatric facial fractures in the United States: a survey of the national trauma data bank. J Am Coll Surg. 2008; 207:710–716. PMID: 18954784.
Article12. Gopalakrishna G, Peek-Asa C, Kraus JF. Epidemiologic features of facial injuries among motorcyclists. Ann Emerg Med. 1998; 32:425–430. PMID: 9774925.13. Kambalimath HV, Agarwal SM, Kambalimath DH, Singh M, Jain N, Michael P. Maxillofacial injuries in children: a 10 year retrospective study. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2013; 12:140–144. PMID: 24431831.14. Joshi SR, Saluja H, Pendyala GS, Chaudhari S, Mahindra U, Kini Y. Pattern and prevalence of maxillofacial fractures in rural children of central maharashtra, India. A retrospective study. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2013; 12:307–311. PMID: 24431857.
Article15. Kumaraswamy SV, Madan N, Keerthi R, Singh DS. Pediatric injuries in maxillofacial trauma: a 5 year study. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2009; 8:150–153. PMID: 23139495.
Article16. Eggensperger Wymann NM, Hölzle A, Zachariou Z, Iizuka T. Pediatric craniofacial trauma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 66:58–64. PMID: 18083416.
Article17. Gassner R, Tuli T, Hächl O, Moreira R, Ulmer H. Craniomaxillofacial trauma in children: a review of 3,385 cases with 6,060 injuries in 10 years. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004; 62:399–407. PMID: 15085503.
Article18. Karim T, Khan AH, Ahmed SS. Trauma of facial skeleton in children: an indian perspective. Indian J Surg. 2010; 72:232–235. PMID: 23133253.
Article19. Thorén H, Iizuka T, Hallikainen D, Lindqvist C. Different patterns of mandibular fractures in children. An analysis of 220 fractures in 157 patients. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1992; 20:292–296. PMID: 1401106.
Article20. Arosarena OA, Fritsch TA, Hsueh Y, Aynehchi B, Haug R. Maxillofacial injuries and violence against women. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2009; 11:48–52. PMID: 19153293.
Article21. Singh R, Singh HK, Gupta SC, Kumar Y. Pattern, severity and circumtances of injuries sustained in road traffic accidents: a tertiary care hospital-based study. Indian J Community Med. 2014; 39:30–34. PMID: 24696537.
Article22. Agnihotri A, Galfat D, Agnihotri D. Incidence and pattern of maxillofacial trauma due to road traffic accidents: a prospective study. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2014; 13:184–188. PMID: 24822011.
Article23. Prabhu P, Srinivas R, Vishwanathan K, Raavi A. Factors influencing alcohol and tobacco addiction among patients attending a deaddiction Centre, South India. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2014; 4:103–107. PMID: 25254194.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Single institutional experience of geriatric maxillofacial trauma patients: a retrospective study
- Missing teeth after maxillofacial trauma:a case report and management protocol
- War-related maxillofacial injuries in Ukraine: a retrospective multicenter study
- Submental intubation: alternative short-term airway management in maxillofacial trauma
- Evaluation of safety and usefulness of submental intubation in panfacial trauma surgery