J Korean Soc Radiol.
2010 Dec;63(6):537-546.
Hepatic Angiomyolipoma: Dual-Contrast MRI Findings Using Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide (SPIO) and Gadolinium Agents
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Korea. shkim@radcom.snu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Hospital, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To analyze imaging findings of hepatic angiomyolipomas (AMLs) on dual-contrast MRI using superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) and gadolinium (Gd) agents.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Five histopathologically-proven hepatic AMLs were enrolled in this study. Patients underwent dual-contrast MRI using SPIO and Gd agents on a 3.0T unit and performed a qualitative analysis consisting of measuring the signal intensity (SI) of the lesion, presence of fat, hemorrhage, early draining vein, tortuous tumoral vessels, as well as capsule and enhancement patterns. The signal drop of the lesion on post-SPIO images was also assessed. For the quantitative analysis, relative signal decrease (RSD, %) was calculated.
RESULTS
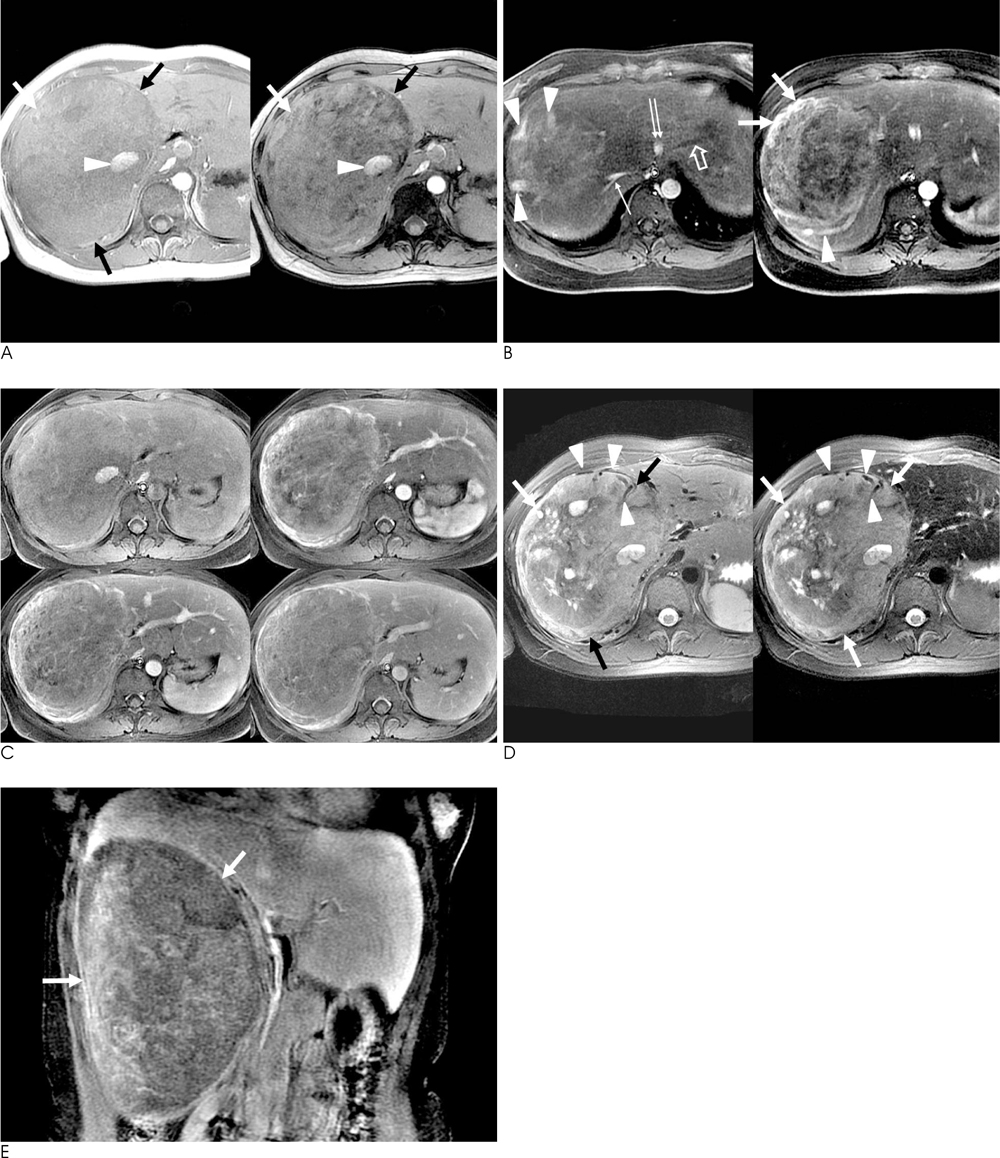
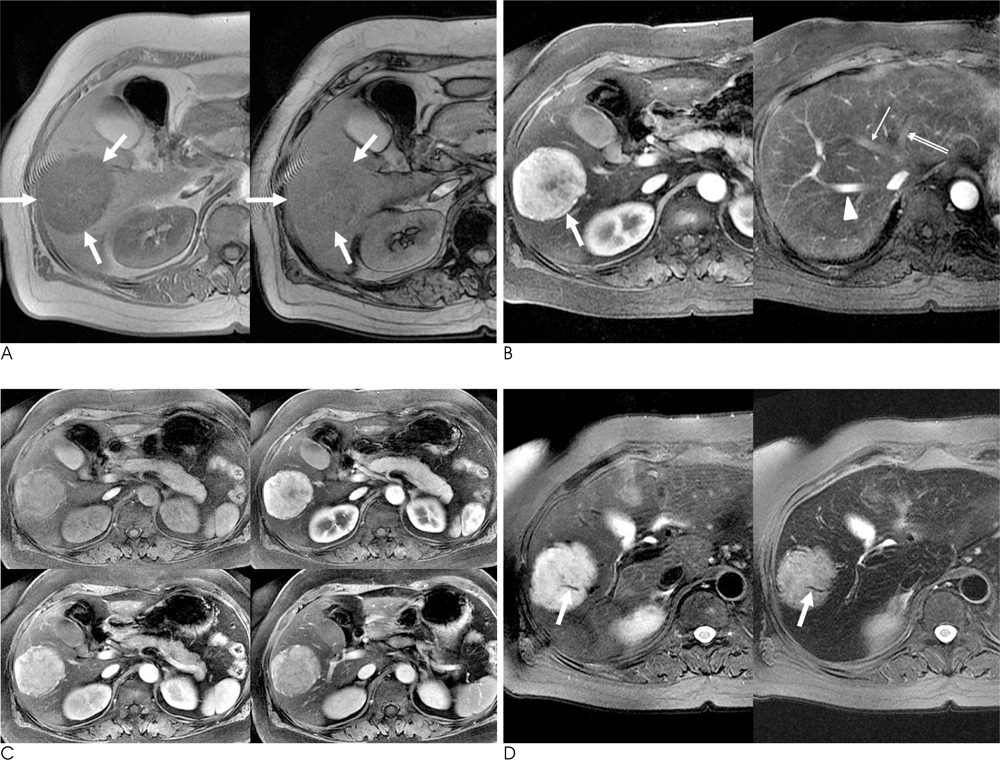
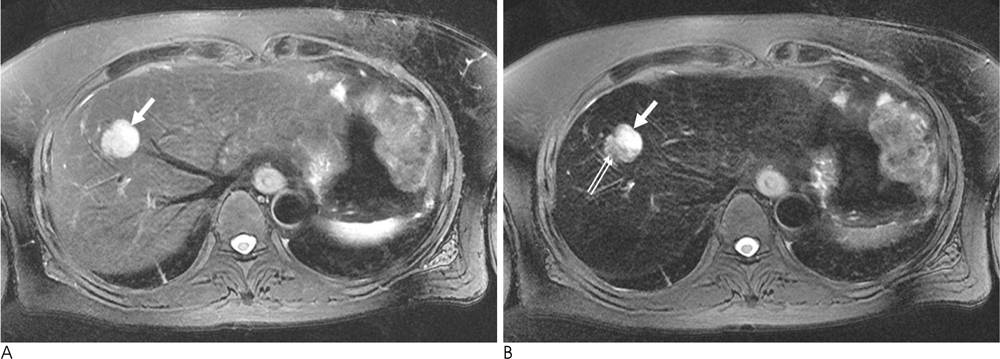
The presence of fat was noted in three lesions. An early draining vein and prominent tortous tumoral vessels were depicted in four lesions. No lesion was found to have a capsule. Four lesions showed early wash-in and early wash-out enhancement patterns, while the remaining lesion depicted strong and persistent enhancement. On post-SPIO images, signal drop was noted in the two lesions with no fat within the lesion. Their RSD was 21.1% and 38.0%, respectively.
CONCLUSION
The presence of an early draining vein and tortuous tumoral vessels are characteristic dynamic enhanced MRI features of hepatic AMLs. In fat-deficient hepatic AMLs, the combination of dynamic enhanced MRI and SPIO-enhanced MRI might findings might increase the accuracy of making a correct diagnosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nonomura A, Mizukami Y, Kadoya M. Angiomyolipoma of the liver: a collective review. J Gastroenterol. 1994; 29:95–105.2. Tsui WM, Colombari R, Portmann BC, Bonetti F, Thung SN, Ferrell LD, et al. Hepatic angiomyolipoma. A clinicopathological study of 30 cases and delineation of unusual morphological variants. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999; 23:34–48.3. Yang CY, Ho MC, Jeng YM, Hu RH, Wu YM, Lee PH. Management of hepatic angiomyolipoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007; 11:452–457.4. Zeng JP, Dong JH, Zhang WZ, Wang J, Pang XP. Hepatic Angiomyolipoma: a clinical experience in diagnosis and treatment. Dig Dis Sci. Forthcoming 2010.5. Yan F, Zeng M, Zhou K, Shi W, Zheng W, Da R, et al. Hepatic angiomyolipoma: various appearances on two-phase contrast scanning of spiral CT. Eur J Radiol. 2002; 41:12–18.6. Zheng RQ, Kudo M. Hepatic angiomyolipoma: identification of an efferent vessel to be hepatic vein by contrast-enhanced harmonic ultrasound. Br J Radiol. 2005; 78:956–960.7. Takayama Y, Moriura S, Nagata J, Hirano A, Ishiguro S, Tabata T, et al. Hepatic angiomyolipoma: radiologic and histopathologic correlation. Abdom Imaging. 2002; 27:180–183.8. Sakamoto Y, Inoue K, Ohtomo K, Mori M, Makuuchi M. Magnetic resonance imaging of an angiomyolipoma of the liver. Abdom Imaging. 1998; 23:158–160.9. Basaran C, Karcaaltincaba M, Akata D, Karabulut N, Akinci D, Ozmen M, et al. Fat-containing lesions of the liver: cross-sectional imaging findings with emphasis on MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:1103–1110.10. Li T, Wang L, Yu HH, Sun HC, Qin LX, Ye QH, et al. Hepatic angiomyolipoma: a retrospective study of 25 cases. Surg Today. 2008; 38:529–535.11. Namkung S, Zech CJ, Helmberger T, Reiser MF, Schoenberg SO. Superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO)-enhanced liver MRI with ferucarbotran: efficacy for characterization of focal liver lesions. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007; 25:755–765.12. Hamm B, Staks T, Taupitz M. SHU 555A: a new superparamagnetic iron oxide contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol. 1994; 29:Suppl 2. S87–S89.13. Reimer P, Rummeny EJ, Daldrup HE, Balzer T, Tombach B, Berns T, et al. Clinical results with resovist: a phase 2 clinical trial. Radiology. 1995; 195:489–496.14. Jeon TY, Kim SH, Lim HK, Lee WJ. Assessment of triple-phase CT findings for the differentiation of fat-deficient hepatic angiomyolipoma from hepatocellular carcinoma in non-cirrhotic liver. Eur J Radiol. 2010; 73:601–606.15. Reimer P, Schneider G, Schima W. Hepatobiliary contrast agents for contrast-enhanced MRI of the liver: properties, clinical development and applications. Eur Radiol. 2004; 14:559–578.16. Prasad SR, Wang H, Rosas H, Menias CO, Narra VR, Middleton WD, et al. Fat-containing lesions of the liver: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2005; 25:321–331.17. Zhong DR, Ji XL. Hepatic angiomyolipoma-misdiagnosis as hepatocellular carcinoma: a report of 14 cases. World J Gastroenterol. 2000; 6:608–612.18. Ren N, Qin LX, Tang ZY, Wu ZQ, Fan J. Diagnosis and treatment of hepatic angiomyolipoma in 26 cases. World J Gastroenterol. 2003; 9:1856–1858.19. Kudo M, Okuno T, Tomita S, Kajiwara T, Shirane H, Usuki N, et al. Hepatic angiomyolipoma pre-operatively diagnosed by imaging. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1993; 8:483–488.20. Ahmadi T, Itai Y, Takahashi M, Onaya H, Kobayashi T, Tanaka YO, et al. Angiomyolipoma of the liver: significance of CT and MR dynamic study. Abdom Imaging. 1998; 23:520–526.21. Clément O, Siauve N, Cuenod CA, Frija G. Liver imaging with ferumoxides (Feridex): fundamentals, controversies, and practical aspects. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 1995; 9:167–182.22. Soyer P, Dufresne AC, Somveille E, Scherrer A. Hepatic cavernous hemangioma: appearance on T2-weighted fast spin-echo MR imaging with and without fat suppression. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997; 168:461–465.23. Montet X, Lazeyras F, Howarth N, Mentha G, Rubbia-Brandt L, Becker CD, et al. Specificity of SPIO particles for characterization of liver hemangiomas using MRI. Abdom Imaging. 2004; 29:60–70.24. Yoshimura H, Murakami T, Kim T, Nakamura H, Hirabuki N, Sakon M, et al. Angiomyolipoma of the liver with least amount of fat component: imaging features of CT, MR, and angiography. Abdom Imaging. 2002; 27:184–187.25. Weinmann HJ, Schuhmann-Giampieri G, Schmitt-Willich H, Vogler H, Frenzel T, Gries H. A new lipophilic gadolinium chelate as a tissue-specific contrast medium for MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1991; 22:233–237.26. Schuhmann-Giampieri G, Schmitt-Willich H, Press WR, Negishi C, Weinmann HJ, Speck U. Preclinical evaluation of Gd-EOB-DTPA as a contrast agent in MR imaging of the hepatobiliary system. Radiology. 1992; 183:59–64.27. Hamm B, Staks T, Mühler A, Bollow M, Taupitz M, Frenzel T, et al. Phase I clinical evaluation of Gd-EOB-DTPA as a hepatobiliary MR contrast agent: safety, pharmacokinetics, and MR imaging. Radiology. 1995; 195:785–792.28. van Montfoort JE, Stieger B, Meijer DK, Weinmann HJ, Meier PJ, Fattinger KE. Hepatic uptake of the magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent gadoxetate by the organic anion transporting polypeptide Oatp1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999; 290:153–157.29. Huppertz A, Balzer T, Blakeborough A, Breuer J, Giovagnoni A, Heinz-Peer G, et al. Improved detection of focal liver lesions at MR imaging: a multicenter comparison of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR images with intraoperative findings. Radiology. 2004; 230:266–275.30. Vogl TJ, Ku¨mmel S, Hammerstingl R, Schellenbeck M, Schumacher G, Balzer T, et al. Liver tumors: comparison of MR imaging with Gd-EOB-DTPA and Gd-DTPA. Radiology. 1996; 200:59–67.31. Reimer P, Rummeny EJ, Daldrup HE, Hesse T, Balzer T, Tombach B, et al. Enhancement characteristics of liver metastases, hepatocellular carcinomas, and hemangiomas with Gd-EOB-DTPA: preliminary results with dynamic MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 1997; 7:275–280.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging before and after Contrast Enhancement with Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide for Assessment of Hepatic Metastasis
- Intrahepatic Extramedullary Hematopoiesis Mimicking a Hypervascular Hepatic Neoplasm on Dynamic- and SPIO-Enhanced MRI
- Detectability of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Comparison of Gd-DT PA-Enhanced and SPIO-Enhanced MR Imaging
- Evaluation of Fibrosis in Liver Cirrhosis by Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide (SPIO)-Enhanced MR Imaging: Does the Radiological Non-Invasive Fibrosis Index Correlate with the Laboratory Non-Invasive Fibrosis Index?
- Usefulness of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide (SPIO) as a Negative Oral Contrast Agent in MR Cholangiopancreatography